|
Whifflet Line
The Whifflet Line is one of the lines within the Strathclyde suburban rail network in Scotland. History The line was built between 1863 and 1865 as the Rutherglen and Coatbridge Railway, part of the Caledonian Railway. It opened to goods traffic (mainly coal and iron) in September 1865 and to passengers in August 1866. It has been in continuous operation ever since. Stations in the first service on the line were at , (now ), , and (until 1964). Passenger services ceased in November 1966 following the Beeching Axe (latterly running to ). Between 1972 and 1974 scheduled passenger trains between Glasgow Central and Perth used the route. For the following twenty years, the route was only used for freight and diverted passenger services. However the line was reopened by British Rail to scheduled passenger services with intermediate stations on 4 October 1993, running to the newly built station at rather than Coatbridge Central as previously. Line description The modern lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whifflet Railway Station
Whifflet railway station is located in the Whifflet area of Coatbridge. Train services are provided by ScotRail. Until December 2014, it was the terminal station on the Whifflet Line, since when it is served by Argyle Line services. To the east of the station is the link line from the North Clyde Line at Sunnyside Junction. There are no platforms on this line, but it is used by empty EMUs laying over between trips from Glasgow. History The station here is a relatively recent addition to the Glasgow suburban network, opening on 21 December 1992 by British Rail and initially served by the Argyle Line branch between and . It subsequently became the terminus for the former Rutherglen and Coatbridge Railway route from when that route reopened to passenger traffic on 4 October 1993. The station on this site is completely new - services originally operated from Glasgow Central High Level to Coatbridge Central over the R&CR route up until their demise (due to the Beeching Axe) on 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bargeddie
Bargeddie (; gd, Bàrr Geadaidh) is a village in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, just inside the suburban fringe of Glasgow, east of the city centre, and close to the junction of the M73 and M8 motorways. The nearest major town is Coatbridge, to the east. History There was no village of Bargeddie before the 1930s when Lanark County Council built a housing estate at Dykehead. Before that the area consisted of a cluster of hamlets and villages such as Bartonshill, Braehead, and Dykehead, populated in the main by coal miners. In the 1950s, another housing estate was built around the site of Bargeddie House which was demolished after World War II. Bargeddie grew further as part of the overall Glasgow area expansion with the addition of the Drumpellier Lawns, Burnside View and The Fairways housing developments. Present day Bargeddie is now populated by just over 6500 people. The village has two primary schools; Bargeddie Primary School and St. Kevins Primary School. The two schools f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines In Scotland
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Glasgow
The city of Glasgow, Scotland has a transport system encompassing air, rail, road, and an underground light metro line. Prior to 1962, the city was also served by trams. Commuters travelling into Glasgow from the neighbouring local authorities of North and South Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire, East Renfrewshire, and East and West Dunbartonshire have a major influence on travel patterns, with tens of thousands of residents commuting into the city each day. The most popular mode of transport in the city is the car, used by two thirds of people for journeys around the city. Most streets in the centre of Glasgow are organised in a grid-iron pattern laid out in the early 19th century, with streets running north to south and east to west. Transport authorities Glasgow's transport network is administered by a number of authorities. Transport Scotland is responsible for the construction, expansion and maintenance of trunk roads and motorways within the city (such as the M8, M73, M74 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Multiple Unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number of the carriages. An EMU is usually formed of two or more semi-permanently coupled carriages, but electrically powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as EMUs. The great majority of EMUs are passenger trains, but versions also exist for carrying mail. EMUs are popular on commuter and suburban rail networks around the world due to their fast acceleration and pollution-free operation. Being quieter than diesel multiple units (DMUs) and locomotive-hauled trains, EMUs can operate later at night and more frequently without disturbing nearby residents. In addition, tunnel design for EMU trains is simpler as no provision is needed for exhausting fumes, although retrofitting existing limited-clearance tunnels to accommodate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyle Line
The Argyle Line is a suburban railway located in West Central Scotland. The line serves the commercial and shopping districts of Glasgow's central area, and connects towns from West Dunbartonshire to South Lanarkshire. Named for Glasgow's Argyle Street, the line uses the earlier cut-and-cover tunnel running beneath that thoroughfare. The term "Argyle Line" is commonly used to describe: * the extensive urban passenger train service that connects the towns and suburbs of North Clyde with Motherwell, Larkhall, and Lanark, to the southeast. Of the 48 stations, 4 are in West Dunbartonshire, 4 in East Dunbartonshire, 17 in Glasgow City, 10 in North Lanarkshire, and 13 in South Lanarkshire. * the central portion of railway infrastructure encompassing less than . History Prior to 1964 The Glasgow Central Railway (GCR) under central Glasgow opened in 1886, connecting the Lanarkshire and Dunbartonshire Railway at and Stobcross Railway at to the Lanarkshire and Ayrshire Railway near , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 158
The British Rail Class 158 '' Express Sprinter'' is a diesel multiple unit (DMU) passenger train. It is a member of the Sprinter series of regional trains, produced as a replacement for British Rail's first generation of DMUs; of the other members, the Class 159 is almost identical to the Class 158, having been converted from Class 158 to Class 159 in two batches to operate express services from London Waterloo to the West of England. The Class 158 was constructed between 1989 and 1992 by British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) at its Derby Litchurch Lane Works. The majority were built as two-car sets, some three-car sets were also produced. During September 1990, the first Express Sprinters were operated by ScotRail; the type was promptly introduced to secondary routes across the Midlands, Northern England, Wales and the South West. The Class 158 enabled the replacement of large numbers of elderly DMUs but also several locomotive-hauled trains as well; this was partially a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Multiple Unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as DMUs. Diesel-powered units may be further classified by their transmission type: diesel–mechanical DMMU, diesel–hydraulic DHMU, or diesel–electric DEMU. Design The diesel engine may be located above the frame in an engine bay or under the floor. Driving controls can be at both ends, on one end, or in a separate car. Types by transmission DMUs are usually classified by the method of transmitting motive power to their wheels. Diesel–mechanical In a diesel–mechanical multiple unit (DMMU), the rotating energy of the engine is transmitted via a gearbox and driveshaft directly to the wheels of the train, like a car. The transmissions can be shifted manually by the driver, as in the great majority of first-gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 101
The British Rail Classes 101 and 102 diesel mechanical multiple units were built by Metro-Cammell at Washwood Heath in Birmingham, England from 1956 to 1959, following construction of a series of prototype units. These classes proved to be some of the most successful and longest-lived of BR's ''First Generation'' DMUs, second in longevity only to the Class 121, with the final five units being withdrawn on 24 December 2003. The oldest set was, by then, just over 47 years old. Background In 1954, British Rail published a Modernisation Plan to streamline the railway network, bringing it up to date in comparison to European standards. Steam power would be phased out in favour of diesel powered railcars and locomotives, and projects were put out to tender. BR hoped that by replacing steam with DMUs, costs would be reduced sufficiently to make rural lines viable. Since there was no time for BR to issue a standard specification, train builders were invited to submit plans on the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 156
The British Rail Class 156 ''Super Sprinter'' is a diesel multiple unit passenger train. A total of 114 sets were built between 1987 and 1989 for British Rail by Metro-Cammell's Washwood Heath works. They were built to replace elderly first-generation DMUs and locomotive-hauled passenger trains. Background By the beginning of the 1980s, British Rail (BR) operated a large fleet of first generation DMUs, which had been constructed in prior decades to various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, British Rail planners recognised that there would be considerable costs incurred by undertaking refurbishment programmes necessary for the continued use of these ageing multiple units, particularly due to the necessity of handling and removing hazardous materials such as asbestos. In light of the high costs involved in retention, planners examined the prospects for the development and introduction of a new generation of DMUs to succeed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest mixed-traffic railway routes in Europe, carrying a mixture of intercity rail, regional rail, commuter rail and rail freight traffic. The core route of the WCML runs from London to Glasgow for and was opened from 1837 to 1869. With additional lines deviating to Northampton, Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh, this totals a route mileage of . The Glasgow–Edinburgh via Carstairs line connects the WCML to Edinburgh, however the main London–Edinburgh route is the East Coast Main Line. Several sections of the WCML form part of the suburban railway systems in London, Coventry, Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Glasgow, with many more smaller commuter stations, as well as providing links to more rural towns. It is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
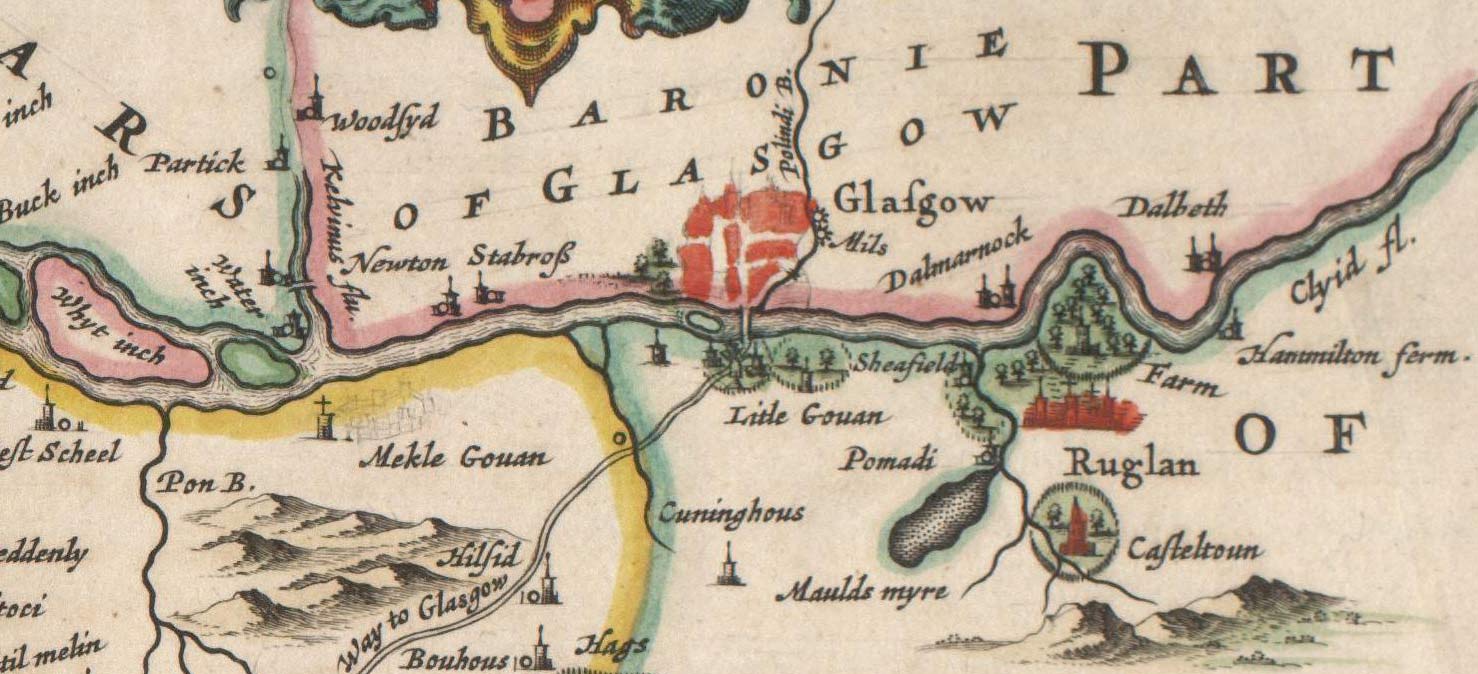
Rutherglen
Rutherglen (, sco, Ruglen, gd, An Ruadh-Ghleann) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, immediately south-east of the city of Glasgow, from its centre and directly south of the River Clyde. Having existed as a Lanarkshire burgh in its own right for more than 800 years, in 1975 Rutherglen lost its own local council and administratively became a component of the City of Glasgow (1975–1996), City of Glasgow District within the Strathclyde Local government areas of Scotland 1973–96, region (along with neighbouring Cambuslang). In 1996 the towns were reallocated to the South Lanarkshire Subdivisions of Scotland, council area.From a pawnbrokers to Parliament - Tommy McAvoy looks back on a career that too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |