|
Welfare Cost Of Business Cycles
In macroeconomics, the cost of business cycles is the decrease in social welfare, if any, caused by business cycle fluctuations. Nobel economist Robert Lucas proposed measuring the cost of business cycles as the percentage increase in consumption that would be necessary to make a representative consumer indifferent between a smooth, non-fluctuating, consumption trend and one that is subject to business cycles. Under the assumptions that business cycles represent random shocks around a trend growth path, Robert Lucas argued that the cost of business cycles is extremely small, and as a result the focus of both academic economists and policy makers on economic stabilization policy rather than on long term growth has been misplaced. Lucas himself, after calculating this cost back in 1987, reoriented his own macroeconomic research program away from the study of short run fluctuations. However, Lucas' conclusion is controversial. In particular, Keynesian economists typically argue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. For example, using interest rates, taxes, and government spending to regulate an economy's growth and stability. This includes regional, national, and global economies. According to a 2018 assessment by economists Emi Nakamura and Jón Steinsson, economic "evidence regarding the consequences of different macroeconomic policies is still highly imperfect and open to serious criticism." Macroeconomists study topics such as Gross domestic product, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), national income, price index, price indices, output (economics), output, Consumption (economics), consumption, inflation, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Review Of Economics And Statistics
''The'' ''Review of Economics and Statistics'' is a peer-reviewed 103-year-old general journal that focuses on applied economics, with specific relevance to the scope of quantitative economics. The ''Review'', edited at the Harvard University’s Kennedy School of Government The Harvard Kennedy School (HKS), officially the John F. Kennedy School of Government, is the school of public policy and government of Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The school offers master's degrees in public policy, public ... (JSTOR), has the long-term aim of publishing influential articles in mainly theoretical and empirical economics that will contribute to the broader readership in economics in both the present and the continual future. Over the time, the journal has published several of the most significant articles in empirical economics (JSTOR) based on its recognizable history which includes works from “Kenneth Arrow, Milton Friedman, Robert Merton, Paul Samuelson, Robert Sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Risk Aversion
In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome. Risk aversion explains the inclination to agree to a situation with a more predictable, but possibly lower payoff, rather than another situation with a highly unpredictable, but possibly higher payoff. For example, a risk-averse investor might choose to put their money into a bank account with a low but guaranteed interest rate, rather than into a share capital, stock that may have high expected returns, but also involves a chance of losing value. Example A person is given the choice between two scenarios: one with a guaranteed payoff, and one with a risky payoff with same average value. In the former scenario, the person receives $50. In the uncertain scenario, a coin is flipped to decide whether the person receives $100 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Log
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant , which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to . The natural logarithm of is generally written as , , or sometimes, if the base is implicit, simply . Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving , , or . This is done particularly when the argument to the logarithm is not a single symbol, so as to prevent ambiguity. The natural logarithm of is the power to which would have to be raised to equal . For example, is , because . The natural logarithm of itself, , is , because , while the natural logarithm of is , since . The natural logarithm can be defined for any positive real number as the area under the curve from to (with the area being negative when ). The simplicity of this definition, which is matched in many other formulas involving the natural logarithm, leads to the term "natural". The definition of the natural logarithm can then be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
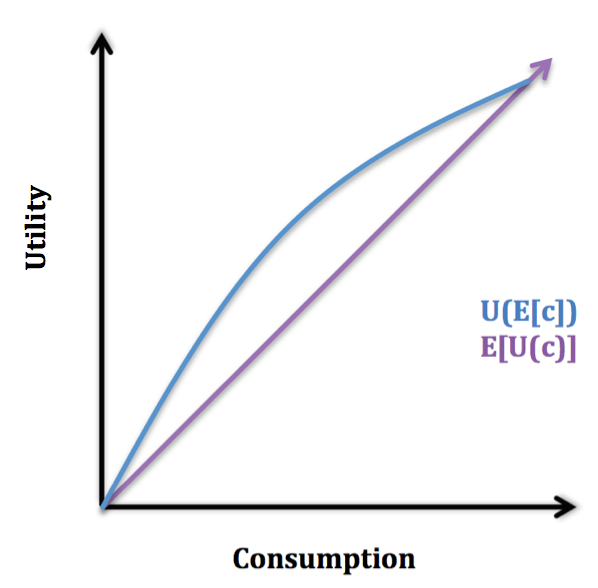
Consumption Smoothing
Consumption smoothing is an economic concept for the practice of optimizing a person's standard of living through an appropriate balance between savings and consumption over time. An optimal consumption rate should be relatively similar at each stage of a person's life rather than fluctuate wildly. Luxurious consumption at an old age does not compensate for an impoverished existence at other stages in one's life. Since income tends to be hump-shaped across an individual's life, economic theory suggests that individuals should on average have low or negative savings rate at early stages in their life, high in middle age, and negative during retirement. Although many popular books on personal finance advocate that individuals should at all stages of their life set aside money in savings, economist James Choi states that this deviates from the advice of economists. Expected utility model The graph below illustrates the expected utility model, in which U(c) is increasing in and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willingness To Pay
In behavioral economics, willingness to pay (WTP) is the maximum price at or below which a consumer will definitely buy one unit of a product.Varian, Hal R. (1992), Microeconomic Analysis, Vol. 3. New York: W.W. Norton. This corresponds to the standard economic view of a consumer reservation price. Some researchers, however, conceptualize WTP as a range. According to the constructive preference view, consumer willingness to pay is a context-sensitive construct; that is, a consumer's WTP for a product depends on the concrete decision context. For example, consumers tend to be willing to pay more for a soft drink in a luxury hotel resort in comparison to a beach bar or a local retail store. See also * Cost-benefit analysis * Welfare economics Welfare economics is a branch of economics that uses microeconomic techniques to evaluate well-being (welfare) at the aggregate (economy-wide) level. Attempting to apply the principles of welfare economics gives rise to the field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Welfare Function
In welfare economics, a social welfare function is a function that ranks social states (alternative complete descriptions of the society) as less desirable, more desirable, or indifferent for every possible pair of social states. Inputs of the function include any variables considered to affect the economic welfare of a society. In using welfare measures of persons in the society as inputs, the social welfare function is individualistic in form. One use of a social welfare function is to represent prospective patterns of collective choice as to alternative social states. The social welfare function provides the government with a simple guideline for achieving the optimal distribution of income. The social welfare function is analogous to the consumer theory of indifference-curve– budget constraint tangency for an individual, except that the social welfare function is a mapping of individual preferences or judgments of everyone in the society as to collective choices, which ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Surplus
In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or total social welfare or Marshallian surplus (after Alfred Marshall), is either of two related quantities: * Consumer surplus, or consumers' surplus, is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay. * Producer surplus, or producers' surplus, is the amount that producers benefit by selling at a market price that is higher than the least that they would be willing to sell for; this is roughly equal to profit (since producers are not normally willing to sell at a loss and are normally indifferent to selling at a break-even price). Overview In the mid-19th century, engineer Jules Dupuit first propounded the concept of economic surplus, but it was the economist Alfred Marshall who gave the concept its fame in the field of economics. On a standard supply and demand diagram, consumer sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Aversion
In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome. Risk aversion explains the inclination to agree to a situation with a more predictable, but possibly lower payoff, rather than another situation with a highly unpredictable, but possibly higher payoff. For example, a risk-averse investor might choose to put their money into a bank account with a low but guaranteed interest rate, rather than into a stock that may have high expected returns, but also involves a chance of losing value. Example A person is given the choice between two scenarios: one with a guaranteed payoff, and one with a risky payoff with same average value. In the former scenario, the person receives $50. In the uncertain scenario, a coin is flipped to decide whether the person receives $100 or nothing. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |