|
Wien Bridge
The Wien bridge is a type of bridge circuit that was developed by Max Wien in 1891. The bridge consists of four resistors and two capacitors. At the time of the Wien bridge's invention, bridge circuits were a common way of measuring component values by comparing them to known values. Often an unknown component would be put in one arm of a bridge, and then the bridge would be nulled by adjusting the other arms or changing the frequency of the voltage source. See, for example, the Wheatstone bridge. The Wien bridge is one of many common bridges. Wien's bridge is used for precision measurement of capacitance in terms of resistance and frequency. It was also used to measure audio frequencies. The Wien bridge does not require equal values of ''R'' or ''C''. At some frequency, the reactance of the series ''R''2–''C''2 arm will be an exact multiple of the shunt ''R''''x''–''C''''x'' arm. If the two ''R''3 and ''R''4 arms are adjusted to the same ratio, then the bridge is ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mostek Wiena
Mostek was a semiconductor integrated circuit manufacturer, founded in 1969 by L. J. Sevin, Louay E. Sharif, Richard L. Petritz and other ex-employees of Texas Instruments. At its peak in the late 1970s, Mostek held an 85% market share of the dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) memory chip market worldwide, until being eclipsed by lower-priced Japanese DRAM manufacturers who were accused of dumping memory on the market. Initially Mostek products were manufactured in Worcester, Massachusetts in cooperation with Sprague Electric, however by 1974 most of its manufacturing was done in the Carrollton, Texas facility on Crosby Road. In 1979, soon after its market peak, Mostek was purchased by United Technologies Corporation for . In 1985, after several years of red ink and declining market share, UTC closed Mostek completely and sold it for to the French electronics firm Thomson-CSF, which later spun it off into STMicroelectronics. Early Products Mostek's first contract was from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Circuit
A bridge circuit is a topology of electrical circuitry in which two circuit branches (usually in parallel with each other) are "bridged" by a third branch connected between the first two branches at some intermediate point along them. The bridge was originally developed for laboratory measurement purposes and one of the intermediate bridging points is often adjustable when so used. Bridge circuits now find many applications, both linear and non-linear, including in instrumentation, filtering and power conversion. The best-known bridge circuit, the Wheatstone bridge, was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie and popularized by Charles Wheatstone, and is used for measuring resistance. It is constructed from four resistors, two of known values R1 and R3 (see diagram), one whose resistance is to be determined Rx, and one which is variable and calibrated R2. Two opposite vertices are connected to a source of electric current, such as a battery, and a galvanometer is connected across t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Wien
Max Karl Werner Wien (; 25 December 1866 – 22 February 1938) was a German physicist and the director of the Institute of Physics at the University of Jena. He was born in Königsberg, Prussia (now Kaliningrad, Russia), the son of the co-owner of the well-known Castell grain company, Otto Wien. Wien, Max. Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen für Wissenschaft und Forschun(in German). He was a cousin of Nobel laureate Wilhelm Wien. Wien studied in Konigsberg, Freiburg, and Berlin under Hermann von Helmholtz and August Kundt, receiving his PhD under Helmholtz in 1888.Karl Willy Wagner, "Max Wien zum 70. Geburtstag", Naturwissenschaften, Volume 25, Number 5, 65-67,(link to pdf)(in German). In 1892 he worked with Wilhelm Röntgen in Würzburg, where in 1893 he received the ''habilitation'', qualifying him to be a professor. He moved to the Technical High School of Aachen in 1898 where he became Extraordinary Professor in 1899. In 1904 he became full Professor at the Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
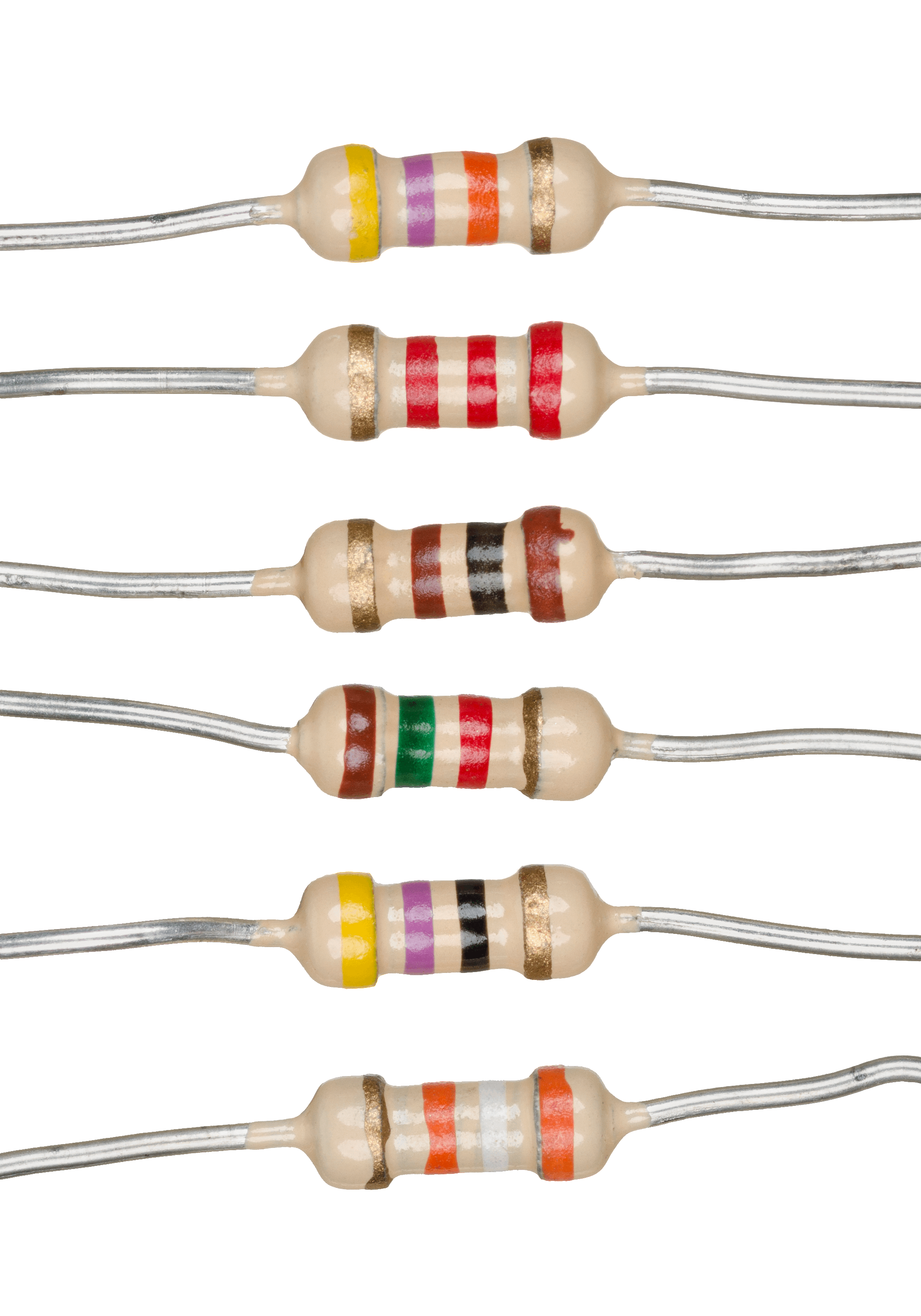
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheatstone Bridge
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of the circuit is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider). Its operation is similar to the original potentiometer. The Wheatstone bridge was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie (sometimes spelled "Christy") in 1833 and improved and popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1843. One of the Wheatstone bridge's initial uses was for soil analysis and comparison."The Genesis of the Wheatstone Bridge" by Stig Ekelof discusses Christie's and Wheatstone's contributions, and why the bridge carries Wheatstone's name. Published in "Engineering Science and Education Journal", volume 10, no 1, February 2001, pages 37–40. Operation In the figure, is the fixed, yet unknown, resistance to be measured. and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Harmonic Distortion Analyzer
A total harmonic distortion analyzer calculates the total harmonic content of a sinewave with some distortion, expressed as total harmonic distortion (THD). A typical application is to determine the THD of an amplifier by using a very-low-distortion sinewave input and examining the output. The figure measured will include noise, and any contribution from imperfect filtering out of the fundamental frequency. Harmonic-by-harmonic measurement, without wideband noise, can be measured by a more complex wave analyser. Another application is measurement of the effectiveness of an electronic filter with extremely narrow passband, such as a notch filter in a parametric equalizer. Types of THD meter There are several types of distortion analyzers: # Fundamental suppression # Heterodyne type # Tuned circuit # Spectrum analyzer Fundamental suppression analyzer This type of THD analyzer filters out the fundamental frequency of a signal with a notch filter, leaving only distortion products pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wien Bridge Oscillator
A Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It can generate a large range of frequencies. The oscillator is based on a bridge circuit originally developed by Max Wien in 1891 for the measurement of impedances. The bridge comprises four resistors and two capacitors. The oscillator can also be viewed as a positive gain amplifier combined with a bandpass filter that provides positive feedback. Automatic gain control, intentional non-linearity and incidental non-linearity limit the output amplitude in various implementations of the oscillator. The circuit shown to the right depicts a once-common implementation of the oscillator, with automatic gain control using an incandescent lamp. Under the condition that R1=R2=R and C1=C2=C, the frequency of oscillation is given by: f_=\frac and the condition of stable oscillation is given by R_b = \frac Background There were several efforts to improve oscillators in the 1930s. Linearity was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annalen Der Physik
''Annalen der Physik'' (English: ''Annals of Physics'') is one of the oldest scientific journals on physics; it has been published since 1799. The journal publishes original, peer-reviewed papers on experimental, theoretical, applied, and mathematical physics and related areas. The editor-in-chief is Stefan Hildebrandt. Prior to 2008, its ISO 4 abbreviation was ''Ann. Phys. (Leipzig)'', after 2008 it became ''Ann. Phys. (Berl.)''. The journal is the successor to , published from 1790 until 1794, and ', published from 1795 until 1797. The journal has been published under a variety of names (', ', ', ''Wiedemann's Annalen der Physik und Chemie'') during its history. History Originally, was published in German, then a leading scientific language. From the 1950s to the 1980s, the journal published in both German and English. Initially, only foreign authors contributed articles in English but from the 1970s German-speaking authors increasingly wrote in English in order to reach an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Circuits
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impedance Measurements
Impedance is the complex-valued generalization of resistance. It may refer to: *Acoustic impedance, a constant related to the propagation of sound waves in an acoustic medium *Electrical impedance, the ratio of the voltage phasor to the electric current phasor, a measure of the opposition to time-varying electric current in an electric circuit **High impedance, when only a small amount of current is allowed through ** Characteristic impedance of a transmission line **Impedance (accelerator physics), a characterization of the self interaction of a charged particle beam ** Nominal impedance, approximate designed impedance **Impedance matching, the adjustment of input impedance and output impedance *Mechanical impedance, a measure of opposition to motion of a structure subjected to a force *Wave impedance, a constant related to electromagnetic wave propagation in a medium **Impedance of free space The impedance of free space, , is a physical constant relating the magnitudes of the ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
