|
Widcombe, Bath
Widcombe is a district of Bath, England, immediately south-east of the city centre, across the River Avon. The electoral ward was merged with Lyncombe at the boundary changes effected at the elections held on 2 May 2019; the two places have historically been connected (refer to the Lyncombe article). History Widcombe was part of the hundred of Bath Forum. In 1877 Halfpenny Bridge, a pedestrian toll bridge, across the River Avon from Bath Spa railway station to Widcombe collapsed with the loss of about 10 lives amongst a large crowd going to the Bath and West Agricultural show. Architecture Widcombe Parade is a commercial street lined with a mix of Georgian and Victorian buildings located near the Halfpenny Bridge, with buildings dating back as far as 1750. The area has been through many changes over the years, altered to improve traffic movement, removing an entire row of terraced houses at the west end of Widcombe Parade with the development of Rossiter Road as part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widcombe Crescent, Bath
Widcombe Crescent in Bath, Somerset, England is a terrace of 14 Georgian houses built in 1808 by Thomas Baldwin, and designated a Grade I listed building. The three-storey houses, which have mansard roofs, are stepped up from either side to central 2 houses which project slightly. Famous residents include Sir James Brooke, the 'White Rajah' of Sarawak in Borneo, who lived in Number 1 from 1831–1834.Portrait of Bath by John Haddon, 1982, Robert Hale, London, p. 152-153. See also * List of Grade I listed buildings in Bath and North East Somerset Bath and North East Somerset (commonly referred to as BANES or B&NES) is a unitary authority created on 1 April 1996, following the abolition of the County of Avon, which had existed since 1974. Part of the ceremonial county of Somerset, Bath an ... References Houses completed in 1808 Grade I listed buildings in Bath, Somerset Streets in Bath, Somerset {{UK-listed-building-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely applied to various country houses, frequently dating from the Late Middle Ages, which formerly housed the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, and were intended more for show than for defencibility. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular manorial courts, which appointed manorial officials such as the bailiff, granted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulteney Bridge
Pulteney Bridge is a bridge over the River Avon in Bath, England. It was completed by 1774, and connected the city with the land of the Pulteney family which it wished to develop. Designed by Robert Adam in a Palladian style, it is highly unusual in that it has shops built across its full span on both sides. It has been designated as a Grade I listed building. Within 20 years of its construction, alterations were made that expanded the shops and changed the façades. By the end of the 18th century, it had been damaged by floods, but was rebuilt to a similar design. Over the next century alterations to the shops included cantilevered extensions on the bridge's north face. In the 20th century, several schemes were carried out to preserve the bridge and partially return it to its original appearance, enhancing its appeal as a tourist attraction. The bridge is now long and wide. Although there have been plans to pedestrianise the bridge, it is still used by buses and taxis. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Lock
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and naval en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Locks
Bath Locks () are a series of locks, now six locks, situated at the start of the Kennet and Avon Canal, at Bath, England. Bath Bottom Lock, which is numbered as No 7 on the canal, is the meeting with the River Avon just south of Pulteney Bridge. Alongside the lock is a side pond and pumping station which pumps water up the locks to replace that used each time the lock is opened. The next stage of Bath Deep Lock is numbered 8/9 as two locks were combined when the canal was restored in 1976. A road constructed while the canal was in a state of disrepair passes over the original site of the lower lock. The new chamber has a depth of , making it Britain's second deepest canal lock. Just above the 'deep lock' is an area of water enabling the lock to refill and above this is Wash House Lock (number 10), and soon after by Abbey View Lock (number 11), a Grade II listed building by which there is another pumping station and in quick succession Pulteney Lock (12) and Bath top Lock (13). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennet And Avon Canal
The Kennet and Avon Canal is a waterway in southern England with an overall length of , made up of two lengths of navigable river linked by a canal. The name is used to refer to the entire length of the navigation rather than solely to the central canal section. From Bristol to Bath the waterway follows the natural course of the River Avon before the canal links it to the River Kennet at Newbury, and from there to Reading on the River Thames. In all, the waterway incorporates 105 locks. The two river stretches were made navigable in the early 18th century, and the canal section was constructed between 1794 and 1810. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the canal gradually fell into disuse after the opening of the Great Western Railway. In the latter half of the 20th century the canal was restored in stages, largely by volunteers. After decades of dereliction and much restoration work, it was fully reopened in 1990. The Kennet and Avon Canal has been developed as a pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Images Of England
Images of England is an online photographic record of all the listed buildings in England at the date of February 2002. The archive gives access to over 323,000 colour images, each of which is matched with the item's listed designation architectural description. It is a snapshot rather than an up-to-date record: it does not include all listed buildings, only those listed at February 2001, and is not updated as listing details change. the Images of England content moved to the main Historic England website alongside the list entry. Purpose Images of England was a stand-alone project funded jointly by English Heritage and the Heritage Lottery Fund. The aim of the project was to photograph every listed building and object (some 370,000) in England and to make the images available online to create, what was at the time, one of the largest free-to-view picture libraries of buildings in the world. It is part of the Historic England Archive of England's historic environment. The projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Baldwin (architect)
Thomas Baldwin (c.1750 – 7 March 1820) was an English architect in the city of Bath, who was responsible for designing some of Bath's principal Georgian buildings. In 1775, he was appointed as the official Bath City Architect. In this role he designed Guildhall, Argyle Street, Laura Place, Great Pulteney Street and many others. In 1793, he was dismissed for financial irregularities, and as a result he was forced into bankruptcy and his reputation was ruined. Jane Root, biographer of Baldwin, writes; "he had a history not merely of imprudence, but of deliberate dishonesty". Career Baldwin was born in 1749 or 1750. His place of birth is not recorded, however, he was not native to Bath. He was first recorded in the city of Bath in 1774. He was initially a clerk (later builder and assistant) to plumber, glazier, and politician Thomas Warr Attwood. By 1775, he was appointed as the Bath City Architect after Attwood's death. During the construction of the Guildhall he was officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotto
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave used by humans in both modern times and antiquity, and historically or prehistorically. Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high tide. Sometimes, artificial grottoes are used as garden features. The '' Grotta Azzurra'' at Capri and the grotto at Tiberius' Villa Jovis in the Bay of Naples are examples of popular natural seashore grottoes. Whether in tidal water or high up in hills, grottoes are generally made up of limestone geology, where the acidity of standing water has dissolved the carbonates in the rock matrix as it passes through what were originally small fissures. Etymology The word ''grotto'' comes from Italian ''grotta'', Vulgar Latin ''grupta'', and Latin ''crypta'' ("a crypt"). It is also related by a historical accident to the word ''grotesque''. In the late 15th century, Romans accidentally unearthed Nero's ''Domus Aurea'' on the Palatine Hill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
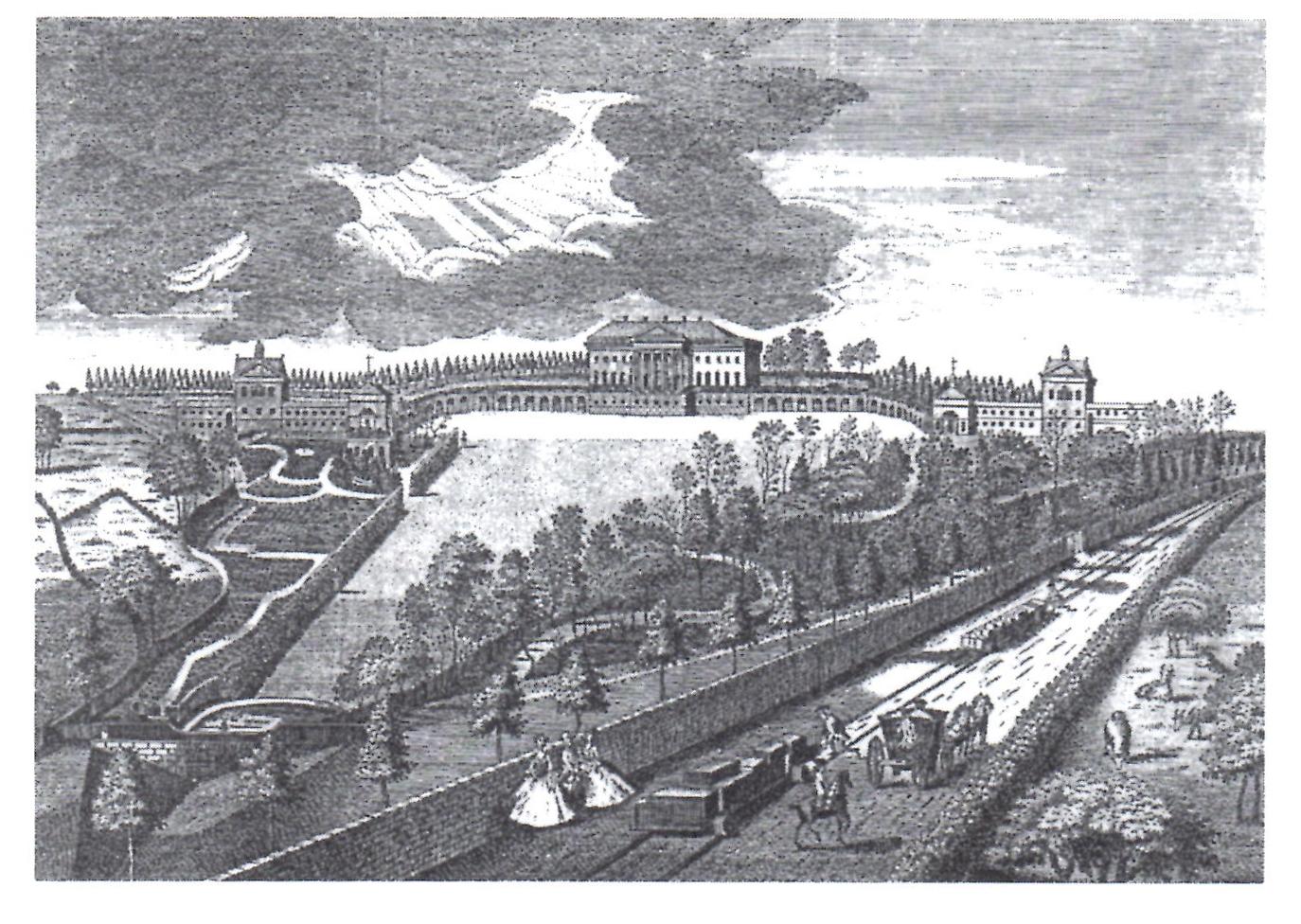
Prior Park
Prior Park is a Neo-Palladian house that was designed by John Wood, the Elder, and built in the 1730s and 1740s for Ralph Allen on a hill overlooking Bath, Somerset, England. It has been designated as a Grade I listed building. The house was built in part to demonstrate the properties of Bath stone as a building material. The design followed work by Andrea Palladio and was influenced by drawings originally made by Colen Campbell for Wanstead House in Essex as well as the twelve sided plan form of the Roman theatre (of which the house's natural setting reminded Wood). The main block had 15 bays and each of the wings 17 bays each. The surrounding parkland had been laid out in 1100 but following the purchase of the land by Allen were established as a landscape garden. Features in the garden include a bridge covered by Palladian arches, which is also Grade I listed. Following Allen's death the estate passed down through his family. In 1828, Bishop Baines bought it for use as a Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register Of Historic Parks And Gardens Of Special Historic Interest In England
The Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in England provides a listing and classification system for historic parks and gardens similar to that used for listed buildings. The register is managed by Historic England under the provisions of the National Heritage Act 1983. Over 1,600 sites are listed, ranging from the grounds of large stately homes to small domestic gardens, as well other designed landscapes such as town squares, public parks and cemeteries.Registered Parks & Gardens page on . Retrieved 23 December 2010. Purpose The register aims to "celebrate designed landscape ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)