|
WHSC1
Probable histone-lysine N-methyltransferase NSD2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NSD2'' gene. This gene encodes a protein that contains four domains present in other developmental proteins: a PWWP domain, an HMG box, a SET domain, and a PHD-type zinc finger. It is expressed ubiquitously in early development. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) is a malformation syndrome associated with a hemizygous deletion of the distal short arm of chromosome 4. This gene maps to the 165 kb WHS critical region and has also been involved in the chromosomal translocation t(4;14)(p16.3;q32.3) in multiple myelomas. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso .... Some transcrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-box
In molecular biology, the HMG-box (high mobility group box) is a protein domain which is involved in DNA binding. Structure The structure of the HMG-box domain contains three alpha helices separated by loops (see figure to the right). Function HMG-box containing proteins only bind non- B-type DNA conformations (kinked or unwound) with high affinity. HMG-box domains are found in some high mobility group proteins, which are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, and DNA repair, all of which require changing the conformation of chromatin Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in r .... The single and the double box HMG proteins alter DNA architecture by inducing bends upon binding.D. Murugesapillai ''et al''Single-molecule stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SET Domain
Set, The Set, SET or SETS may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Mathematics *Set (mathematics), a collection of elements * Category of sets, the category whose objects and morphisms are sets and total functions, respectively Electronics and computing * Set (abstract data type), a data type in computer science that is a collection of unique values ** Set (C++), a set implementation in the C++ Standard Library * Set (command), a command for setting values of environment variables in Unix and Microsoft operating-systems * Secure Electronic Transaction, a standard protocol for securing credit card transactions over insecure networks * Single-electron transistor, a device to amplify currents in nanoelectronics * Single-ended triode, a type of electronic amplifier * Set!, a programming syntax in the scheme programming language Biology and psychology * Set (psychology), a set of expectations which shapes perception or thought *Set or sett, a badger's den *Set, a small t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf–Hirschhorn Syndrome
Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) is a chromosomal deletion syndrome resulting from a partial deletion on the short arm of chromosome 4 (del(4p16.3)). Features include a distinct craniofacial phenotype and intellectual disability. Signs and symptoms The most common characteristics include a distinct craniofacial phenotype (microcephaly, micrognathia, short philtrum, prominent glabella, ocular hypertelorism, dysplasia, dysplastic ears and periauricular tags), growth restriction, intellectual disability, muscle hypotonia, seizures, and congenital heart defects. Less common characteristics include hypospadias, colobomata of the iris, renal anomalies, and deafness. Antibody deficiencies are also common, including common variable immunodeficiency and IgA deficiency. T-cell immunity is normal. Genetics Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome is a microdeletion syndrome caused by a Deletion (genetics), deletion within HSA band 4p16.3 of the short arm of chromosome 4, particularly in the region of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemizygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 4
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 186 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genomics The chromosome is ~191 megabases in length. In a 2012 paper, 775 protein-encoding genes were identified on this chromosome.Chen LC, Liu MY, Hsiao YC, Choong WK, Wu HY, Hsu WL, Liao PC, Sung TY, Tsai SF, Yu JS, Chen YJ (2012) Decoding the disease-associated proteins encoded in the human chromosome 4. J Proteome Res 211 (27.9%) of these coding sequences did not have any experimental evidence at the protein level, in 2012. 271 appear to be membrane proteins. 54 have been classified as cancer-associated proteins. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 4. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes. Two detached fragments of two different chromosomes are switched. Robertsonian translocation occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes get attached, meaning that given two healthy pairs of chromosomes, one of each pair "sticks" and blends together homogeneously. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise-separated genes. It is detected on cytogenetics or a karyotype of affected cells. Translocations can be balanced (in an even exchange of material with no genetic information extra or missing, and ideally full functionality) or unbalanced (where the exchange of chromosome material is unequal resulting in extra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one tumor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
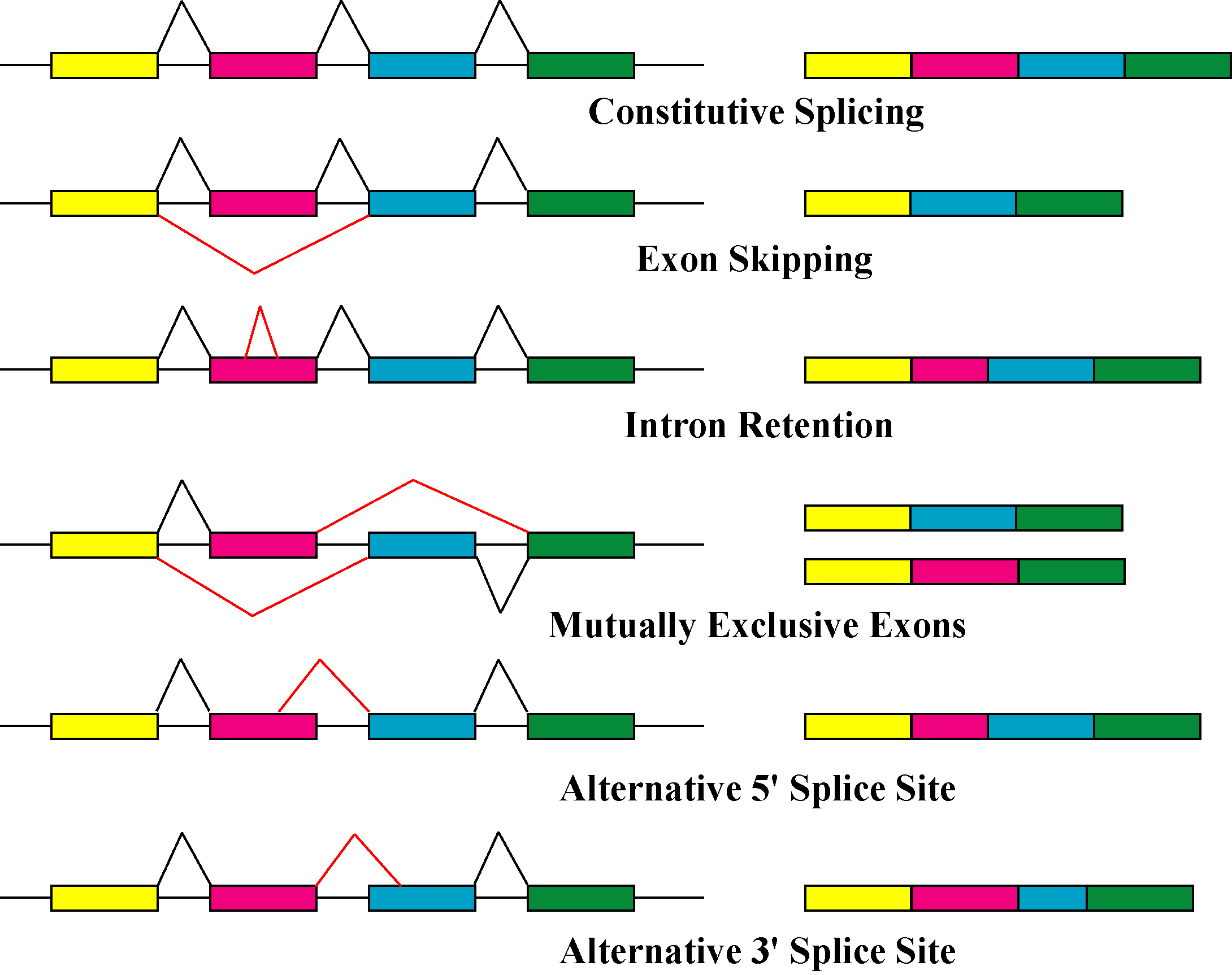
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |