|
Western Australian Secession Movement
Secessionism has been a recurring feature of Western Australia's political landscape since shortly after Federation in 1901. The idea of self-governance or secession has often been discussed through local newspaper articles and editorials. On a number of occasions secession has been a serious political issue for the State, including in a successful but unimplemented 1933 state referendum. One recurring argument by proponents of secession is based on the assumption that a federal government in Canberra will favour the business and popular interests of the larger population centres lying to the east of this state. A common complaint is that Western Australia is a forgotten or Cinderella state, which contributes more to federal funds than it gets back, and is discriminated against by the more populous states. The Constitution of Australia, however, describes the union as "one indissoluble Federal Commonwealth" and makes no provision for states to secede. Western Australia is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Dominion Of Westralia (secession Movement)
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Forrest
Sir John Forrest (22 August 1847 – 2 SeptemberSome sources give the date as 3 September 1918 1918) was an Australian explorer and politician. He was the first premier of Western Australia (1890–1901) and a long-serving cabinet minister in federal politics. Forrest was born in Bunbury, Western Australia, to Scottish immigrant parents. He was the colony's first locally born surveyor, coming to public notice in 1869 when he led an expedition into the interior in search of Ludwig Leichhardt. The following year, Forrest accomplished the first land crossing from Perth to Adelaide across the Nullarbor Plain. His third expedition in 1874 travelled from Geraldton to Adelaide through the centre of Australia. Forrest's expeditions were characterised by a cautious, well-planned approach and diligent record-keeping. He received the Patron's Medal of the Royal Geographical Society in 1876. Forrest became involved in politics through his promotion to surveyor-general, a powerful posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretary Of State For The Colonies
The secretary of state for the colonies or colonial secretary was the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, British Cabinet government minister, minister in charge of managing the United Kingdom's various British Empire, colonial dependencies. History The position was first created in 1768 to deal with the increasingly troublesome Thirteen colonies, North American colonies, following passage of the Townsend Acts. Previously, colonial responsibilities were held jointly by the Board of Trade, lords of trade and plantations and the Secretary of State for the Southern Department, secretary of state for the Southern Department, who was responsible for Ireland, the American colonies, and relations with the Roman Catholicism in Europe, Catholic and Islam in Europe, Muslim states of Europe, as well as being jointly responsible for domestic affairs with the Secretary of State for the Northern Department. Joint responsibility continued under the secretary of state for the colonies, but led to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of colonies of the British Empire. Despite its name, the Colonial Office was never responsible for all Britain's Imperial territories; for example, protectorates fell under the purview of the Foreign Office, and British India was ruled by the East India Company until 1858 (the British Raj ruled the India Office as a result of the Indian Mutiny), while the role of the Colonial Office in the affairs of the Dominions changed as time passed. It was headed by the Secretary of State for the Colonies, also known more informally as the Colonial Secretary. First Colonial Office (1768–1782) Prior to 1768, responsibility for the affairs of the British colonies was part of the duties of the Secretary of State for the Southern Department and a committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Griffiths
Walter Griffiths (4 July 1867 – 4 September 1900) was a politician in the Northern Territory of Australia. He was a member of the South Australian House of Assembly from 1893 to 1900, representing the Northern Territory electorate. Background Born in Kent Town, South Australia, the son of Frederick Griffiths, a wealthy ironmonger, and his wife Helen, née Giles, Griffiths attended St Aloysius College and Saint Peter's College in Adelaide. Aged fifteen Griffiths moved to Yam Creek in the Northern Territory to work for his uncle William Griffiths, a mine owner, before becoming a business partner of Vaiben Louis Solomon in mining ventures in the Northern Territory and the Western Australian goldfields, co-owned the ''Northern Territory Times'' and became a prominent member of the Kalgoorlie Chamber of Mines. On his uncle's death in 1892, Griffiths took over the business, retaining his association with Solomon, who in 1890, had become one of the two members for the Electoral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auralia
Auralia was a proposed colony that would have been formed out of the south-eastern portion of the colony of Western Australia in the early twentieth century, and would have joined the newly formed Commonwealth of Australia. The name, meaning 'golden' in Latin, denotes the gold industries that were alive at the time and which helped foment the ideas of secession. The proposed colony would have comprised the Goldfields, the western portion of the Nullarbor Plain and the port town of Esperance. Its capital would have been Kalgoorlie. The push to secession was prompted by perceptions that the Western Australian colony under Sir John Forrest was parochial, self-serving and evasive towards federating the colony with the emerging Commonwealth. Many inhabitants in the goldfields had come to Western Australia from the other colonies in the previous decade when Kalgoorlie experienced a gold rush and their loyalties were thus not usually directed towards Perth. Sir John Forrest's effo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holland's Track
''Holland's Magazine'' (originally known as ''Street's Weekly'', also known as ''Holland's: The Magazine of the South'') was a magazine published from 1876 to 1953. It was a women's magazine that published recipes, fashion tips, gardening tips, sewing patterns, non-fiction, and short fiction. It was known for being a vehicle for social change and was influential in securing the passage of the Texas Pure Food law. ''Street's Weekly'' From its founding in 1876 until its 23rd volume in 1905 the magazine was ''Street's Weekly'' and published weekly. Beginning with its 24th volume in 1905 it published monthly under a new name. ''Holland's Magazine'' In 1905 F. P. Holland changed the name of ''Street's Weekly'' to ''Holland's Magazine'' and moved its headquarters to Dallas, Texas. ''Holland's'' became a monthly magazine, with page sizes measuring and a full color cover. Roughly 40% of the magazine's contents were advertising. At ten cents an issue, it was more affordable than com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broomehill, Western Australia
Broomehill is a town on the Great Southern Highway between Katanning and Albany, in the Great Southern region of Western Australia. Its local government area is the Shire of Broomehill-Tambellup. History The town of Broomehill owes its creation to the Great Southern Railway, which was completed in 1889. The railway runs from Beverley to Albany. Broomehill is named after Sir Frederick Napier Broome (1842–96) who was then the Governor of Western Australia. Gold bearing quartz was discovered by the station master around Broomehill in 1889. In the same year Patrick Garrity purchased two lots facing Jasper Street and built a galvanised iron hotel. By 1905 the hotel had been rebuilt in brick with more extensions added in 1908. Known as the Broomehill Hotel and later as the Imperial Hotel, the two storey tuck pointed building is now heritage listed. The townsite was gazetted by the Western Australian Land Company in 1890, which was recognised by the state government in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albany, Western Australia
Albany ( ; nys, Kinjarling) is a port city in the Great Southern region in the Australian state of Western Australia, southeast of Perth, the state capital. The city centre is at the northern edge of Princess Royal Harbour, which is a part of King George Sound. The central business district is bounded by Mount Clarence to the east and Mount Melville to the west. The city is in the local government area of the City of Albany. While it is the oldest colonial, although not European, settlement in Western Australia - predating Perth and Fremantle by over two years - it was a semi-exclave of New South Wales for over four years until it was made part of the Swan River Colony. The settlement was founded on 26 December 1826 as a military outpost of New South Wales for the purpose of forestalling French ambitions in the region. To that end, on 21 January 1827, the commander of the outpost, Major Edmund Lockyer, formally took possession for the British Crown of the portion of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fremantle Harbour
Fremantle Harbour is Western Australia's largest and busiest general cargo port and an important historical site. The inner harbour handles a large volume of sea containers, vehicle imports and livestock exports, cruise shipping and naval visits, and operates 24 hours a day. It is located adjacent to the city of Fremantle, in the Perth metropolitan region. Fremantle Harbour consists of the Inner Harbour, which is situated on the mouth of the Swan River; the Outer Harbour, which is south at Kwinana in Cockburn Sound and handles bulk cargo ports, grain, petroleum, liquefied petroleum gas, alumina, mineral sands, fertilisers, sulphur and other bulk commodities; and Gage Roads, which is the anchorage between Rottnest Island and the mainland. The Inner Harbour includes northern and southern wharves named North Quay and Victoria Quay respectively. All of this area is managed by the Fremantle Port Authority, a government trading enterprise, under the registered business name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
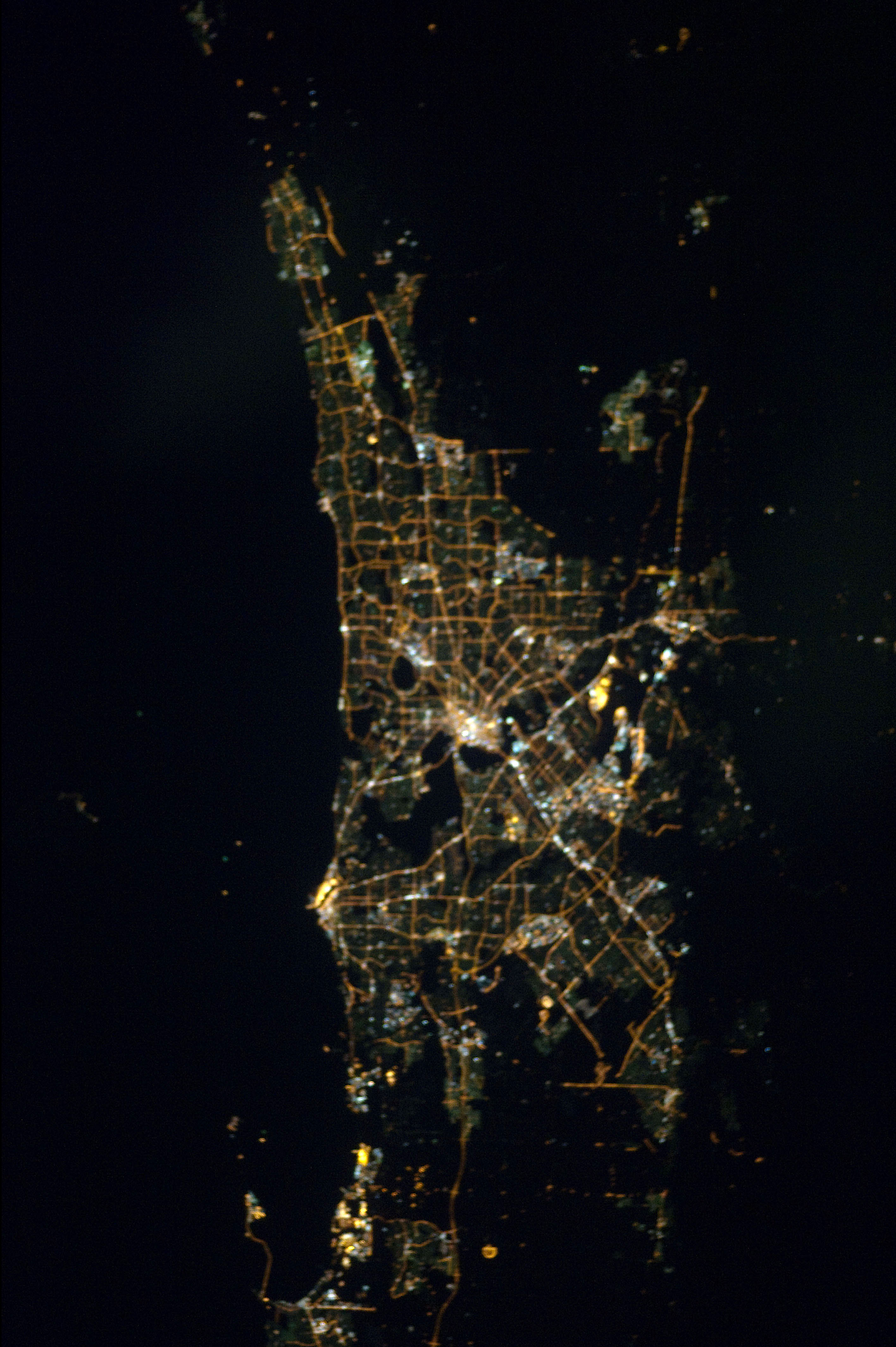
Perth Metropolitan Area
The Perth metropolitan region or the Perth metropolitan area is the administrative area and geographical extent of the Western Australian capital city of Perth and its conurbation. It generally includes the coastal strip from Two Rocks in the north to Singleton in the south, and inland to The Lakes in the east, but its extent can be defined in a number of ways: *The metropolitan region is defined by the ''Planning and Development Act 2005'' to include 30 local government areas with the outer extent being the City of Wanneroo and the City of Swan to the north, the Shire of Mundaring, City of Kalamunda, and the City of Armadale to the east, the Shire of Serpentine-Jarrahdale to the southeast and the City of Rockingham to the southwest, and including the islands of Rottnest Island and Garden Island off the west coast. This extent correlates with the Metropolitan Region Scheme. *The Australian Bureau of Statistics' Perth (Major Statistical Division) accords with the Metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern States Of Australia
The eastern states of Australia are the states adjoining the east continental coastline of Australia. These are the mainland states of Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland, and the island state of Tasmania. The Australian Capital Territory and Jervis Bay Territory, while not states, are also included. On some occasions, the southern state of South Australia is also included in this grouping due to its economic ties with the eastern states. Regardless of which definition is used, the eastern states include the great majority of the Australian population. They contain the federal capital Canberra and Australia's three largest cities Sydney, Melbourne and Brisbane (all capitals of the respective east coast states), as well as the three largest non-capital cities in the country: Gold Coast, Queensland; Newcastle, New South Wales; and Wollongong, New South Wales. In terms of climate, the area is dominated by a humid subtropical zone, with some tropical (Queensland) and oceani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |