|
Witherlea
Witherlea is a suburb to the south of Blenheim's central district. The Blenheim hospital campus, which includes Wairau Hospital, is in Witherlea. Omaka Cemetery has graves from early Pākehā settlement in the Wairau area. Demographics Witherlea covers . It had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Witherlea had a population of 5,409 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 576 people (11.9%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 846 people (18.5%) since the 2006 census. There were 2,115 households, comprising 2,631 males and 2,775 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.95 males per female, with 987 people (18.2%) aged under 15 years, 741 (13.7%) aged 15 to 29, 2,409 (44.5%) aged 30 to 64, and 1,269 (23.5%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 90.0% European/Pākehā, 10.0% Māori, 2.1% Pasifika, 4.0% Asian, and 2.8% other ethnicities. People may identify with more than one ethnicity. The percentage of people born overseas w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blenheim, New Zealand
Blenheim ( ; mi, Waiharakeke) is the most populous town in the regions of New Zealand, region of Marlborough Region, Marlborough, in the north east of the South Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of The surrounding Marlborough wine region is well known as the centre of the New Zealand wine industry. It enjoys one of New Zealand's sunniest climates, with warm, relatively dry summers and cool, crisp winters. Blenheim is named after the Battle of Blenheim (1704), where troops led by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough defeated a combined French and Bavarian force. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "Phormium tenax, flax stream" for . History The sheltered coastal bays of Marlborough supported a small Māori people, Māori population possibly as early as the 12th century. Archaeological evidence dates Polynesian human remains uncovered at Wairau Bar to the 13th century. The rich sea and bird life of the area would easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redwoodtown
Redwoodtown is a suburb to the south of Blenheim's central business district. Demographics Redwoodtown, comprising the statistical areas of Whitney West, Whitney East, Redwoodtown West and Redwoodtown East, covers . It had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Redwoodtown had a population of 10,401 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 681 people (7%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 1,017 people (10.8%) since the 2006 census 6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second small .... There were 4,302 households. There were 5,028 males and 5,370 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.94 males per female, with 1,833 people (17.6%) aged under 15 years, 1,755 (16.9%) aged 15 to 29, 4,431 (42.6%) aged 30 to 64, and 2,373 (22.8%) aged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burleigh, New Zealand
Burleigh is a suburb in inner Blenheim, in the Marlborough region of the South Island of New Zealand. Ōmaka Marae is located in Burleigh. It is a '' marae'' (meeting ground) for the Tarakaipa ''hapū In Māori and New Zealand English, a ' ("subtribe", or "clan") functions as "the basic political unit within Māori society". A Māori person can belong to or have links to many hapū. Historically, each hapū had its own chief and normally opera ...'' (sub-tribe) of Ngāti Apa ki te Rā Tō and includes Te Aroha o te Waipounamu '' wharenui'' (meeting house). References Suburbs of Blenheim, New Zealand Populated places in the Marlborough Region {{Marlborough-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairau Hospital
The Nelson Marlborough District Health Board (Nelson Marlborough DHB or NMDHB) was a district health board with the focus on providing healthcare to the Nelson, Tasman and Marlborough districts of New Zealand. In July 2022, it was merged into the national health service Te Whatu Ora (Health New Zealand). History The Nelson Marlborough District Health Board, like most other district health boards, came into effect on 1 January 2001 established by the New Zealand Public Health and Disability Act 2000. On 1 July 2022, the Nelson Marlborough DHB (trading as Nelson Marlborough Health) as an entity was disestablished and became part of Te Whatu Ora (Health New Zealand) and Te Aka Whai Ora (Māori Health Authority), New Zealand's new national health authorities. The Nelson Marlborough DHB's functions and responsibilities were assumed by Te Whatu Ora's Te Waipounamu division, which covers the entire South Island. Geographic area The area covered by the Nelson Marlborough District He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marlborough District Council
Marlborough District Council ( mi, Te Tauihu-o-te-waka) is the unitary local authority for the Marlborough District of New Zealand. The council is led by the mayor of Marlborough, who is currently . There are also 13 councillors representing three wards. Composition There are seven Blenheim Ward councillors: Brian Dawson, David Croad, Jamie Arbuckle, Jenny Andrews, Mark Peters, Michael Fitzpatrick, and Thelma Sowman. There are three Marlborough Sounds Ward councillors: deputy mayor Nadine Taylor, Barbara Faulls, and David Oddie. There are also three Wairau-Awatere Ward councillors: Cynthia Brooks, Francis Maher and Gerald Hope. History The council was formed in 1989, replacing Blenheim County Council (1869–1989), Picton Council Council (1876–1989) and Marlborough County Marlborough County was one of the counties of New Zealand on the South Island. During the period 1853 to 1859, the area that would become Marlborough County was administered by Nelson Province. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
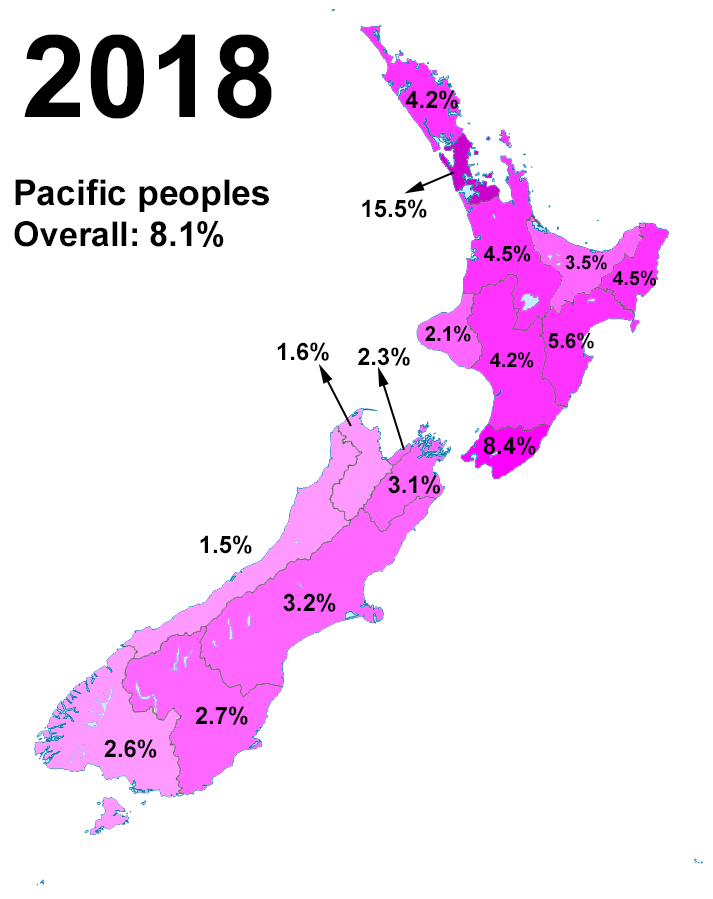
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands outside of New Zealand itself (also known as Pacific Islanders). They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European-descended Pākehā, indigenous Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. There are over 380,000 Pasifika people in New Zealand, with the majority living in Auckland. 8% of the population of New Zealand identifies as being of Pacific origin. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both Labour and National), migration officials, and special police squads targeted Pasifika illegal overstayers. Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the 1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopted Buddhist practices and teachings. Since the 1980s Asian migrants and refugees have established their varied forms of Buddhism in New Zealand. In the 2010s more than 50 groups, mostly in the Auckland region, offered different Buddhist traditions at temples, centres, monasteries and retreat centres. Many migrant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In New Zealand
Islam in New Zealand is a religious affiliation representing about 1.3% of the total population. Small numbers of Muslim immigrants from South Asia and eastern Europe settled in New Zealand from the early 1900s until the 1960s. Large-scale Muslim immigration began in the 1970s with the arrival of Fiji Indians, followed in the 1990s by refugees from various war-torn countries. The first Islamic centre in New Zealand opened in 1959 and there are now several mosques and two Islamic schools. The majority of Muslims in New Zealand are Sunni, with significant Shia and Ahmadiyya minorities. The Ahmadiyya Community has translated the Qur'an into the Māori language. History Early migration, 19th century The earliest Muslim presence in New Zealand dates back to the late 19th century. The first Muslims in New Zealand were an Indian family who settled in Cashmere, Christchurch, in the 1850s. The 1874 government census reported 15 Chinese Muslim gold diggers working in the Dunstan gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In New Zealand
Hinduism is the second largest religion in New Zealand. It is also one of the fastest-growing religions in New Zealand. According to the 2018 census, Hindus form 2.65% of the population of New Zealand. There are about 123,534 Hindus in New Zealand. Hindus from all over India continue to immigrate today, with the largest Indian ethnic subgroup being Gujaratis. A later wave of immigrants also includes Hindu immigrants who were of Indian descent from nations that were historically under European colonial rule, such as Fiji. Today there are Hindu temples in all major New Zealand cities. History Early settlement In 1836 the missionary William Colenso saw Māori women near Whangarei using a broken bronze bell to boil potatoes. The inscription is in very old Tamil script. This discovery has led to speculation that Tamil-speaking Hindus may have visited New Zealand hundreds of years ago. However, the first noted settlement of Hindus in New Zealand dates back to the arrival of sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Religion
Māori religion encompasses the various religious beliefs and practices of the Māori, the Polynesian indigenous people of New Zealand. Traditional Māori religion Traditional Māori religion, that is, the pre-European belief-system of the Māori, differed little from that of their tropical Eastern Polynesian homeland ( Hawaiki Nui), conceiving of everything - including natural elements and all living things - as connected by common descent through whakapapa or genealogy. Accordingly, Māori regarded all things as possessing a life force or mauri. Illustrating this concept of connectedness through genealogy are the major personifications dating from before the period of European contact: * Tangaroa was the personification of the ocean and the ancestor or origin of all fish. * Tāne was the personification of the forest and the origin of all birds. * Rongo was the personification of peaceful activities and agriculture and the ancestor of cultivated plants. (Some sources ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people with an estimated 60% of Māori pledging allegiance to the Christian message within the first 35 years. It remains New Zealand's largest religious group despite there being no official state church. Today, slightly less than half the population identify as Christian. The largest Christian groups are Catholic, Anglican and Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian services conducted in New Zealand were carried out by Father Paul-Antoine Léonard de Villefeix, the Dominican chaplain on the ship ''Saint Jean Baptiste'' commanded by the French navigator and explorer Jean-François-Marie de Surville. Villefeix was the first Christian minister to set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Terminology In the New Zealand census, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese New Zealanders, Korean New Zealanders, Japanese New Zealanders), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino New Zealanders, Vietnamese New Zealanders, Malaysian New Zealanders), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese New Zealanders, Indian New Zealanders, Sri Lankan New Zealanders, Bangladeshi New Zealanders, Pakistani New Zealanders). Notably, New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asian ancestry are excluded from this term. Colloquial usage of ''Asian'' in New Zealand excludes Indians and other peoples of South Asian descent. ''Asian'' as used by Statistics New Zealand includes South Asian ethnic group. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |