|
Waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indicates the draft of the ship and the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of waves that may arise. Varying water temperatures will affect a ship's draft, because warm water is less dense than cold water, providing less buoyancy. In the same way, fresh water is less dense than salinated or seawater with a similar lessening effect upon buoyancy. For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is defined by, among other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat. A waterline can also refer to any l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterline Length
A vessel's length at the waterline (abbreviated to L.W.L)Note: originally Load Waterline Length is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water (the ''waterline''). The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat overall (''length overall'' or LOA) as most boats have bows and stern protrusions that make the LOA greater than the LWL. As a ship becomes more loaded, it will sit lower in the water and its ambient waterline length may change; but the registered L.W.L it is measured from a default load condition. This measure is significant in determining several of a vessel's properties, such as how much water it displaces, where the bow and stern waves occur, hull speed, amount of bottom-paint needed, etc. Traditionally, a stripe called the "boot top" is painted around the hull just above the waterline. In sailing boats, longer waterline length will usually enable a greater maximum speed, because it allows greater sail area, without increasing beam or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Plimsoll
Samuel Plimsoll (10 February 1824 – 3 June 1898) was a British politician and social reformer, now best remembered for having devised the Plimsoll line (a line on a ship's hull indicating the maximum safe draught, and therefore the minimum freeboard for the vessel in various operating conditions). Early life Samuel Plimsoll was born in Bristol and soon moved to Whiteley Wood Hall, Sheffield, also spending part of his childhood in Penrith, Cumberland. Leaving school at an early age, he became a clerk at Rawson's Brewery, and rose to be manager. In 1853, he attempted to become a coal merchant in London. He failed and was reduced to destitution. He himself told how for a time he lived in a common lodging for seven shillings and two pence a week. Through this experience, he learnt to sympathise with the struggles of the poor, and when his good fortune returned, he resolved to devote his time to improving their condition. His efforts were directed especially against what were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
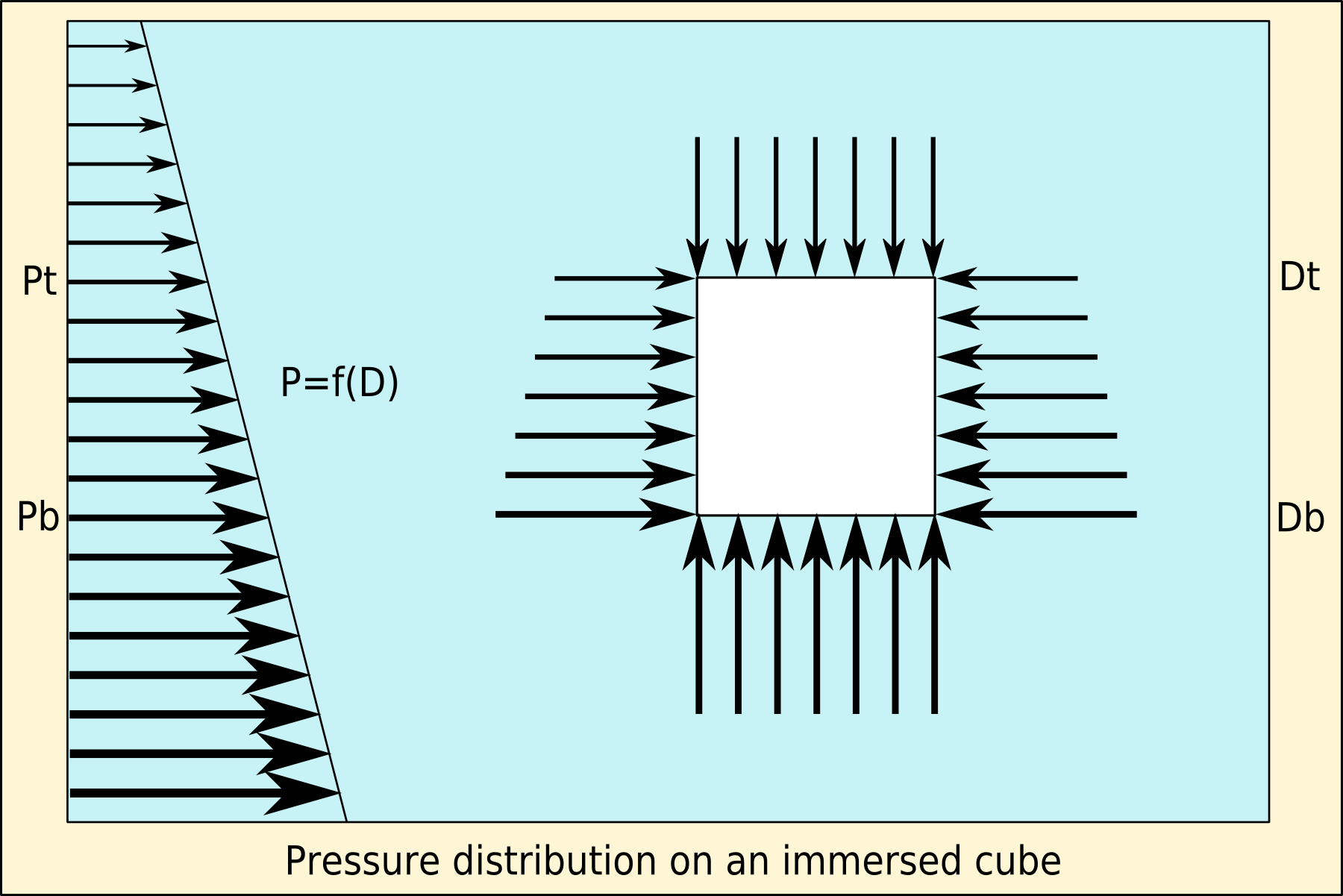
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization (IMO) damage stability regulations, due to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd's Register
Lloyd's Register Group Limited (LR) is a technical and professional services organisation and a maritime classification society, wholly owned by the Lloyd’s Register Foundation, a UK charity dedicated to research and education in science and engineering. The organisation dates to 1760. Its stated aims are to enhance the safety of life, property, and the environment, by helping its clients (including by validation, certification, and accreditation) to improve the safety and performance of complex projects, supply chains and critical infrastructure. In July 2012, the organisation converted from an industrial and provident society to a company limited by shares, named Lloyd’s Register Group Limited, with the new Lloyd’s Register Foundation as the sole shareholder. At the same time the organisation gave to the Foundation a substantial bond and equity portfolio to assist it with its charitable purposes. It will benefit from continued funding from the group’s operating arm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Maritime Organization
The International Maritime Organization (IMO, French: ''Organisation maritime internationale'') is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, IMO currently has 175 Member States and three Associate Members. The IMO's primary purpose is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes maritime safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation, maritime security and the efficiency of shipping. IMO is governed by an assembly of members which meets every two years. Its finance and organization is administered by a council of 40 members elected from the assembly. The work of IMO is conducted through five committees and these are supported by technical subcommitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant Shipping Act 1894
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry, commerce, and trade have existed. In 16th-century Europe, two different terms for merchants emerged: referred to local traders (such as bakers and grocers) and ( nl, koopman) referred to merchants who operated on a global stage, importing and exporting goods over vast distances and offering added-value services such as credit and finance. The status of the merchant has varied during different periods of history and among different societies. In modern times, the term ''merchant'' has occasionally been used to refer to a businessperson or someone undertaking activities (commercial or industrial) for the purpose of generating profit, cash flow, sales, and revenue using a combination of human, financial, intellectual and physical capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Convention On Load Lines
The International Convention on Load Lines (CLL), was signed in London on 5 April 1966, amended by the 1988 Protocol and further revised in 2003. The convention pertains specifically to a ship's load line (also referred to as the "waterline"), a marking of the highest point on a ship's hull that can safely meet the surface of the water; a ship that is loaded to the point where its load line is underwater and no longer visible has exceeded its draft and is in danger because its capacity has been exceeded. The 1988 Protocol was adopted to harmonise the survey and certification requirement of the 1966 Convention with those contained in the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) and MARPOL 73/78 The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973 as modified by the Protocol of 1978, or "MARPOL 73/78" is one of the most important international marine environmental conventions. MARPOL 73/78, MARPOL is an amalg .... In accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
733 How-deep
__NOTOC__ Year 733 ( DCCXXXIII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 733 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Emperor Leo III confiscates the papal territories in Sicily and Calabria (Southern Italy), from which Pope Gregory III derives most of his income tax. He transfers ecclesiastical jurisdiction in the former Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum to Anastasius, patriarch of Constantinople. Gregory begins his support of a revolt in Italy against iconoclasm. By now the break between the papacy and the Byzantine Empire is almost complete. * Arab-Byzantine Wars: Arab forces under Mu’awiya ibn Hisham penetrate deep into Anatolia and conquer the cities of Antalya, Doralyum and Afyonkarahisar. These conquests differ from previous ones, as Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Line , a method of determining operating points in circuits with non-linear elements.
{{disambig ...
Load line may refer to: * Ship's load line, related to ship construction * Load line (electronics) In graphical analysis of nonlinear electronic circuits, a load line is a line drawn on the characteristic curve, a graph of the current vs. the voltage in a nonlinear device like a diode or transistor. It represents the constraint put on the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)