|
Whitworth Hall
The Whitworth Building is a grade II* listed building on Oxford Road and Burlington Street in Chorlton-on-Medlock, Manchester, England. It has been listed since 18 December 1963 and is part of the University of Manchester. It lies at the south-east range of the old quadrangle of the University, with the Manchester Museum adjoined to the north, and the former Christie Library connected to the west. History The building was constructed c. 1895–1902, in the style of the Gothic Revival, and was designed by Paul Waterhouse. The official opening ceremony took place 12 March 1902, when the Prince and Princess of Wales (later King George V and Queen Mary) were present. The Whitworth Building is named after Mancunian industrialist, Joseph Whitworth, who bequeathed much of his fortune to fund public developments in Manchester. The legatees, among whom was Richard Copley Christie, funded the construction of the building and the adjoining Christie Library (the library was completed fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the "Anglo-Catholicism" tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Copley Christie
Richard Copley Christie (22 July 1830 – 9 January 1901) was an English lawyer, university teacher, philanthropist and bibliophile. He was born at Lenton in Nottinghamshire, the son of a mill owner. He was educated at Lincoln College, Oxford where he was tutored by Mark Pattison, and was called to the bar at Lincoln's Inn in 1857. He also held numerous academic appointments, notably the professorships of history (from 1854 to 1856) and of political economy (from 1855 to 1866) at Owens College. He always took an active interest in this college, of which he was one of the governors. In 1898 he gave the Christie Library building, designed by Alfred Waterhouse: the plan connected this on the east with the Whitworth Hall. Philanthropy Christie was a friend of the industrialist Sir Joseph Whitworth. By Whitworth's will, Christie was appointed one of three legatees, each of whom was left more than half a million pounds for their own use, ‘they being each of them aware of the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II* Listed Buildings In Manchester
There are 236 Grade II* listed buildings in Greater Manchester, England. In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance; Grade II* structures are those considered to be "particularly significant buildings of more than local interest". In England, the authority for listing under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 rests with English Heritage, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The metropolitan county of Greater Manchester is made up of 10 metropolitan boroughs: Bolton, Bury, Manchester, Oldham, Rochdale, Salford, Stockport, Tameside, Trafford and Wigan. The Grade II* buildings in each borough are listed separately. Manchester, the world's first industrialised city, has 77 of Greater Manchester's 238 Grade II* listed buildings, the highest number of any borough. Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings At The University Of Manchester
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduation
Graduation is the awarding of a diploma to a student by an educational institution. It may also refer to the ceremony that is associated with it. The date of the graduation ceremony is often called graduation day. The graduation ceremony is also sometimes called: commencement, congregation, convocation or invocation. History Ceremonies for graduating students date from the first universities in Europe in the twelfth century. At that time Latin was the language of scholars. A ''universitas'' was a guild of masters (such as MAs) with licence to teach. "Degree" and "graduate" come from ''gradus'', meaning "step". The first step was admission to a bachelor's degree. The second step was the masters step, giving the graduate admission to the ''universitas'' and license to teach. Typical dress for graduation is gown and hood, or hats adapted from the daily dress of university staff in the Middle Ages, which was in turn based on the attire worn by medieval clergy. The tradition of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Wedding
A wedding is a ceremony where two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriage vows by a couple, presentation of a gift (offering, rings, symbolic item, flowers, money, dress), and a public proclamation of marriage by an authority figure or celebrant. Special wedding garments are often worn, and the ceremony is sometimes followed by a wedding reception. Music, poetry, prayers, or readings from religious texts or literature are also commonly incorporated into the ceremony, as well as superstitious customs. Common elements across cultures Some cultures have adopted the traditional Western custom of the white wedding, in which a bride wears a white wedding dress and veil. This tradition was popularized through the marriage of Queen Victoria. Some say Victoria's choice of a white gown may have simply been a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriqueta Rylands
Enriqueta Augustina Rylands (31 May 1843 – 4 February 1908) was a British philanthropist who founded the John Rylands Library in Manchester. Early life Enriqueta Augustina was born in Havana, Cuba, and was one of five children including José Esteban (later Stephen Joseph, who was her twin brother), Blanca Catalina and Leocadia Fernanda. Her father was Stephen Cattley Tennant (1800–1848), a merchant whose family came from Yorkshire, and her mother, Juana Camila Dalcour (1818–1855).Farnie (2006) Tennant retired to Liverpool, but died within a year. His widow migrated to Paris and married pianist and polymath Julian Fontana. Juana and Julian had one son, Enriqueta's half brother, Julian (Jules) Camillo Adam Fontana, who was born in 1853. Enriqueta Tennant was raised a Roman Catholic and completed her education in New York, London and Paris. In later life she abandoned Catholicism and became a Congregationalist, under the influence of the Rev. Thomas Raffles (1788–1863). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (music)
Carol Williams performing at the United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel.">West_Point_Cadet_Chapel.html" ;"title="United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel">United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel. In music, the organ is a keyboard instrument of one or more Pipe organ, pipe divisions or other means for producing tones, each played from its own Manual (music), manual, with the hands, or pedalboard, with the feet. Overview Overview includes: * Pipe organs, which use air moving through pipes to produce sounds. Since the 16th century, pipe organs have used various materials for pipes, which can vary widely in timbre and volume. Increasingly hybrid organs are appearing in which pipes are augmented with electric additions. Great economies of space and cost are possible especially when the lowest (and largest) of the pipes can be replaced; * Non-piped organs, which include: ** pump organs, also known as reed organs or harmoniums, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
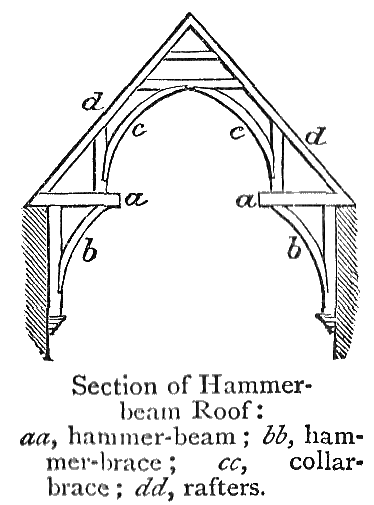
Hammerbeam Roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "...the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Tower
A bell tower is a tower that contains one or more bells, or that is designed to hold bells even if it has none. Such a tower commonly serves as part of a Christian church, and will contain church bells, but there are also many secular bell towers, often part of a municipal building, an educational establishment, or a tower built specifically to house a carillon. Church bell towers often incorporate clocks, and secular towers usually do, as a public service. The term campanile (, also , ), deriving from the Italian ''campanile'', which in turn derives from ''campana'', meaning "bell", is synonymous with ''bell tower''; though in English usage campanile tends to be used to refer to a free standing bell tower. A bell tower may also in some traditions be called a belfry, though this term may also refer specifically to the substructure that houses the bells and the ringers rather than the complete tower. The tallest free-standing bell tower in the world, high, is the Mortegliano B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular (architecture)
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture. The pointed arches used in Perpendicular were often four-centred arches, allowing them to be rather wider and flatter than in other Gothic styles. Perpendicular tracery is characterized by mullions that rise vertically as f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral (sideways) forces arising out of inadequately braced roof structures. The term ''counterfort'' can be synonymous with buttress and is often used when referring to dams, retaining walls and other structures holding back earth. Early examples of buttresses are found on the Eanna Temple (ancient Uruk), dating to as early as the 4th millennium BC. Terminology In addition to flying and ordinary buttresses, brick and masonry buttresses that support wall corners can be classified according to their ground plan. A clasping or clamped buttress has an L shaped ground plan surrounding the corner, an angled buttress has two buttresses meeting at the corner, a setback buttress is similar to an angled buttress but the buttresses are set back from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |