|
Ward Goodenough
Ward Hunt Goodenough II (May 30, 1919 – June 9, 2013) was an American anthropologist, who has made contributions to kinship studies, linguistic anthropology, cross-cultural studies, and cognitive anthropology. Biography and major works Goodenough was born May 30, 1919, in Cambridge Massachusetts, the son of Helen Miriam (Lewis) and Erwin Ramsdell Goodenough, a scholar in the history of religion, who was then a graduate student at Harvard Divinity School. He was a brother to noted solid-state physicist John B. Goodenough. As a child his family moved between Europe and Germany as his father conducted research on a Ph.D. As a result Goodenough developed an early interest in German and languages in general. He began attending Groton School in 1932. In 1937 he began studying at Cornell University. He majored in Scandinavian languages and literature, but was also influenced by the psychologist Leonard S. Cottrell, Jr. and the anthropologist Lauriston Sharp. He earned a B.A. in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinship And Descent
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that the study of kinship is the study of what humans do with these basic facts of lifemating, gestation, parenthood, socialization, siblingship etc. Human society is unique, he argues, in that we are "working with the same raw material as exists in the animal world, but ecan conceptualize and categorize it to serve social ends." These social ends include the socialization of children and the formation of basic economic, political and religious groups. Kinship can refer both to the patterns of social relationships themselves, or it can refer to the study of the patterns of social relationships in one or more human cultures (i.e. kinship studies). Over its history, anthropology has developed a number of related concepts and terms in the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Linton
Ralph Linton (27 February 1893 – 24 December 1953) was an American anthropologist of the mid-20th century, particularly remembered for his texts ''The Study of Man'' (1936) and ''The Tree of Culture'' (1955). One of Linton's major contributions to anthropology was defining a distinction between status and role. Early life and education Linton was born into a family of Quaker restaurant entrepreneurs in Philadelphia in 1893 and entered Swarthmore College in 1911. He was an indifferent student and resisted his father's pressures to prepare himself for the life of a professional. He grew interested in archaeology after participating in a field school in the southwest and took a year off of his studies to participate in another archaeological excavation at Quiriguá in Guatemala. Having found a strong focus he graduated Phi Beta Kappa in 1915. Although Linton became a prominent anthropologist, his graduate education took place largely at the periphery of the discipline. He att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Anthropology
Applied anthropology is the application of the methods and theory of anthropology to the analysis and solution of practical problems. In ''Applied Anthropology: Domains of Application'', Kedia and Van Willigen define the process as a "complex of related, research-based, instrumental methods which produce change or stability in specific cultural systems through the provision of data, initiation of direct action, and/or the formulation of policy". More simply, applied anthropology is the praxis-based side of anthropological research; it includes researcher involvement and activism within the participating community. John Van Willengen simply defined anthropology as " anthropology put to use". However, the concept of applied anthropology was put forward by Daniel G. Brinton. Spanning academic disciplines The American Anthropological Association (AAA) website describes anthropology as a focus on "the study of humans, past and present. To understand the full sweep and complexity of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edith Valentine
Edith is a feminine given name derived from the Old English words ēad, meaning 'riches or blessed', and is in common usage in this form in English, German, many Scandinavian languages and Dutch. Its French form is Édith. Contractions and variations of this name include Ditte, Dita, and Edie. It was a common first name prior to the 16th century, when it fell out of favour. It became popular again at the beginning of the 19th century, and in 2016 it was ranked at 488th most popular female name in the United States, according to the Social Security online database. It became far less common as a name for children by the late 20th century. The name Edith has five name days: May 14 in Estonia, January 13 in the Czech Republic, October 31 in Sweden, July 5 in Latvia, and September 16 in France, Hungary, Poland and Lithuania. Edith *Edith of Polesworth (died c. 960), abbess *Edith of Wessex (1025–1075), Queen of England *Edith of Wilton (961–984), English nun *Edith the Fair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Valentine (anthropologist) (1879–1964), British educationalist and psychologist
{{hndis, Valentine, Charles ...
Charles Valentine may refer to: * Charles James Valentine (1837–1900), English ironmaster and politician * Charles L. Valentine (1846–1925), member of the Wisconsin State Assembly * Charles Wilfred Valentine Charles Wilfred Valentine (16 August 1879 – 26 May 1964) was a British educationalist and psychologist. He was a student at Cambridge University and there befriended William Gidley Emmett with whom he later co-wrote a book, ''The Reliability of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ann Chowning
Martha Ann Chowning (born 18 April 1929 in Little Rock, Arkansas; died 25 September 2016 in Auckland) was an anthropologist, ethnographer, archaeologist and linguist known for her work on the peoples, languages, cultures and histories of Oceania. Biography Born and raised in Arkansas, Chowning studied Spanish at Bryn Mawr College and anthropology at Barnard College, Columbia, before beginning her PhD in anthropology at the University of Pennsylvania in 1952. There she was taught by Ward Goodenough, who engaged her in a project on the Lakalai people of Papua New Guinea. After finishing her PhD in 1957, Chowning subsequently revisited the Lakalai many times between the 1960s and 1990s, and carried out comparative fieldwork on Molima, Sengseng, and Kove. Chowning held an assistant professorship in anthropology at Barnard College, Columbia University, from 1960 to 1965, and was Senior Research Fellow in social anthropology at the Australian National University from 1965 to 1970. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
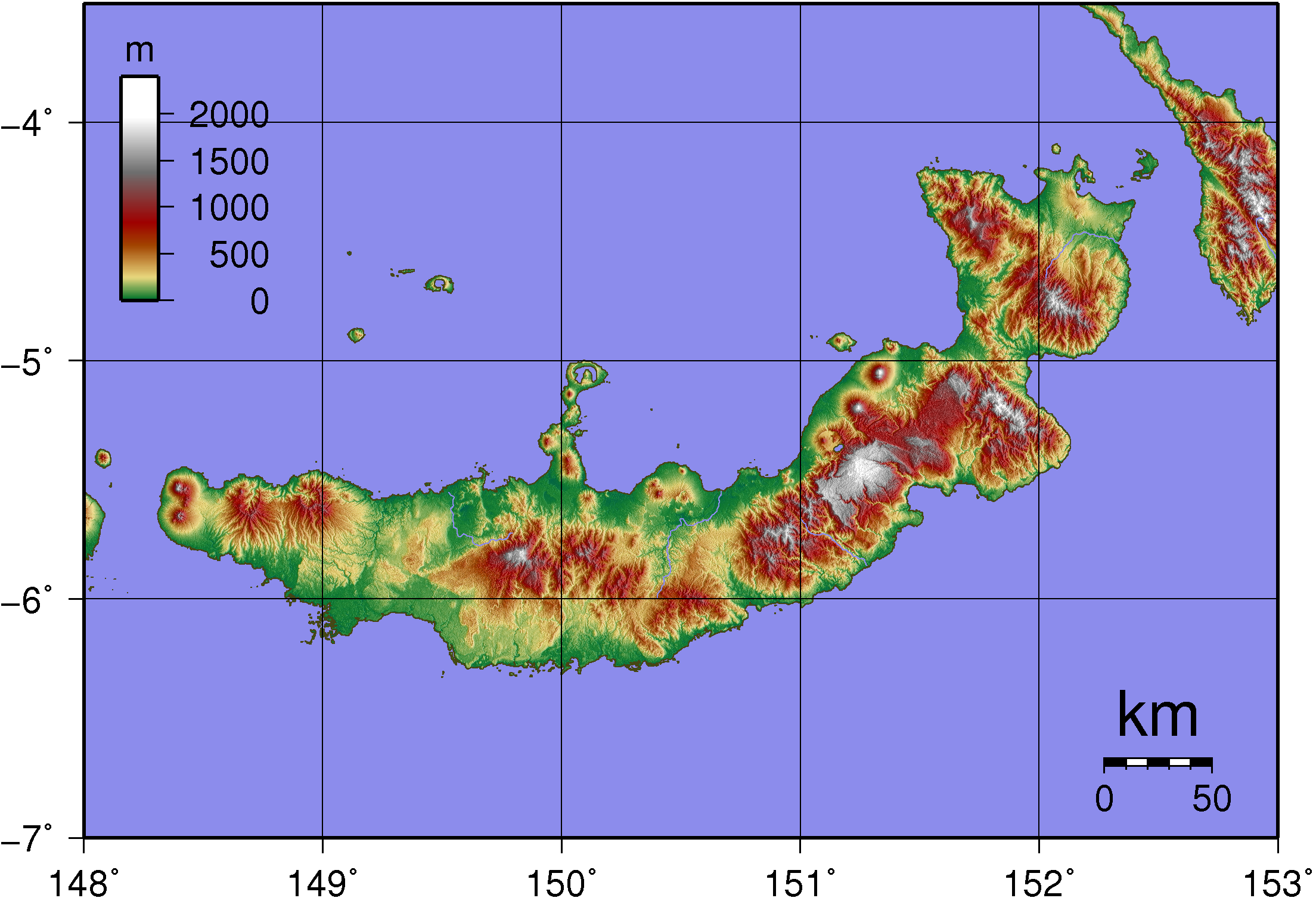
New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the town still lies under metres of ash, and the capital has been moved to nearby Kokopo. Geography New Britain e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati ''The World Factbook''. Europa (web portal). Retrieved 29 January 2016. is an in in the central . The permanent population is over 119,000 (2020), more than half of whom live on |
University Of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universities by numerous organizations and scholars. While the university dates its founding to 1740, it was created by Benjamin Franklin and other Philadelphia citizens in 1749. It is a member of the Ivy League. The university has four undergraduate schools as well as twelve graduate and professional schools. Schools enrolling undergraduates include the College of Arts and Sciences, the School of Engineering and Applied Science, the Wharton School, and the School of Nursing. Among its highly ranked graduate schools are its law school, whose first professor wrote the first draft of the United States Constitution, its medical school, the first in North America, and Wharton, the first collegiate business school. Penn's endowment is US$20.7 billio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an educational institution, institution of higher education, higher (or Tertiary education, tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)