|
Walter Penck
Cerro Walther Penck (also known as Cerro Cazadero or Cerro Tipas) is a massive complex volcano in the Andes, located in northwestern Argentina, Catamarca Province, Tinogasta Department, at the Puna de Atacama. It is just southwest of Ojos del Salado, the highest volcano in the world. Walther Penck itself is perhaps the third highest active volcano in the world. Vulcanism The complex covers a surface area of , it consists of stratovolcanoes, lava domes, and lava flows. There are reports of fumarolic activity, and de Silva and Francis (1991) considered that the volcano was last active in the Holocene. Crater lakes with a smell of sulfur were reported in 2013. The Tipas-Cerro Bayo complex was active 2.9-1.2 million years ago with dacites and rhyolites. Magma composition is typical for Andean stratovolcanoes. Tomographic studies of the underlying crust indicate a pattern of seismic attenuation beneath Tipas. Elevation It has an official height of 6658 meters, however, based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyolite i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzanne Imber
Suzanne Mary Imber (born May 1983) is a British planetary scientist specialising in space weather at the University of Leicester. She was the winner of the 2017 BBC Two television programme ''Astronauts, Do You Have What It Takes?''.Conversation with Imber – ''Love and Science'' podcast for BCfm, 2 October 2017 Education Imber was born in Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire and attended in Hertfordshire. One highlight of her school years was winning the |
Kilometers
The kilometre ( SI symbol: km; or ), spelt kilometer in American English, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousand metres (kilo- being the SI prefix for ). It is now the measurement unit used for expressing distances between geographical places on land in most of the world; notable exceptions are the United States and the United Kingdom where the statute mile is the unit used. The abbreviations k or K (pronounced ) are commonly used to represent kilometre, but are not recommended by the BIPM. A slang term for the kilometre in the US, UK, and Canadian militaries is ''klick''. Pronunciation There are two common pronunciations for the word. # # The first pronunciation follows a pattern in English whereby metric units are pronounced with the stress on the first syllable (as in kilogram, kilojoule and kilohertz) and the pronunciation of the actual base unit does not change irrespective of the prefix (as in centimetre, millimetre, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
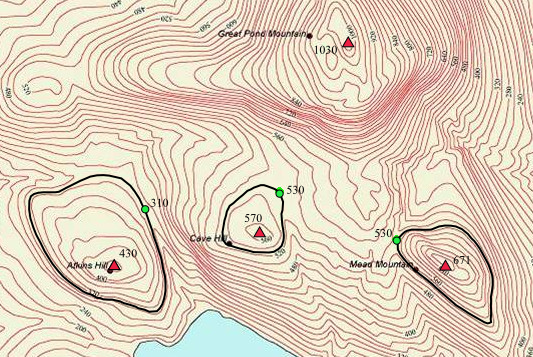
Topographic Isolation
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major mountain peaks and can even be calculated for submarine summits. Isolation table The following sortable table lists Earth's 40 most topographically isolated summits. Examples *The nearest peak to Germany's highest mountain, the 2,962-metre-high Zugspitze, that has a 2962-metre-contour is the Zwölferkogel (2,988 m) in Austria's Stubai Alps. The distance between the Zugspitze and this contour is 25.8 km; the Zugspitze is thus the highest peak for a radius of 25.8 km around. Its isolation is thus 25.8 km. *Because there are no higher mountains than Mount Everest, it has no definitive isolation. Many sources list its isolation as the circumference of the earth over the poles or – questionably, because there is no agreed def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parent Peak
In topography, prominence (also referred to as autonomous height, relative height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop or relative height in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. A peak's ''key col'' (the highest col surrounding the peak) is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak may be defined as the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following way: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''key saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prominence
In topography, prominence (also referred to as autonomous height, relative height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop or relative height in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. A peak's ''key col'' (the highest col surrounding the peak) is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak may be defined as the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following way: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''key saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meters
The metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its prefixed forms are also used relatively frequently. The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's circumference is approximately km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar (the actual bar used was changed in 1889). In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in of a second. After the 2019 redefiniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Col
In topography, prominence (also referred to as autonomous height, relative height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop or relative height in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. A peak's ''key col'' (the highest col surrounding the peak) is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak may be defined as the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following way: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''key saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximo Kausch
Maximo Kausch (born March 1981 in Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...) is a British mountain guide and expedition leader. He holds the current world record of the most 6,000-metre Andean peaks climbed. His project, "Andes' All 6000m Peaks" aims to climb all 104 of the 6,000-metre peaks in the Andes. He maps all peaks using GPS units and publishes all his work for free in the hope that more climbers might attempt the project. The whole project has not been tried before by other mountaineers. Awards He is the world-record holder with the most 6000 metre Andean peaks and so far (Jan 2017) reached the summit of 83 6000 mountains (not counting secondary peaks). Projects * Andes 6000+: 83 peaks climbed by the date (Jan 2017) and 11 secondary 6000m peaks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TanDEM-X
TanDEM-X (TerraSAR-X add-on for Digital Elevation Measurement) is the name of TerraSAR-X's twin satellite, a German Earth observation satellite using SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) - a modern radar imaging technology. Implemented in a Public-Private-Partnership between the German Aerospace centre (DLR Institute for Planetary Research, DLR) and EADS Astrium (now Airbus Defence and Space), it is a second, almost identical spacecraft to TerraSAR-X. TanDEM-X is also the name of the satellite mission flying the two satellites in a closely controlled formation with typical distances between 250 and 500 m.German Aerospace CenterTanDEM-X - A New High Resolution Interferometric SAR MissionVerified 2010-10-16. The twin satellite constellation allowed the generation of WorldDEM global digital elevation models starting in 2014. Mission The primary mission objective is the generation of WorldDEM, a consistent global Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with an unprecedented accuracy according to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission And Reflection Radiometer
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is a Japanese remote sensing instrument onboard the Terra satellite launched by NASA in 1999. It has been collecting data since February 2000. ASTER provides high-resolution images of Earth in 14 different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from visible to thermal infrared light. The resolution of images ranges between 15 and 90 meters. ASTER data is used to create detailed maps of surface temperature of land, emissivity, reflectance, and elevation. In April 2008, the SWIR detectors of ASTER began malfunctioning and were publicly declared non-operational by NASA in January 2009. All SWIR data collected after 1 April 2008 has been marked as unusable. The ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) is available at no charge to users worldwide via electronic download. As of 2 April 2016, the entire catalogue of ASTER image data became publicly available online at no cost. It can be downloaded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)