|
WMS-2539
WMS-2539 is a fluorinated derivative of dexoxadrol and a potent uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce .... External links Synthesis and SAR studies of chiral non-racemic dexoxadrol analogues as uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists Piperidines Dioxolanes Organofluorides {{organic-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor Antagonist
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown medical history and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexoxadrol
Dexoxadrol (Dioxadrol) is a dissociative anaesthetic drug which has been found to be an NMDA antagonist and produces similar effects to PCP in animals. Dexoxadrol, along with another related drug etoxadrol, were developed as analgesics for use in humans, but development was discontinued after patients reported side effects such as nightmares A nightmare, also known as a bad dream, Retrieved 11 July 2016. is an unpleasant dream that can cause a strong emotional response from the mind, typically fear but also despair, anxiety or great sadness. The dream may contain situations of d ... and hallucinations. References Dissociative drugs Piperidines Dioxolanes Abandoned drugs {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidines
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, and typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name ''Piper'', which is the Latin word for pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of pyridine, usually over a molybdenum disulfide catalyst: : C5H5N + 3 H2 → C5H10NH Pyridine can also be reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
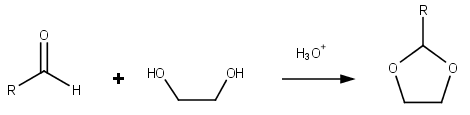
Dioxolanes
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals. As a class of compounds Dioxolanes are a group of organic compounds containing the dioxolane ring. Dioxolanes can be prepared by acetalization of aldehydes and ketalization of ketones with ethylene glycol. (+)-''cis''-Dioxolane is the trivial name for which is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. Protecting groups Organic compounds containing carbonyl groups sometimes need protection so that they do not undergo reactions during transformations of other functional groups that may be present. A variety of approaches to protection and deprotection of carbonyls including as dioxolanes are known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |