|
Wadi Suq Culture
The Wadi Suq culture defines human settlement in the United Arab Emirates and Oman in the period from 2,000 to 1,300 BCE. It takes its name from a wadi, or waterway, west of Sohar in Oman and follows on from the Umm Al Nar culture. Although archaeologists have traditionally tended to view the differences in human settlements and burials between the Umm Al Nar and Wadi Suq periods as the result of major external disruption (climate change, the collapse of trade or threat of war), contemporary opinion has moved towards a gradual change in human society which is centred around more sophisticated approaches to animal husbandry as well as changes in the surrounding trade and social environments. History The transition between Umm Al Nar and Wadi Suq is thought to have taken some 200 years and more, with finds at the important Wadi Suq site of Tell Abraq in modern Umm Al Qawain showing evidence of the continuity of Umm al-Nar burials. Evidence of increased mobility among the popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebel Al-Buhais Burial
{{disambiguation ...
Jabal, Jabel, Jebel or Jibal may refer to: People * Jabal (name), a male Arabic given name * Jabal (Bible), mentioned in the Hebrew Bible Places In Arabic, ''jabal'' or ''jebel'' (spelling variants of the same word) means 'mountain'. * Dzhebel, a town in Bulgaria * Jabal Amman, part of Amman, Jordan * Jabel, a German municipality * Jabal, Amreli, a village in Gujarat, India * Jabal Rural District, in Iran * Jebel, Timiș, a commune in Timiș County, Romania * Jebel, Turkmenistan, a town * Jibal or al-Jabal, a late 1st-millennium-CE West-Asian realm Other uses * Djebel (1937–1958), a racehorse See also * * * * * * Jubal (other) Jubal may refer to: People * Jubal (Bible), named in the Book of Genesis as the father of musicians * Jubal (footballer) (born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Jubal Brown (born c. 1974), controversial video producer and multi-media artist * Jubal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting stone in many uses. Stone Age artifacts that have been discovered include tools used by modern humans, by their predecessor species in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (the UAE or the Emirates) is a country in the eastern part of the Arabian Peninsula located on the southeastern coast of the Persian Gulf and the northwestern coast of the Gulf of Oman. The UAE consists of seven emirates and was founded on 2 December 1971 as a federation. Six of the seven emirates (Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al Quwain and Fujairah) combined on that date. The seventh, Ras al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972. The seven sheikdoms were formerly known as the Trucial States, in reference to the treaty relations established with the British in the 19th century. Artifacts uncovered in the UAE show a history of human habitation, transmigration and trade spanning over 125,000 years. The area was previously home to the Magan people known to the Sumerians, who traded with both coastal towns and bronze miners and smelters from the interior. A rich history of trade with the Harappan culture of the Indus Valley is also ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, Media, Parthia and Persis), Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands (Turkey's Eastern Anatolia Region, Armenia, northwestern Iran, southern Georgia, and western Azerbaijan), the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date it ends varies. The term covers the Bronze Age and the Iron Age in the region, until either the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, that by the Macedonian Empire in the 4th century BC, or the Muslim conquest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of The United Arab Emirates
The area currently known as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) (previously the Trucial States) was formerly populated by inhabitants of a number of coastal and inland settlements, with human remains pointing to a pattern of transmigration and settlement as far back as 125,000 years. Prehistoric settlement in the UAE spanned the Neolithic, with a number of distinctive eras of ancient settlement including the Stone Age Arabian Bifacial and Ubaid cultures from 5,000 to 3,100 BCE; the Hafit period with its distinctive beehive shaped tombs and Jemdet Nasr pottery, from 3,200 to 2,600 BCE; the Umm Al Nar period from 2,600 to 2,000 BCE; the Wadi Suq culture from 2,000–1,300 BCE and the three Iron Ages of the UAE. The UAE's Iron Age I spanned 1,200–1,000 BCE; Iron Age II, 1,000–600 BCE and Iron Age III from 600–300 BCE. This was followed by the Hellenistic Mleiha (or Late Pre-Islamic) era, from 300 BCE onwards through to the Islamic era which commenced with the culmination of the 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidaa Bint Saud
Bidaa Bint Saud ( ar, بِـدَع بِـنْـت سـعـوْد, Bidaʿ Bint Saud) is an archaeological site in Al-Ain Region, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, notable for its Hafit Period tombs, Iron Age irrigation systems and rare remains of an Iron Age building thought to have been a distribution centre for water from two ''aflaj'' (systems of underground and surface waterways). It is a listed UN World Heritage Site. Finds from the site are displayed at Al Ain National Museum. The dating of pottery from the ''aflaj'' (singular falaj) waterways found at the site demonstrates a south-eastern Arabian origin for this distinctive system of irrigation, previously thought by many scholars to have been Persian in origin. The dating of ''aflaj'' in Bidaa bint Saud, Al Ain and Buraimi, both of which are in the historical region of Tawam, has been placed several centuries prior to the Achaemenid Empire, which had previously been credited with the innovation. The site, located some n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Qusais
Al Qusais or Al Gusais ( ar, اﻟﻘﺼﻴﺺ ) is a large community in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). It is located in the Deira area of east Dubai. Al Qusais borders the localities of Hor Al Anz and Al Twar and is further subdivided into residential (Al Qusais) and industrial (Al Qusais Industrial Area) localities. Neighborhoods Al Qusais residential areas are subdivided into: * Al Qusais First * Al Qusais Second * Al Qusais Third The industrial areas are subdivided into: * Al Qusais Industrial Area First * Al Qusais Industrial Area Second * Al Qusais Industrial Area Third * Al Qusais Industrial Area Fourth * Al Qusais Industrial Area Fifth The industrial areas lead into the industrial areas of the emirate of Dubai. Education Education in Al Qusais is provided by a number of public and privates schools and colleges. There are Arabic, Australian, British, American and Indian schools. There are also various private institutes providing dance, music, art and computer less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qidfa
Qidfa is a settlement and oasis in Fujairah, United Arab Emirates (UAE). It is the site of the Fujairah power and desalination plant, the largest in the UAE The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (The Middle East). It is located at th .... Qidfa Oasis is the location of a Wadi Suq period (2,000 to 1,300 BCE) burial, a distinctive horse-shoe shaped tomb which is displayed at the Fujairah National Museum. The find at Qidfa was unusual in that the site yielded hundreds of weapons and vessels, including longswords, bows and arrows. References {{UnitedArabEmirates-geo-stub Oases of the United Arab Emirates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
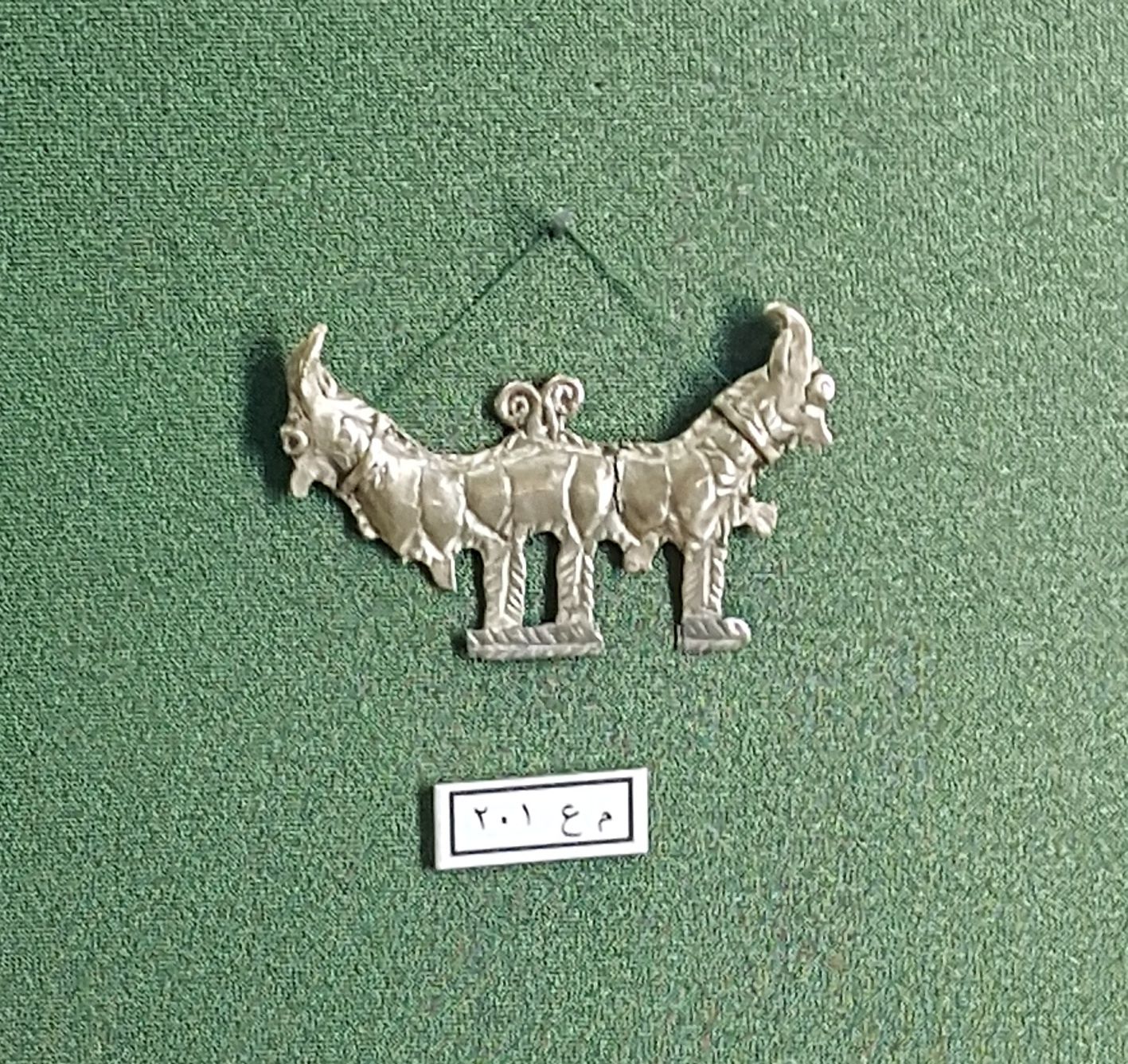
Qattara Oasis
Qattara Oasis ( ar, وَاحَـة الْـقَـطَّـارَة, Wāḥat al-Qaṭṭārah) is an area of irrigated date farm in Al Ain, United Arab Emirates featuring a distinctive ''falaj'' ( ar, فَـلَـج) irrigation system as well as a late Bronze Age archaeological site dated to 1800–1500 BCE. The oasis has been extensively surveyed by students from Al Ain University since 2015, and is home to 19 buildings of varying antiquity, of which nine are mosques. Among these are thought to be some of the oldest buildings still standing in Al Ain. History Finds from the Bronze Age burial at Qattara include Wadi Suq era chlorite jugs and bowls, bronze swords of between in length, and late Bronze Age and Iron Age short swords and daggers. Artefacts recovered also include carnelian jewellery, often associated by UAE historians with trading links to the Indus Valley. A find of particular interest from Qattara is a Bronze Age pendant discovered in the 1970s depicting a double- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
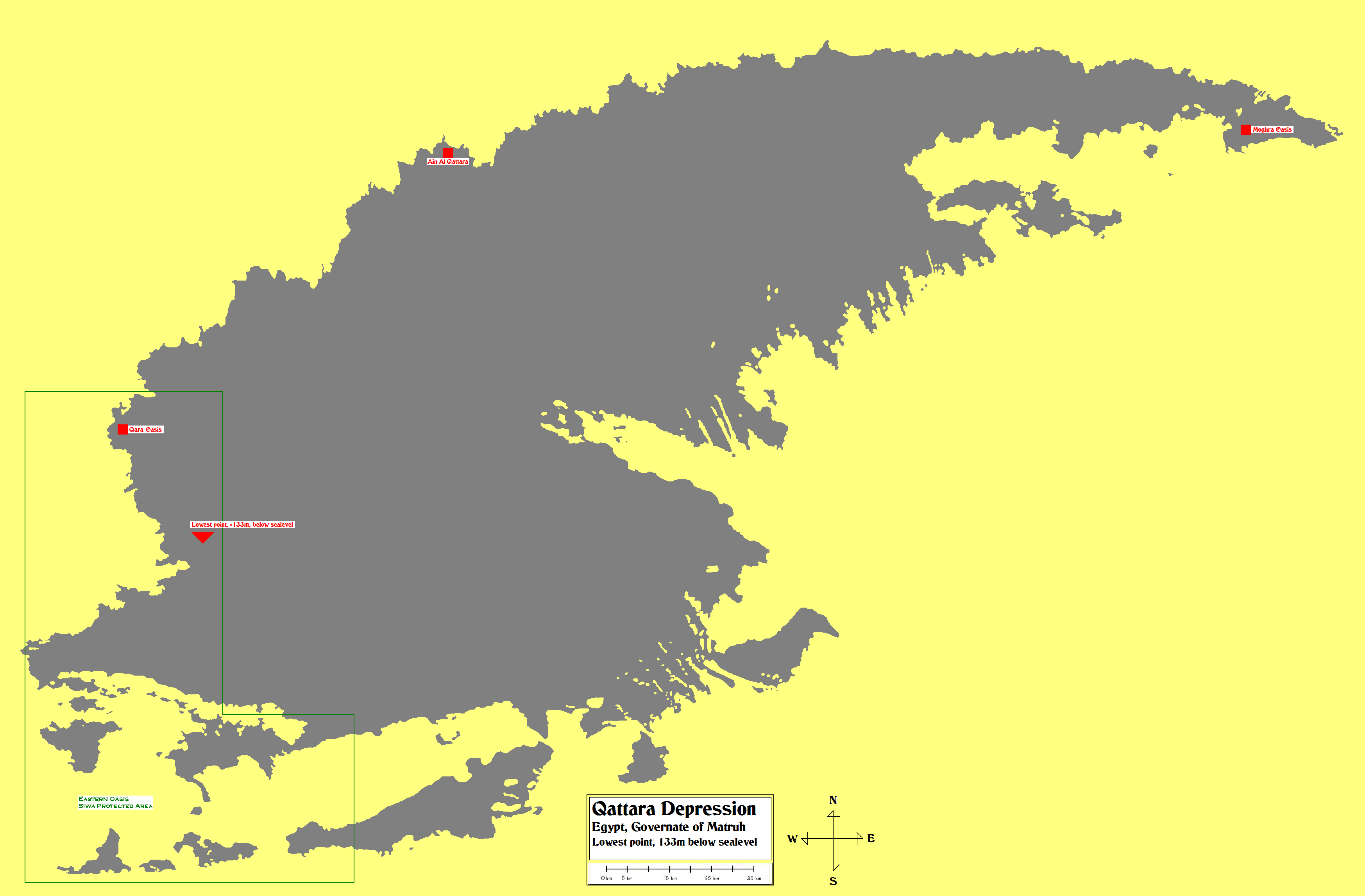
Qattara Animals
The Qattara Depression ( ar, منخفض القطارة, Munḫafaḍ al-Qaṭṭārah) is a depression in northwestern Egypt, specifically in the Matruh Governorate. The depression is part of the Western Desert of Egypt. The Qattara Depression lies below sea level, and its bottom is covered with salt pans, sand dunes, and salt marshes. The depression extends between the latitudes of 28°35' and 30°25' north and the longitudes of 26°20' and 29°02' east.El Bassyony, Abdou. 1995. ''"Introduction to the geology of the Qattara Depression,"'' International Conference on the Studies and Achievements of Geosciences in Egypt, 69 (85-eoa) The Qattara Depression was created by the interplay of salt weathering and wind erosion. Some west of the depression lie the oases of Siwa in Egypt and Jaghbub in Libya in smaller but similar depressions. The Qattara Depression contains the second lowest point in Africa at an elevation of below sea level, the lowest point being Lake Assal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)