|
Waltz In C-sharp Minor, Op. 64, No. 2 (Chopin)
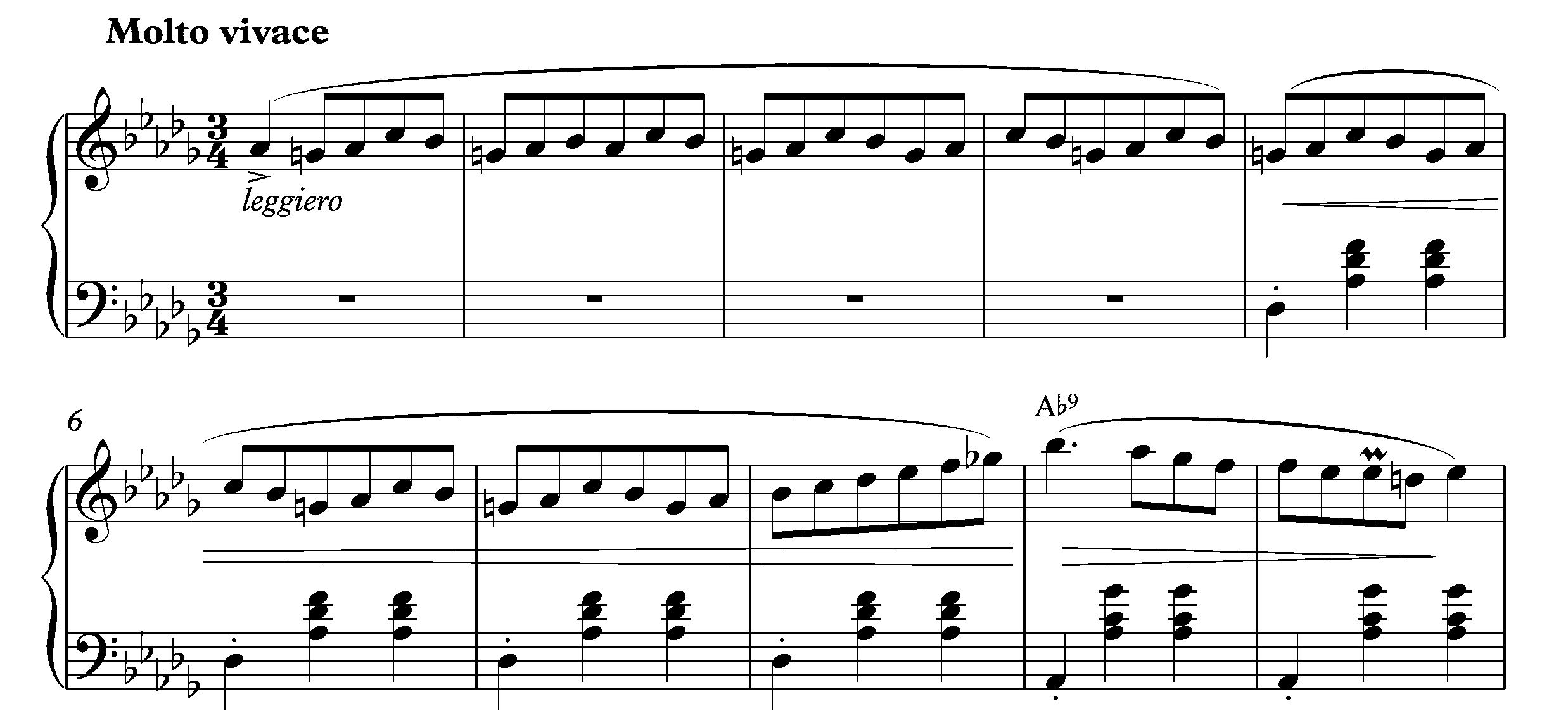
The Waltz in C minor is a piano waltz composed by Frédéric Chopin in 1847, the second work of his opus 64 and the companion to the ''"Minute Waltz"'' (Op. 64, No. 1). Chopin dedicated this Waltz to Madame Nathaniel de Rothschild. It consists of three main themes: * Theme A ''tempo giusto'' chordal with a walking pace feel; * Theme B ''più mosso'' (faster) — theme stated in running eighth notes, with all harmony in the left hand. * Theme C ''più lento'' (slower) — a sostenuto in the parallel key of C minor (D major, enharmonic equivalent to C major). Besides the slower general pace, the melody is in quarter notes except for a few flourishes in eighth notes, giving this section the quality of an interlude before the dramatic restatement of Theme B. The overall layout of the piece is A B C B A B. In an orchestrated version, it forms part of the ballet ''Les Sylphides ''Les Sylphides'' () is a short, non-narrative ''ballet blanc'' to piano music by Frédéric Chopin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltz (music)
A waltz (German: ''Walzer''; French: ''Valse'', Italian: ''Valzer'', Spanish: ''Vals'', Polish: ''Walc''), probably deriving from German ''Ländler'', is dance music in triple meter, often written in time. A waltz typically sounds one chord per measure, and the accompaniment style particularly associated with the waltz is (as seen in the example to the right) to play the root of the chord on the first beat, the upper notes on the second and third beats. History The name "waltz" comes from the German verb ''walzen''. Although French writers have attempted to connect the waltz to the 16th century volta, firm evidence is lacking connecting this Italian form to the earliest occurrence in the mid‑18th century of ''walzen'' to describe dancing. Classical composers traditionally supplied music for dancing when required, and Franz Schubert's waltzes (including the '' Valses Sentimentales and Valses Nobles'') were written for household dancing, without any pretense at being art m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Chopin
Frédéric François Chopin (born Fryderyk Franciszek Chopin; 1 March 181017 October 1849) was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leading musician of his era, one whose "poetic genius was based on a professional technique that was without equal in his generation". Chopin was born in Żelazowa Wola in the Duchy of Warsaw and grew up in Warsaw, which in 1815 became part of Congress Poland. A child prodigy, he completed his musical education and composed his earlier works in Warsaw before leaving Poland at the age of 20, less than a month before the outbreak of the November 1830 Uprising. At 21, he settled in Paris. Thereafterin the last 18 years of his lifehe gave only 30 public performances, preferring the more intimate atmosphere of the salon. He supported himself by selling his compositions and by giving piano lessons, for which he was in high demand. Chopin formed a fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minute Waltz
The Waltz in D-flat major, Op. 64, No. 1, sometimes known as "" (French for "Waltz of the puppy"), and popularly known in English as the Minute Waltz, is a piano waltz by Polish composer and virtuoso Frédéric Chopin. It is dedicated to the Countess Delfina Potocka. History Chopin composed the waltz in 1847 and had it published by Breitkopf & Härtel in Leipzig the same year, as the first of the ''Trois Valses'', Op. 64. The second waltz is in the enharmonic parallel minor key of C-sharp minor. Structure The waltz is in the key of D-flat major and has a tempo marking of (very lively). Chopin indicates that the waltz is to be played with the sustain pedal used, and makes frequent use of crescendi and diminuendi. It is in a simple ternary form, as are many of Chopin's compositions. The A section is marked , and the B section . The A section itself can be divided into two themes, separated by a double barline. The first consists of the familiar opening melody over standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte De Rothschild
Baroness Charlotte de Rothschild (6 May 1825 – 20 July 1899) was a French socialite, painter, and a member of the prominent Rothschild banking family of France. Early years She was born in Paris, the daughter of Betty von Rothschild (1805–1886) and James Mayer de Rothschild (1792–1868).Harry W. Paul (2005)Collecting Chardins: Charlotte and Henri de Rothschild. ''The Rothschild Archive: Review of the Year April 2004 – March 2005''. ISSN 1748-9148 (print), 1748-9156 (web). pp. 21–26. Accessed September 2013. Charlotte de Rothschild was raised by very wealthy parents who were at the center of Parisian culture. They patronized a number of major figures in the arts community including Gioacchino Rossini, Frédéric Chopin, Honoré de Balzac, Eugène Delacroix, and Heinrich Heine. Chopin had become Charlotte's piano teacher in 1841, and as a tacit acknowledgment of the many years of support extended by Baron James and his wife Betty, dedicated to her an autograph of his so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (music)
In music, a subject is the material, usually a recognizable melody, upon which part or all of a composition is based. In forms other than the fugue, this may be known as the theme. Characteristics A subject may be perceivable as a complete musical expression in itself, separate from the work in which it is found. In contrast to an idea or motif, a subject is usually a complete phrase or period. The ''Encyclopédie Fasquelle'' defines a theme (subject) as " y element, motif, or small musical piece that has given rise to some variation becomes thereby a theme". Thematic changes and processes are often structurally important, and theorists such as Rudolph Reti have created analysis from a purely thematic perspective. Fred Lerdahl describes thematic relations as "associational" and thus outside his cognitive-based generative theory's scope of analysis. In different types of music Music based on a single theme is called 'monothematic', while music based on several themes is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes (also called "pitches") that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords (in which the notes of the chord are sounded one after the other, rather than simultaneously), or sequences of chord tones, may also be considered as chords in the right musical context. In tonal Western classical music (music with a tonic key or "home key"), the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: the root note, and intervals of a third and a fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz and almost any other genre. A series of chords is called a chord progression. One example of a widely used chord progression in Western traditional music and blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth Note
180px, Figure 1. An eighth note with stem extending up, an eighth note with stem extending down, and an eighth rest. 180px, Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together. An eighth note (American) or a quaver (British) is a musical note played for one eighth the duration of a whole note (semibreve). Its length relative to other rhythmic values is as expected—e.g., half the duration of a quarter note (crotchet), one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), and twice the value of a sixteenth note. It is the equivalent of the ''fusa'' in mensural notation. Eighth notes are notated with an oval, filled-in note head and a straight note stem with one note flag (see Figure 1). The stem is on the right of the notehead extending upwards or on the left extending downwards, depending primarily on where the notehead lies relative to the middle line of the staff. A related symbol is the eighth rest (or quaver rest), which denotes a silence for the same duration. Eighth notes may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sostenuto
Piano pedals are foot-operated levers at the base of a piano that change the instrument's sound in various ways. Modern pianos usually have three pedals, from left to right, the soft pedal (or una corda), the #Sostenuto pedal, sostenuto pedal, and the sustaining pedal (or damper pedal). Some pianos omit the sostenuto pedal, or have a middle pedal with a different purpose such as a muting function also known as silent piano. The development of the piano's pedals is an evolution that began from the very earliest days of the piano, and continued through the late 19th century. Throughout the years, the piano had as few as one modifying stop, and as many as six or more, before finally arriving at its current configuration of three. Individual pedals Soft pedal The ''soft pedal'', or ''una corda'' pedal, was invented by Bartolomeo Cristofori. It was the first mechanism invented to modify the piano's sound. This function is typically operated by the left pedal on modern pianos. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Note
A quarter note (American) or crotchet ( ) (British) is a note (music), musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem (music), stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the musical staff, staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left (see image). The Unicode symbol is U+2669 (♩). A quarter rest (music), rest (or crotchet rest) denotes a silence of the same duration as a quarter note. It typically appears as the symbol , or occasionally, as the older symbol .''Rudiments and Theory of Music'' Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music, London 1958. I,33 and III,25. The former section shows both forms without distinction, the latter the "old" form only. The book was the Official ABRSM theory manual in the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Sylphides
''Les Sylphides'' () is a short, non-narrative ''ballet blanc'' to piano music by Frédéric Chopin, selected and orchestrated by Alexander Glazunov. The ballet, described as a "romantic reverie","Ballet Theater", until 1955. A compact disk of ABT's production, with Mikhail Baryshnikov as the dreamer, is available from Kultor, entitled "American Ballet Theatre at the Met – Mixed Bill (1985)". See Olga Maynard's definitive account, based on information from Fokine's son Vitale Fokine: "Les Sylphides", ''Dance Magazine'' Portfolio: December 1971, advertised separately by some online booksellers. is frequently cited as the first ballet to be simply about mood and dance. ''Les Sylphides'' has no plot but instead consists of several white-clad sylphs dancing in the moonlight with the "poet" or "young man" dressed in white tights and a black tunic. Its original choreography was by Michel Fokine, with Chopin's music orchestrated by Alexander Glazunov. Glazunov had already set som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltzes By Frédéric Chopin
The waltz ( ), meaning "to roll or revolve") is a ballroom and folk dance, normally in triple ( time), performed primarily in closed position. History There are many references to a sliding or gliding dance that would evolve into the waltz that date from 16th-century Europe, including the representations of the printmaker Hans Sebald Beham. The French philosopher Michel de Montaigne wrote of a dance he saw in 1580 in Augsburg, where the dancers held each other so closely that their faces touched. Kunz Haas (of approximately the same period) wrote, "Now they are dancing the godless ''Weller'' or ''Spinner''."Nettl, Paul. "Birth of the Waltz." In ''Dance Index'' vol 5, no. 9. 1946 New York: Dance Index-Ballet Caravan, Inc. pages 208, 211 "The vigorous peasant dancer, following an instinctive knowledge of the weight of fall, uses his surplus energy to press all his strength into the proper beat of the bar, thus intensifying his personal enjoyment in dancing." Around 1750, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |