|
Wet Oxidation
Wet oxidation is a form of hydrothermal treatment. It is the oxidation of dissolved or suspended components in water using oxygen as the oxidizer. It is referred to as "Wet Air Oxidation" (WAO) when air is used. The oxidation reactions occur in superheated water at a temperature above the normal boiling point of water (100 °C), but below the critical point (374 °C). The system must be maintained under pressure to avoid excessive evaporation of water. This is done to control energy consumption due to the latent heat of vaporization. It is also done because liquid water is necessary for most of the oxidation reactions to occur. Compounds oxidize under wet oxidation conditions that would not oxidize under dry conditions at the same temperature and pressure. Wet oxidation has been used commercially for around 60 years. It is used predominantly for treating wastewater. It is often referred to as Zimpro (from ZIMmerman PROcess), after Fred J. Zimmermann who commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spent Caustic
Spent caustic is a waste industrial caustic solution that has become exhausted and is no longer useful (or spent). Spent caustics are made of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, water, and contaminants. The contaminants have consumed the majority of the sodium (or potassium) hydroxide and thus the caustic liquor is spent, for example, in one common application H2S (''gas'') is scrubbed by the NaOH (''aqueous'') to form NaHS (''aq'') and H2O (''l''), thus consuming the caustic. Types * Ethylene spent caustic comes from the caustic scrubbing of cracked gas from an ethylene cracker. This liquor is produced by a caustic scrubbing tower. Ethylene product gas is contaminated with (g) and (g), and those contaminants are removed by absorption in the caustic scrubbing tower to produce (aq) and {{chem, Na, 2, CO, 3(aq). The sodium hydroxide is consumed and the resulting wastewater (ethylene spent caustic) is contaminated with the sulfides and carbonates and a small fraction of or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Treatment
Thermal treatment is any waste treatment technology that involves high temperatures in the processing of the waste feedstock. Commonly this involves the combustion of waste materials. Systems that are generally considered to be thermal treatment include: *Cement kiln * Gasification *Incineration *Mechanical heat treatment *Pyrolysis *Thermal depolymerization *Waste autoclaves See also *Anaerobic digestion *List of solid waste treatment technologies *Mechanical biological treatment *Waste-to-energy *Pyrolysis The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ... Weblinks * Germany and thermal treatment – an exemplary German companyREMEX Mineralstoff GmbH* Recycling solutions for tar contaminated stratification material – thermal treatment ants.verwertungin Germany {{Waste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Processes
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt ( sodium chloride) and refined sugar ( sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Waste-water Treatment Technologies
This page consists of a list of wastewater treatment technologies: See also *Agricultural wastewater treatment * Industrial wastewater treatment *List of solid waste treatment technologies * Waste treatment technologies *Water purification *Sewage sludge treatment Sewage sludge treatment describes the processes used to manage and dispose of sewage sludge produced during sewage treatment. Sludge treatment is focused on reducing sludge weight and volume to reduce transportation and disposal costs, and on red ... References * * Industrial Wastewater Treatment Technology DatabaseEPA. {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Waste Water Treatment Technologies Chemical processes Environmental engineering *List Water pollution Water technology Waste-water treatment technologies Sanitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incineration
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high-temperature waste treatment systems are described as "thermal treatment". Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas. The flue gases must be cleaned of gaseous and particulate pollutants before they are dispersed into the atmosphere. In some cases, the heat that is generated by incineration can be used to generate electric power. Incineration with energy recovery is one of several waste-to-energy technologies such as gasification, pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion. While incineration and gasification technologies are similar in principle, the energy produced f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
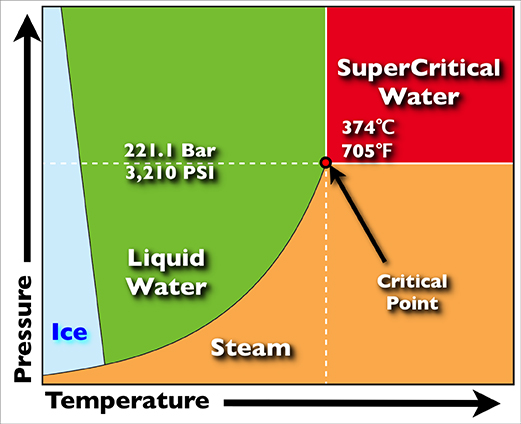
Supercritical Water Oxidation
Supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) is a process that occurs in water at temperatures and pressures above a mixture's thermodynamic critical point. Under these conditions water becomes a fluid with unique properties that can be used to advantage in the destruction of recalcitrant and hazardous wastes such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) or Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Supercritical water has a density between that of water vapor and liquid at standard conditions, and exhibits high gas-like diffusion rates along with high liquid-like collision rates. In addition, the behavior of water as a solvent is altered (in comparison to that of subcritical liquid water) - it behaves much less like a polar solvent. As a result, the solubility behavior is "reversed" so that oxygen, and organics such as chlorinated hydrocarbons become soluble in the water, allowing single-phase reaction of aqueous waste with a dissolved oxidizer. The reversed solubility also causes salts to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powdered Activated Carbon Treatment
Powdered Activated Carbon Treatment (PACT) is a wastewater technology in which powdered activated carbon is added to an anaerobic or aerobic treatment system.Jafarinejad, S. “Activated sludge combined with powdered activated carbon (PACT process) for the petroleum industry wastewater treatment: A review.” Chemistry International. 3(4) (2017) 26. The carbon in the biological treatment process adsorbs recalcitrant compounds that are not readily biodegradable, thereby reducing the chemical oxygen demand of the wastewater and removing toxins.Meidl, John. “Use of the PACT System to Treat Industrial Wastewaters for Direct Discharge or Reuse.” Jubilee XX Conference of Science & Technology. The carbon also acts as a "buffer" against the effects of toxic organics in the wastewater. In such a system, biological treatment and carbon adsorption are combined into a single, synergistic treatment step. The result is a system which offers significant cost reduction compared to activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mother Liquor
The mother liquor (or spent liquor) is the solution Solution may refer to: * Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another * Solution (equation), in mathematics ** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds * Soluti ... remaining after a component has been removed by a some process such as filtration or more commonly crystallization. It is encountered in chemical processes including sugar refining. In crystallization, a solid (usually impure) is dissolved in a solvent at high temperature, taking advantage of the fact that most solids are more soluble at higher temperatures. As the solution cools, the solubility of the solute in the solvent will gradually become smaller. The resultant solution is described as supersaturated, meaning that there is more solute dissolved in the solution than would be predicted by its solubility at that temperature. Crystallization can then be induced from this supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations have a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene and several copolymers. Approximately 25 million tonnes of styrene were produced in 2010, increasing to around 35 million tonnes by 2018. Natural occurrence Styrene is named after storax balsam (often commercially sold as ''styrax''), the resin of Liquidambar trees of the Altingiaceae plant family. Styrene occurs naturally in small quantities in some plants and foods (cinnamon, coffee beans, balsam trees and peanuts) and is also found in coal tar. History In 1839, the German apothecary Eduard Simon isolated a volatile liquid from the resin (called ''storax'' or ''styrax'' (Latin)) of the American sweetgum tree (''Liquidambar styraciflua''). He called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Inhibitor
Kinetic Inhibitors are a new and evolving technology of a class of Low Dosage Hydrate Inhibitors (LDHI) that are polymers and copolymers (or a mix thereof). The most common of which is polyvinylcaprolactam (PVCap). Kelland, Malcolm et al. A New Class of Hydrate Inhibitor. 2000. http://www.iris.no/internet/student.nsf/199f312efd2a0cacc125680e00635b85/b58dcb01591e3feac125768f004f4a66/$FILE/Fagernes%20paper.pdf These inhibitors are primarily utilized to retard the formation of clathrate hydrates. This problem becomes most prominent in flow lines when hydrocarbons and water flow through a line. The pressure and cold temperatures that could be exposed to the flow lines provides an environment in which clathrate hydrates can form and plug up the flow line. The inhibitors generally slow the formation of the hydrates enough so the fluid reaches storage without causing blockage. Structure There may be variations on the types and structure of the polymer used as the inhibitor. However, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteurize
Pasteurization or pasteurisation is a process of food preservation in which packaged and non-packaged foods (such as milk and fruit juices) are treated with mild heat, usually to less than , to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life. The process is intended to destroy or deactivate microorganisms and enzymes that contribute to food spoilage or risk of disease, including vegetative bacteria, but most bacterial spores survive the process. The process is named after the French microbiologist Louis Pasteur whose research in the 1860s demonstrated that thermal processing would deactivate unwanted microorganisms in wine. Spoilage enzymes are also inactivated during pasteurization. Today, pasteurization is used widely in the dairy industry and other food processing industries to achieve food preservation and food safety. By the year 1999, most liquid products were heat treated in a continuous system where heat can be applied using a plate heat exchanger or the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
