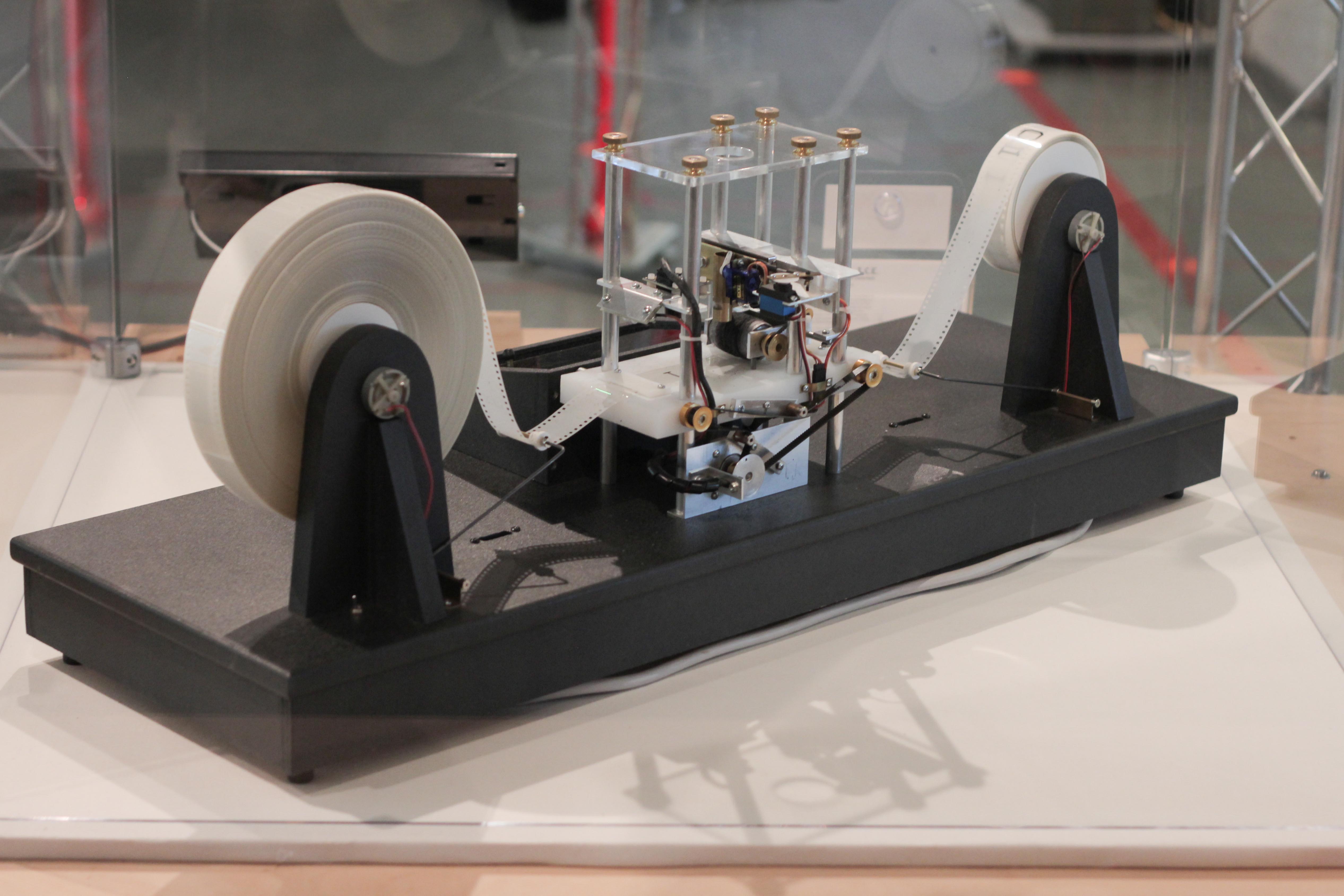
|
Wang B-machine
As presented by Hao Wang (1954, 1957), his basic machine B is an extremely simple computational model equivalent to the Turing machine. It is "the first formulation of a Turing-machine theory in terms of computer-like models" (Minsky, 1967: 200). With only 4 sequential instructions it is very similar to, but even simpler than, the 7 sequential instructions of the Post–Turing machine. In the same paper, Wang introduced a variety of equivalent machines, including what he called the W-machine, which is the B-machine with an "erase" instruction added to the instruction set. Description As defined by Wang (1954) the B-machine has at its command only 4 instructions: *(1) → : Move tape-scanning head one tape square to the right (or move tape one square left), then continue to next instruction in numerical sequence; *(2) ← : Move tape-scanning head one tape square to the left (or move tape one square right), then continue to next instruction in numerical sequence; *(3) * : In scan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hao Wang (academic)
Hao Wang (; 20 May 1921 – 13 May 1995) was a Chinese-American logician, philosopher, mathematician, and commentator on Kurt Gödel. Biography Born in Jinan, Shandong, in the Republic of China (today in the People's Republic of China), Wang received his early education in China. He obtained a BSc degree in mathematics from the National Southwestern Associated University in 1943 and an M.A. in Philosophy from Tsinghua University in 1945, where his teachers included Feng Youlan and Jin Yuelin, after which he moved to the United States for further graduate studies. He studied logic under W.V. Quine at Harvard University, culminating in a Ph.D. in 1948. He was appointed to an assistant professorship at Harvard the same year. During the early 1950s, Wang studied with Paul Bernays in Zürich. In 1956, he was appointed Reader in the Philosophy of Mathematics at the University of Oxford. In 1959, Wang wrote on an IBM 704 computer a program that in only 9 minutes mechanically pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algorithm. The machine operates on an infinite memory tape divided into discrete cells, each of which can hold a single symbol drawn from a finite set of symbols called the alphabet of the machine. It has a "head" that, at any point in the machine's operation, is positioned over one of these cells, and a "state" selected from a finite set of states. At each step of its operation, the head reads the symbol in its cell. Then, based on the symbol and the machine's own present state, the machine writes a symbol into the same cell, and moves the head one step to the left or the right, or halts the computation. The choice of which replacement symbol to write and which direction to move is based on a finite table that specifies what to do for each comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post–Turing Machine
A Post–Turing machineRajendra Kumar, ''Theory of Automata'', Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2010, p. 343. is a "program formulation" of a type of Turing machine, comprising a variant of Emil Post's Turing-equivalent model of computation. Post's model and Turing's model, though very similar to one another, were developed independently. Turing's paper was received for publication in May 1936, followed by Post's in October. A Post–Turing machine uses a binary alphabet, an infinite sequence of binary storage locations, and a primitive programming language with instructions for bi-directional movement among the storage locations and alteration of their contents one at a time. The names "Post–Turing program" and "Post–Turing machine" were used by Martin Davis in 1973–1974 (Davis 1973, p. 69ff). Later in 1980, Davis used the name "Turing–Post program" (Davis, in Steen p. 241). 1936: Post model In his 1936 paper "Finite Combinatory Processes—Formulation 1", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codd's Cellular Automaton
Codd's cellular automaton is a cellular automaton (CA) devised by the British computer scientist Edgar F. Codd in 1968. It was designed to recreate the computation- and construction-universality of von Neumann's CA but with fewer states: 8 instead of 29. Codd showed that it was possible to make a self-reproducing machine in his CA, in a similar way to von Neumann's universal constructor, but never gave a complete implementation. History In the 1940s and '50s, John von Neumann posed the following problem: *What kind of logical organization is sufficient for an automaton to be able to reproduce itself? He was able to construct a cellular automaton with 29 states, and with it a universal constructor. Codd, building on von Neumann's work, found a simpler machine with eight states. This modified von Neumann's question: *What kind of logical organization is ''necessary'' for an automaton to be able to reproduce itself? Three years after Codd's work, Edwin Roger Banks showed a 4-stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-machine Model
Although some authors use the name "register machine" synonymously with "counter machine", this article will give details and examples of only of the most primitive speciesthe "counter machine"of the genus "register machine." Within the species "counter machine" there are a number of varieties: the models of Hermes (1954), Kaphengst (1957), Ershov (1958), Péter (1958), Minsky (1961) and Minsky (1967), Melzak (1961), Lambek (1961), Shepherdson and Sturgis (1963), and Schönhage (1980). These models will be described in more detail in the following. The models in more detail 1954: Hermes' model Shepherdson and Sturgis observe that "the proof of this universality f digital computers to Turing machines... seems to have been first written down by Hermes, who showed in --their reference numberhow an idealized computer could be programmed to duplicate the behavior of any Turing machine" (Shepherdson and Sturgis, p. 219). Shepherdson and Sturgis observe that: :"Kaphengst' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Mathematical Bulletin
The ''Canadian Mathematical Bulletin'' (french: Bulletin Canadien de Mathématiques) is a mathematics journal, established in 1958 and published quarterly by the Canadian Mathematical Society. The current editors-in-chief of the journal are Antonio Lei and Javad Mashreghi. The journal publishes short articles in all areas of mathematics that are of sufficient interest to the general mathematical public. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted in: for the Canadian Mathematical Bulletin. * '''' * '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Hamming
Richard Wesley Hamming (February 11, 1915 – January 7, 1998) was an American mathematician whose work had many implications for computer engineering and telecommunications. His contributions include the Hamming code (which makes use of a Hamming matrix), the Hamming window, Hamming numbers, sphere-packing (or Hamming bound), Hamming graph concepts, and the Hamming distance. Born in Chicago, Hamming attended University of Chicago, University of Nebraska and the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, where he wrote his doctoral thesis in mathematics under the supervision of Waldemar Trjitzinsky (1901–1973). In April 1945 he joined the Manhattan Project at the Los Alamos Laboratory, where he programmed the IBM calculating machines that computed the solution to equations provided by the project's physicists. He left to join the Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1946. Over the next fifteen years he was involved in nearly all of the Laboratories' most prominent achievements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doug McIlroy
Malcolm Douglas McIlroy (born 1932) is a mathematician, engineer, and programmer. As of 2019 he is an Adjunct Professor of Computer Science at Dartmouth College. McIlroy is best known for having originally proposed Unix pipelines and developed several Unix tools, such as spell, diff, sort, join, graph, speak, and tr. He was also one of the pioneering researchers of macro processors and programming language extensibility. He participated in the design of multiple influential programming languages, particularly PL/I, SNOBOL, ALTRAN, TMG (language), TMG and C++. His seminal work on software componentization and code reuse makes him a pioneer of component-based software engineering and software product line engineering. Biography McIlroy earned his bachelor's degree in engineering physics from Cornell University, and a Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in applied mathematics from MIT in 1959 for his thesis ''On the Solution of the Differential Equations of Conical Shells'' (advisor Eri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor A
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to: * Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname Arts and entertainment Film * ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film * ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French short film * ''Victor'' (2008 film), a 2008 TV film about Canadian swimmer Victor Davis * ''Victor'' (2009 film), a French comedy * ''Victor'', a 2017 film about Victor Torres by Brandon Dickerson * ''Viktor'' (film), a 2014 Franco/Russian film Music * ''Victor'' (album), a 1996 album by Alex Lifeson * "Victor", a song from the 1979 album ''Eat to the Beat'' by Blondie Businesses * Victor Talking Machine Company, early 20th century American recording company, forerunner of RCA Records * Victor Company of Japan, usually known as JVC, a Japanese electronics corporation originally a subsidiary of the Victor Talking Machine Company ** Victor Entertainment, or JVCKenwood Victor Entertainment, a Japanese record label ** Victor Interactive So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Lambek
Joachim "Jim" Lambek (5 December 1922 – 23 June 2014) was a German-born Canadian mathematician. He was Peter Redpath Emeritus Professor of Pure Mathematics at McGill University, where he earned his PhD degree in 1950 with Hans Zassenhaus as advisor. Biography Lambek was born in Leipzig, Germany, where he attended a Gymnasium. He came to England in 1938 as a refugee on the ''Kindertransport''. From there he was interned as an enemy alien and deported to a prison work camp in New Brunswick, Canada. There, he began in his spare time a mathematical apprenticeship with Fritz Rothberger, also interned, and wrote the McGill Junior Matriculation in fall of 1941. In the spring of 1942, he was released and settled in Montreal, where he entered studies at McGill University, graduating with an honours mathematics degree in 1945 and an MSc a year later. In 1950, he completed his doctorate under Hans Zassenhaus becoming McGill's first PhD in mathematics. Lambek became assistant p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky (August 9, 1927 – January 24, 2016) was an American cognitive and computer scientist concerned largely with research of artificial intelligence (AI), co-founder of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory, and author of several texts concerning AI and philosophy. Minsky received many accolades and honors, including the 1969 Turing Award. Biography Marvin Lee Minsky was born in New York City, to an eye surgeon father, Henry, and to a mother, Fannie (Reiser), who was a Zionist activist. His family was Jewish. He attended the Ethical Culture Fieldston School and the Bronx High School of Science. He later attended Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts. He then served in the US Navy from 1944 to 1945. He received a B.A. in mathematics from Harvard University in 1950 and a Ph.D. in mathematics from Princeton University in 1954. His doctoral dissertation was titled "Theory of neural-analog reinforcement systems and its application to the brain- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |