|
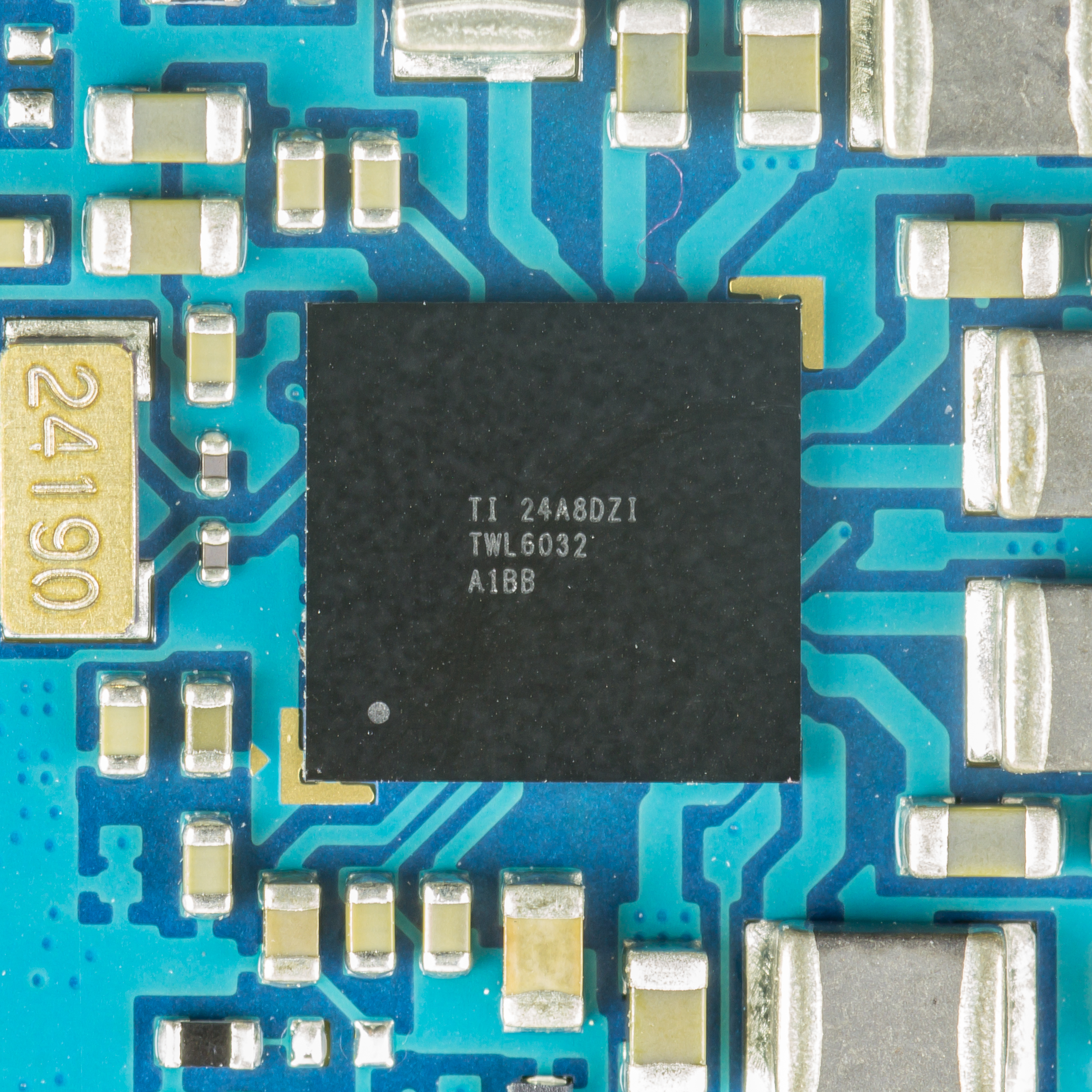
WL-CSP
Wafer-level packaging (WLP) is a process where packaging components are attached to an integrated circuit (IC) ''before'' the wafer – on which the IC is fabricated – is diced. In WSP, the top and bottom layers of the packaging and the solder bumps are attached to the integrated circuits while they are still in the wafer. This process differs from a conventional process, in which the wafer is sliced into individual circuits (dice) before the packaging components are attached. WLP is essentially a true chip-scale package (CSP) technology, since the resulting package is practically of the same size as the die. Wafer-level packaging allows integration of wafer fab, packaging, test, and burn-in at wafer level in order to streamline the manufacturing process undergone by a device from silicon start to customer shipment. There is no single industry-standard method of wafer-level packaging at present. A major application area of WLPs are smartphones due to the size constraints. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip Scale Package
A chip scale package or chip-scale package (CSP) is a type of integrated circuit package. Originally, CSP was the acronym for ''chip-size packaging.'' Since only a few packages are chip size, the meaning of the acronym was adapted to ''chip-scale packaging''. According to IPC's standard J-STD-012, ''Implementation of Flip Chip and Chip Scale Technology'', in order to qualify as chip scale, the package must have an area no greater than 1.2 times that of the die and it must be a single-die, direct surface mountable package. Another criterion that is often applied to qualify these packages as CSPs is their ball pitch should be no more than 1 mm. The concept was first proposed by Junichi Kasai of Fujitsu and Gen Murakami of Hitachi Cable in 1993. The first concept demonstration however came from Mitsubishi Electric. The die may be mounted on an interposer upon which pads or balls are formed, like with flip chip ball grid array (BGA) packaging, or the pads may be etched or prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip-scale Package
A chip scale package or chip-scale package (CSP) is a type of integrated circuit package. Originally, CSP was the acronym for ''chip-size packaging.'' Since only a few packages are chip size, the meaning of the acronym was adapted to ''chip-scale packaging''. According to IPC's standard J-STD-012, ''Implementation of Flip Chip and Chip Scale Technology'', in order to qualify as chip scale, the package must have an area no greater than 1.2 times that of the die and it must be a single-die, direct surface mountable package. Another criterion that is often applied to qualify these packages as CSPs is their ball pitch should be no more than 1 mm. The concept was first proposed by Junichi Kasai of Fujitsu and Gen Murakami of Hitachi Cable in 1993. The first concept demonstration however came from Mitsubishi Electric. The die may be mounted on an interposer upon which pads or balls are formed, like with flip chip ball grid array (BGA) packaging, or the pads may be etched or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip Carriers
Integrated circuits are put into protective packages to allow easy handling and assembly onto printed circuit boards and to protect the devices from damage. A very large number of different types of package exist. Some package types have standardized dimensions and tolerances, and are registered with trade industry associations such as JEDEC and Pro Electron. Other types are proprietary designations that may be made by only one or two manufacturers. Integrated circuit packaging is the last assembly process before testing and shipping devices to customers. Occasionally specially-processed integrated circuit dies are prepared for direct connections to a substrate without an intermediate header or carrier. In flip chip systems the IC is connected by solder bumps to a substrate. In beam-lead technology, the metallized pads that would be used for wire bonding connections in a conventional chip are thickened and extended to allow external connections to the circuit. Assemblies using " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Integrated Circuit Packaging Types
Integrated circuits are put into protective packages to allow easy handling and assembly onto printed circuit boards and to protect the devices from damage. A very large number of different types of package exist. Some package types have standardized dimensions and tolerances, and are registered with trade industry associations such as JEDEC and Pro Electron. Other types are proprietary designations that may be made by only one or two manufacturers. Integrated circuit packaging is the last assembly process before testing and shipping devices to customers. Occasionally specially-processed integrated circuit dies are prepared for direct connections to a substrate without an intermediate header or carrier. In flip chip systems the IC is connected by solder bumps to a substrate. In beam-lead technology, the metallized pads that would be used for wire bonding connections in a conventional chip are thickened and extended to allow external connections to the circuit. Assemblies using " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASE Group
Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. (), also known as ASE Group (), is a provider of independent semiconductor assembling and test manufacturing services, with its headquarters in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Overview The company was founded in 1984 by brothers Jason Chang and Richard Chang, who opened its first factory in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Jason Chang currently serves as company chairman and is on the 2016 ''Forbes'' list of the world's billionaires. As of 1 April 2016, the company's market cap was US$8.77 billion. In May 2015, ASE Group entered into an agreement with TDK to establish a joint venture company in Kaohsiung, Taiwan, named ASE Embedded Electronics Inc. The company manufactures IC embedded substrates utilizing TDK's SESUB technology. On 26 May 2016, ASE and Siliconware Precision Industries (SPIL) announced that they signed an agreement to form a new holding company, as part of the consolidation in the global semiconductor industry. Both companies said that each will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raspberry Pi 2
Raspberry Pi () is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in association with Broadcom. The Raspberry Pi project originally leaned towards the promotion of teaching basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. The original model became more popular than anticipated, selling outside its target market for uses such as robotics. It is widely used in many areas, such as for weather monitoring, because of its low cost, modularity, and open design. It is typically used by computer and electronic hobbyists, due to its adoption of the HDMI and USB standards. After the release of the second board type, the Raspberry Pi Foundation set up a new entity, named Raspberry Pi Trading, and installed Eben Upton as CEO, with the responsibility of developing technology. The Foundation was rededicated as an educational charity for promoting the teaching of basic computer science in schools and developing count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Galaxy Tab 2 10
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ''Samsung'' brand, and is the largest South Korean (business conglomerate). Samsung has the eighth highest global brand value. Samsung was founded by Lee Byung-chul in 1938 as a trading company. Over the next three decades, the group diversified into areas including food processing, textiles, insurance, securities, and retail. Samsung entered the electronics industry in the late 1960s and the construction and shipbuilding industries in the mid-1970s; these areas would drive its subsequent growth. Following Lee's death in 1987, Samsung was separated into five business groups – Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group and Hansol Group, and JoongAng Group. Notable Samsung industrial affiliates include Samsung Electronics (the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Grid Array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put on a dual in-line or flat package. The whole bottom surface of the device can be used, instead of just the perimeter. The traces connecting the package's leads to the wires or balls which connect the die to package are also on average shorter than with a perimeter-only type, leading to better performance at high speeds. BGAs were introduced in the 1990s and became popular by 2001. Soldering of BGA devices requires precise control and is usually done by automated processes such as in computer-controlled automatic reflow ovens. Description The BGA is descended from the pin grid array (PGA), which is a package with one face covered (or partly covered) with pins in a grid pattern which, in operation, conduct electrical signals betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer Bonding
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on Wafer (electronics), wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed encapsulation. The wafers' diameter range from 100 mm to 200 mm (4 inch to 8 inch) for MEMS/NEMS and up to 300 mm (12 inch) for the production of microelectronic devices. Smaller wafers were used in the early days of the microelectronics industry, with wafers being just 1 inch in diameter in the 1950s. Overview In microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), the package protects the sensitive internal structures from environmental influences such as temperature, moisture, high pressure and oxidizing species. The long-term stability and reliability of the functional elements depend on the encapsulation process, as does the overall device cost. The package has to fulfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer-scale Integration
Wafer-scale integration (WSI) is a rarely used system of building very-large integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") networks from an entire silicon wafer to produce a single "super-chip". Combining large size and reduced packaging, WSI was expected to lead to dramatically reduced costs for some systems, notably massively parallel supercomputers. The name is taken from the term very-large-scale integration, the state of the art when WSI was being developed. Overview In the normal integrated circuit manufacturing process, a single large cylindrical crystal ( boule) of silicon is produced and then cut into disks known as wafers. The wafers are then cleaned and polished in preparation for the fabrication process. A photographic process is used to pattern the surface where material ought to be deposited on top of the wafer and where not to. The desired material is deposited and the photographic mask is removed for the next layer. From then on the wafer is repeatedly processed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid state and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the light's intensity or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flashtube
A flashtube (flashlamp) is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for a very short time. A flashtube is a glass tube with an electrode at each end and is filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes and conducts a high-voltage pulse to make light. Flashtubes are used most in photography; they also are used in science, medicine, industry, and entertainment. Construction The lamp comprises a hermetically sealed glass tube, which is filled with a noble gas, usually xenon, and electrodes to carry electrical current to the gas. Additionally, a high voltage power source is necessary to energize the gas as a trigger event. A charged capacitor is usually used to supply energy for the flash, so as to allow very speedy delivery of very high electrical current when the lamp is triggered. Glass envelopes The glass envelope is most commonly a thin tube, often made of fused quartz, borosilicate or Pyrex, which may be straight, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)



