|
WS2C
''WS2C'' is a putative gene associated with Waardenburg syndrome type 2. It has not yet been isolated from its locus of chromosome 8p23 since it was first reported in 2001. History This locus was first linked to Waardenburg syndrome in 2001, when a study of an Italian family with Waardenburg syndrome type 2 features found that they were due to an unknown gene on chromosome 8 at locus 8q23 which had been broken by a chromosomal translocation. The study established a provisional name for the gene, ''WS2C''. However, mutations in this region in Waardenburg syndrome patients have not been found since. References {{gene-8-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waardenburg Syndrome
Waardenburg syndrome is a group of rare genetic conditions characterised by at least some degree of congenital hearing loss and pigmentation deficiencies, which can include bright blue eyes (or Heterochromia iridum, one blue eye and one brown eye), a white forelock or patches of light skin. These basic features constitute type 2 of the condition; in type 1, there is also a wider gap between the inner corners of the eyes called telecanthus, telecanthus, or dystopia canthorum. In type 3, which is rare, the arms and hands are also malformed, with Camptodactyly, permanent finger contractures or fused fingers, while in type 4, the person also has Hirschsprung's disease. There also exist at least two types (2E and PCWH) that can result in central nervous system (CNS) symptoms such as developmental delay and muscle tone abnormalities. The syndrome is caused by mutations in any of several genes that affect the Cell division, division and Cell migration, migration of neural crest cells d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
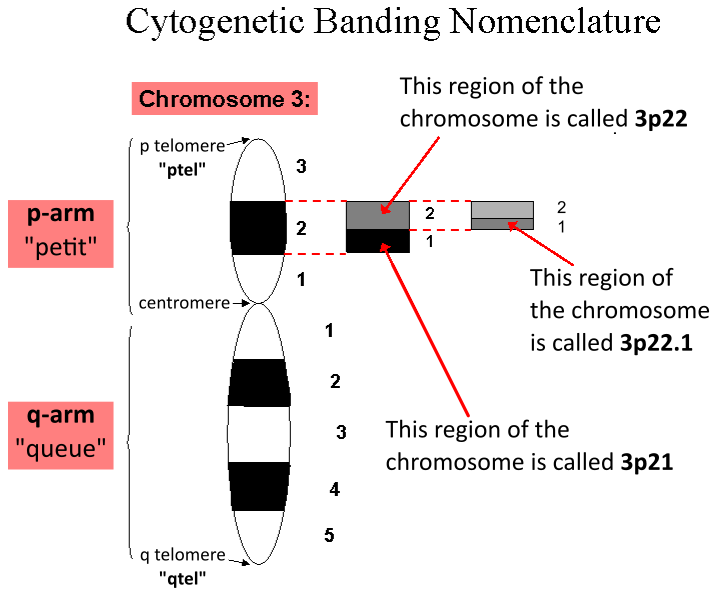
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |