|
WNT10B
Protein Wnt-10b (formerly Wnt12) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WNT10B'' gene. The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It may be involved in breast cancer, and its protein signaling is, it is presumed, a molecular switch that governs adipogenesis. Gain-of-function of Wnt10b in mouse hearts has shown to improve cardiac tissue repair after myocardial injury, by promoting coronary vessel formation and attenuating pathological fibrosis.Paik DT, Rai M, Ryzhov S, Sanders LN, Aisagbonhi O, Funke MJ, Feoktistov I, Hatzopoulos AK. Wnt10b gain-of-function improves cardiac repair by arteriole formation and attenuation of fibrosis. Circ Res. 2015; 117:804-816. This protein is 96% identical to the mouse Wnt10b pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
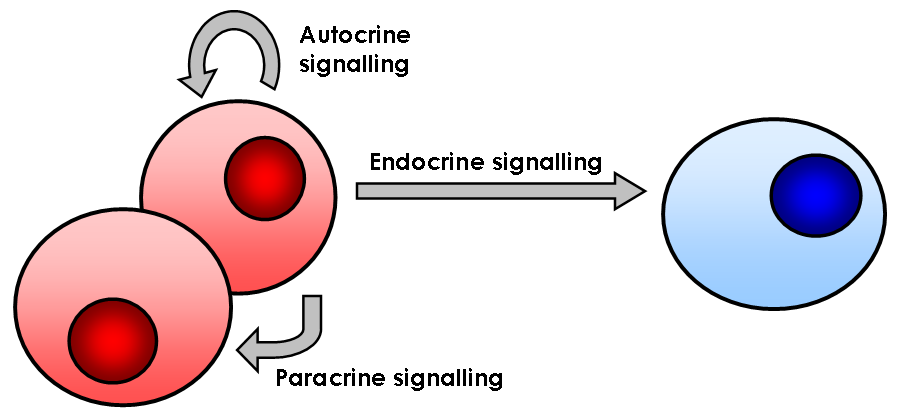
Signaling Proteins
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to cance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipogenesis
Adipogenesis is the formation of adipocytes (fat cells) from stem cells. It involves 2 phases, determination, and terminal differentiation. Determination is mesenchymal stem cells committing to the adipocyte precursor cells, also known as preadipocytes which lose the potential to differentiate to other types of cells such as chondrocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Terminal differentiation is that preadipocytes differentiate into mature adipocytes. Adipocytes can arise either from preadipocytes resident in adipose tissue, or from bone-marrow derived progenitor cells that migrate to adipose tissue. Introduction Adipocytes play a vital role in energy homeostasis and process the largest energy reserve as triglycerol in the body of animals. Adipocytes stay in a dynamic state, they start expanding when the energy intake is higher than the expenditure and undergo mobilization when the energy expenditure exceeds the intake. This process is highly regulated by counter regulatory hormones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Vessel
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels. Structure Coronary arte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |