|
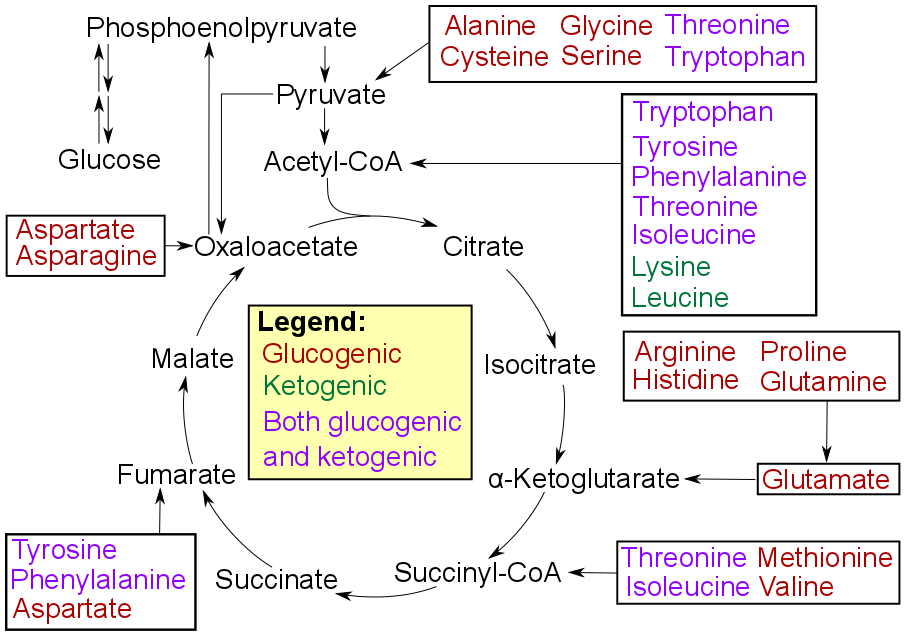
Warburg Effect Inversion
The inversion to the Warburg effect is a corollary to the Warburg hypothesis or Warburg effect that was discovered in obesity. Warburg's hypothesis suggests that tumor cells proliferate quickly and aggressively by obtaining energy or ATP, through high glucose consumption and lactate production. When tumor cells are found in an obesity environment, the researchers perceive that the cells instead of consuming glucose in glycolysis produce glucose through gluconeogenesis using as substrates the lactate that instead of being produced is consumed. The authors explain that this is due to the increase in nutrients that are found in an obese organism and that the cell obtains energy through more caloric nutrients such as fatty acids that are completely oxidized through the Krebs cycle The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warburg Hypothesis
The Warburg hypothesis (), sometimes known as the Warburg theory of cancer, postulates that the driver of tumorigenesis is an insufficient cellular respiration caused by insult to mitochondria. The term '' Warburg effect'' in oncology describes the observation that cancer cells, and many cells grown ''in vitro'', exhibit glucose fermentation even when enough oxygen is present to properly respire. In other words, instead of fully respiring in the presence of adequate oxygen, cancer cells ferment. The Warburg hypothesis was that the Warburg effect was the root cause of cancer. The current popular opinion is that cancer cells ferment glucose while keeping up the same level of respiration that was present before the process of carcinogenesis, and thus the Warburg effect would be defined as the observation that cancer cells exhibit glycolysis with lactate production and mitochondrial respiration even in the presence of oxygen. Hypothesis The hypothesis was postulated by the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warburg Effect (oncology)
In oncology, the Warburg effect () is the observation that most cancer cells produce energy predominantly not through the 'usual' citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria as observed in normal cells, but through a less efficient process of 'aerobic glycolysis' consisting of high level of glucose uptake and glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation taking place in the cytosol, not the mitochondria, even in the presence of abundant oxygen. This observation was first published by Otto Heinrich Warburg, who was awarded the 1931 Nobel Prize in Physiology for his "discovery of the nature and mode of action of the respiratory enzyme". The precise mechanism and therapeutic implications of the Warburg effect, however, remain unclear. In fermentation, the last product of glycolysis, pyruvate, is converted into lactate ( lactic acid fermentation) or ethanol ( alcoholic fermentation). While fermentation produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) only in low yield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Cells
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all animals (including humans) is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has nipples; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only one species of mammal, the Dayak fruit bat from Southeast Asia, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is critical fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attemptin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen (In anaerobic conditions pyruvate is converted to lactic acid). The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur in the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal. In most organisms, glycolysis occurs in the liquid part of cells, the cytosol. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non- carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels ( hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures, such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons. Some nutrients can be metabolically converted to smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy, such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and fermentation products (ethanol or vinegar), leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acids
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |