|
Walter Sinclair Delamain
Lieutenant-General Sir Walter Sinclair Delamain (18 February 1862 – 6 March 1932) was an officer of the British Indian Army. Early service Delamain was born in Saint Helier, the son of Charles Henry Delamain and Susan Sarah Christina Gun. He attended the Royal Military College and was commissioned as a lieutenant in the Princess Charlotte of Wales's (Berkshire Regiment) on 22 October 1881. On 13 January 1885 he was seconded for service with the Indian Staff Corps, and was commissioned as a lieutenant in the Bombay Staff Corps on 1 February 1885, with seniority of 22 October 1881. He was promoted to captain, 22 October 1892, and given the temporary rank of Major, 4 November 1898. As Commandant of the Native Military Base Depot during the Boxer Rebellion he was mentioned in despatches. On 26 May 1901 he was appointed a Special Service Officer on the staff of the China Field Force, and his rank of major was made substantive on 10 July 1901. In October 1902 he was in command of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helier, Jersey
St Helier (; Jèrriais: ; french: Saint-Hélier) is one of the twelve parishes of Jersey, the largest of the Channel Islands in the English Channel. St Helier has a population of 35,822 – over one-third of the total population of Jersey – and is the capital of the island. The town of St Helier is the largest settlement and only town of Jersey. The town consists of the built-up areas of St Helier, including First Tower, and parts of the parishes of St Saviour and St Clement, with further suburbs in surrounding parishes. The greater part of St Helier is rural. The parish covers a surface area of , being 9% of the total land area of the island (this includes reclaimed land area of or 200 ha). The growth of the town has been described as "spasmodic", its expansion reflecting waves of migration to the island. The parish arms are two crossed gold axes on a blue background, the blue symbolising the sea, and the axes symbolising the martyrdom of Helier at the hands of Saxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Staff Corps
The Indian Staff Corps was a branch of the Indian Army during the British Raj. Separate Staff Corps were formed in 1861 for the Bengal, Madras and Bombay Armies, which were later combined into the Indian Army. They were meant to provide officers for the native regiments and for the staff and army departments. They were also designed to offer placements for civil and political appointments for posts which Indian Army officers might be eligible. Those officers who were already employed by the Army had the option to join the Staff Corps or to stay employed under the old conditions of service. In that sense, the Indian Staff Corps was seen by the majority of entrants as synonymous with the Regular Officer Corps of the Indian Armies. This is not to be confused with officers holding staff appointments. To reduce confusion, the term "Indian Staff Corps" in relation to officers on regimental duty was withdrawn by Lord Kitchener during his unification of the Indian Army. From that time{{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havelock Hudson
General Sir Havelock Hudson, (22 June 1862 – 25 December 1944) was a British Indian Army officer who was General Officer Commanding 8th Division during World War I. Military career Hudson was commissioned into the Northamptonshire Regiment as a lieutenant on 22 October 1881. He transferred to the Indian Staff Corps in 1885Quarterly Army List March 1922 and became an officer of the 19th Lancers from that year.History of the 19th King George's Own Lancers 1858-1921 Promoted to captain on 22 October 1892, he served on the staff during the North West Frontier campaign in 1897. He briefly acted as deputy assistant quartermaster-general at Indian army headquarters June–August 1900, then was appointed a staff officer in the China Field Force for the Boxer Rebellion later that year. In 1901 he took part in the second Miranzai expedition in 1901. He commanded the 19th Lancers from 4 February to 27 August 1910. He was appointed a General Staff Officer Grade 1 with the Direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
117th Mahrattas
The 117th Mahrattas were an infantry regiment of the British Indian Army. The regiment traces their origins to 1800, when they were raised as the Bombay Fencible Regiment. During World War I the regiment was attached to the 6th (Poona) Division and served in the Mesopotamian campaign, delivered a setback at the Battle of Ctesiphon in November 1915. They were forced to withdrew back to Kut, and forced to surrender after the Siege of Kut. After World War I the Indian government reformed the army moving from single battalion regiments to multi battalion regiments.Sumner p.15 In 1922, the 117th Mahrattas became the 5th Battalion 5th Mahratta Light Infantry. After independence they were one of the regiments allocated to the Indian Army The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjutant-General (India)
The Adjutant-General of the Indian Army The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ... is the senior administration officer who reports to the Chief of Army Staff and is also the Colonel of the Corps of Military Police and Judge Advocate General. Role, organisation and function The office of the Adjutant General deals with a wide spectrum of issues relating to Army, which includes manpower planning, human resource policy, recruitment, discipline, matters relating to Judge Advocate General's Department, Provost Marshal Directorate ( Corps of Military Police), missing defence personnel, service matters relating to personnel and welfare of serving soldiers. The Adjutant-General's office is organised as follows: *Director General (Manpower Planning and Personnel Services) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Nixon (Indian Army Officer)
General Sir John Eccles Nixon (16 August 1857 – 15 December 1921) was a senior commander of the British Indian Army. He gave the orders for the ultimately disastrous first British Expedition against Baghdad during the First World War. Early career Educated at Rossall School and then the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, Nixon was commissioned into the 75th Regiment of Foot in 1875. He transferred to the Bengal Staff Corps in 1878 and was posted to the 18th Bengal Lancers and then served in the Second Anglo-Afghan War where he was mentioned in despatches. He also took part in the Mahsud Waziri expedition in 1881, was promoted to captain on 10 September 1886,Hart´s Army list, 1903 and served in the Chitral Relief Force in 1895, following which he was promoted to major on 10 September 1895. He was Chief Staff Officer of the Tochi Field Force in 1897, and later served as an Assistant Quartermaster General (in charge of intelligence) at Indian Headquarters. Nixon served as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
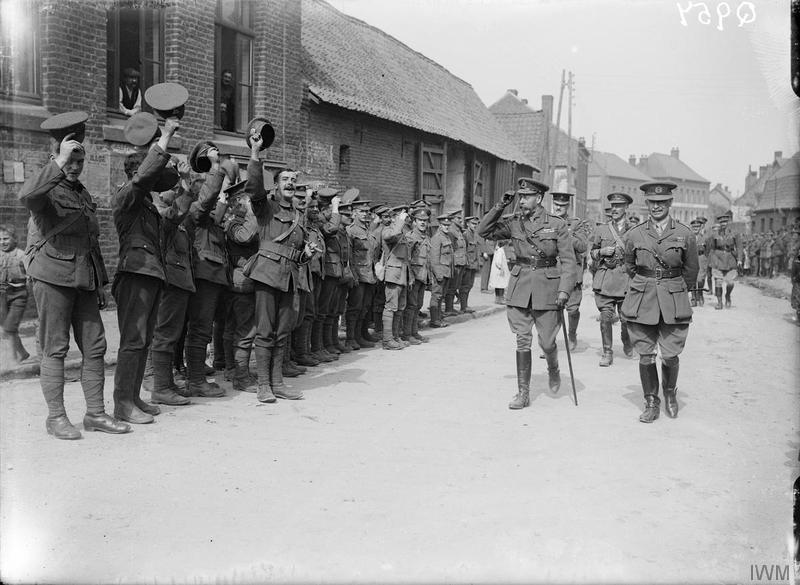
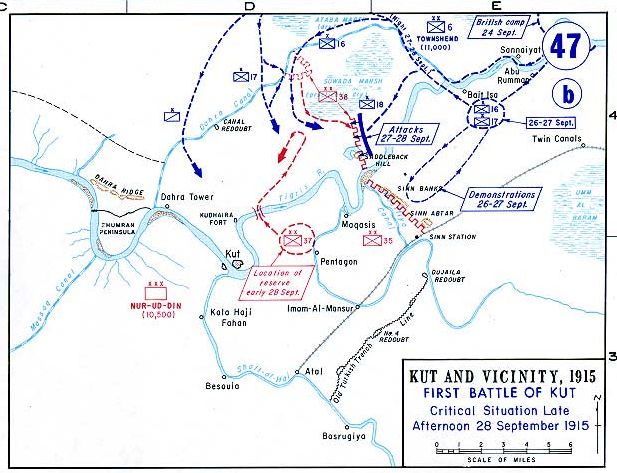
Battle Of Es Sinn
The Battle of Es Sinn was a World War I military engagement between Anglo-Indian and Ottoman forces. It took place on 28 September 1915, during the Mesopotamian Campaign. The sides fought to determine control of the lower Tigres and Euphrates rivers, in what is now Iraq. The British and Indian governments also viewed it as a test of the Ottoman forces, and whether a further advance to capture Baghdad was possible. The Anglo-Indian forces of Indian Expeditionary Force D were under the command of Major-General Charles Vere Ferres Townshend, and the Ottoman forces by Colonel Nureddin. The engagement took place just south of the town of Kut-al-Amarah, along the banks of the Tigris River. Following a night march, the British and Indian troops defeated the Ottoman forces, driving them from their defensive positions along the Tigris. The capture of the Es Sinn position allowed for the capture of Kut, and with it control over the lower Tigris and Euphrates rivers, by British forces the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th (Ahmednagar) Brigade
The 6th (Poona) Division was a division of the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1903, following the Kitchener reforms of the Indian Army. World War I The 6th (Poona) Division served in the Mesopotamian campaign. Led by Major General Barrett then Major General Townshend, the division were the first British Indian troops to land in Mesopotamia in November 1914 at the Fao Landing. After a string of early successes, the 6th Division was delivered a setback at the Battle of Ctesiphon in November 1915. Following this engagement, the division withdrew back to Kut, where Townshend made the decision to hold the city. After a lengthy siege by the Ottomans, Townshend surrendered on April 29, 1916. 10,061 troops and 3,248 followers were taken captive. Following the surrender, the garrisoned force conducted a forced march back to Anatolia. The suffering of the enlisted soldiers was particularly egregious, and over 4,000 died in captivity. After the surrender, the Poona Division ceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th (Poona) Brigade
The 6th (Poona) Division was a division of the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1903, following the Kitchener reforms of the Indian Army. World War I The 6th (Poona) Division served in the Mesopotamian campaign. Led by Major General Barrett then Major General Townshend, the division were the first British Indian troops to land in Mesopotamia in November 1914 at the Fao Landing. After a string of early successes, the 6th Division was delivered a setback at the Battle of Ctesiphon in November 1915. Following this engagement, the division withdrew back to Kut, where Townshend made the decision to hold the city. After a lengthy siege by the Ottomans, Townshend surrendered on April 29, 1916. 10,061 troops and 3,248 followers were taken captive. Following the surrender, the garrisoned force conducted a forced march back to Anatolia. The suffering of the enlisted soldiers was particularly egregious, and over 4,000 died in captivity. After the surrender, the Poona Division ceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet Rank
In many of the world's military establishments, a brevet ( or ) was a warrant giving a commissioned officer a higher rank title as a reward for gallantry or meritorious conduct but may not confer the authority, precedence, or pay of real rank. An officer so promoted was referred to as being brevetted (for example, "he was brevetted major general"). The promotion would be noted in the officer's title (for example, "Bvt. Maj. Gen. Joshua L. Chamberlain" or "Bvt. Col. Arthur MacArthur"). It is not to be confused with a ''Brevet d'état-major'' in Francophone European military circles, where it is an award, nor should it be confused with temporary commissions. France In France, ''brevet'' is a word with a very broad meaning, which includes every document giving a capacity to a person. For instance, the various military speciality courses, such as military parachutism, are ended by the award of a brevet. The more important brevet in the French military is the one of the École ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |