|
Windows On Windows
In computing, Windows on Windows (commonly referred to as WOW) is a discontinued compatibility layer of 32-bit versions of the Windows NT family of operating systems. Since 1993, with the release of Windows NT 3.1, WoW extends NTVDM to provide limited support for running legacy 16-bit programs written for Windows 3.x or earlier. There is a similar subsystem, known as WoW64, on 64-bit Windows versions that runs 32-bit programs. This subsystem will be retired with the end of support of Windows 10 in October 14, 2025. The last version of Windows to include this subsystem is Windows 10, as Windows 11 (and Windows Server 2008 R2 and later) only run the x86-64 processor in long mode and therefore cannot run 16-bit software without emulation software. Background Many 16-bit Windows legacy programs can run without changes on newer 32-bit editions of Windows. The reason designers made this possible was to allow software developers time to remedy their software during the industry t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The early 1980s and home computers, rise of personal computers through software like Windows, and the company has since expanded to Internet services, cloud computing, video gaming and other fields. Microsoft is the List of the largest software companies, largest software maker, one of the Trillion-dollar company, most valuable public U.S. companies, and one of the List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands globally. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to dominate the personal computer operating system market with MS-DOS in the mid-1980s, followed by Windows. During the 41 years from 1980 to 2021 Microsoft released 9 versions of MS-DOS with a median frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer. From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of machine code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. However, not all 64-bit instruction sets support full 64-bit virtual memory addresses; x86-64 and AArch64, for example, support only 48 bits of virtual address, with the remaining 16 bits of the virtual address required to be all zeros (000...) or all ones (111...), and several 64-bit instruction sets support fewer than 64 bits of physical memory address. The term ''64-bit'' also describes a generation of computers in which 64-bit processors are the norm. 64 bits is a word size that defines certain classes of computer archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Address Space
In computing, an address space defines a range of discrete addresses, each of which may correspond to a network host, peripheral device, disk sector, a memory cell or other logical or physical entity. For software programs to save and retrieve stored data, each datum must have an address where it can be located. The number of address spaces available depends on the underlying address structure, which is usually limited by the computer architecture being used. Often an address space in a system with virtual memory corresponds to a highest level translation table, e.g., a segment table in IBM System/370. Address spaces are created by combining enough uniquely identified qualifiers to make an address unambiguous within the address space. For a person's physical address, the ''address space'' would be a combination of locations, such as a neighborhood, town, city, or country. Some elements of a data address space may be the same, but if any element in the address is different, ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pointer (computer Programming)
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer ''references'' a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as ''dereferencing'' the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture. Using pointers significantly improves performance for repetitive operations, like traversing iterable data structures (e.g. strings, lookup tables, control tables, linked lists, and tree structures). In particular, it is often much cheaper in time and space to copy and deref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shim (computing)
In computer programming, a shim is a library that transparently intercepts API calls and changes the arguments passed, handles the operation itself or redirects the operation elsewhere. Shims can be used to support an old API in a newer environment, or a new API in an older environment. Shims can also be used for running programs on different software platforms than they were developed for. Shims for older APIs typically come about when the behavior of an API changes, thereby causing compatibility issues for older applications which still rely on the older functionality; in such cases, the older API can still be supported by a thin compatibility layer on top of the newer code. Shims for newer APIs are defined as: "a library that brings a new API to an older environment, using only the means of that environment." Examples * Web polyfills implement newer web standards using older standards and JavaScript, if the newer standard is not available in a given web browser. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunk
In computer programming Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of proc ..., a thunk is a subroutine used to inject a calculation into another subroutine. Thunks are primarily used to delay a calculation until its result is needed, or to insert operations at the beginning or end of the other subroutine. They have many other applications in Code generation (compiler), compiler code generation and modular programming. The term originated as a whimsical English irregular verbs, irregular form of the verb ''think''. It refers to the original use of thunks in ALGOL 60 compilers, which required special analysis (thought) to determine what type of routine to generate. Background The early years of compiler research saw broad experimentation with different evaluation strategy, evaluation s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
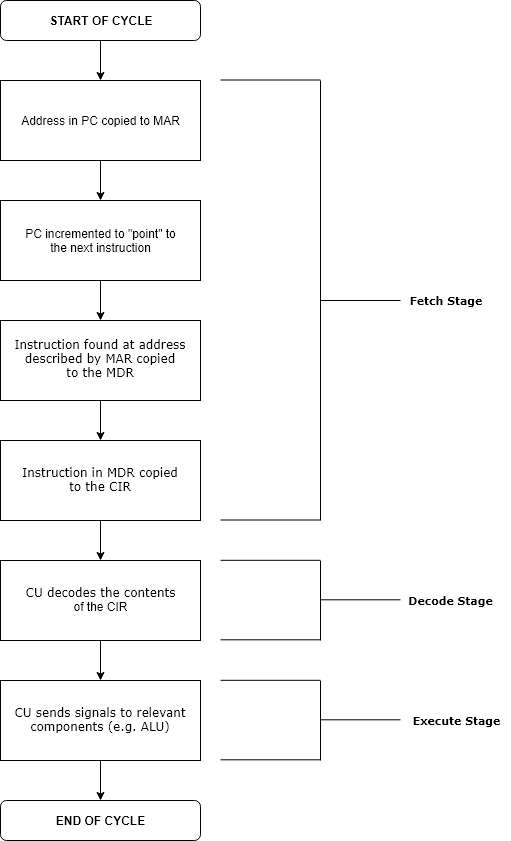
Execution (computing)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 9x
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a line of discontinued Microsoft Windows operating systems released from 1995 to 2000 and supported until 2006, which were based on the kernel introduced in Windows 95 and modified in succeeding versions, with its underlying foundation based on MS-DOS. The first version in the 9x series was Windows 95, which was succeeded by Windows 98 and then Windows Me, which was the third and last version of Windows on the 9x line, until the series was superseded by Windows XP. Windows 9x is predominantly known for its use in Desktop computer, home desktops. In 1998, Windows made up 82% of operating system market share. The internal release number for versions of Windows 9x is 4.x. The internal versions for Windows 95, 98, and Me are 4.0, 4.1, and 4.9, respectively. Previous MS-DOS-based versions of Windows used version numbers of Windows 3.x, 3.2 or lower. Windows NT, which was aimed at professional users such as networks and businesses, used a sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged Microsoft's formerly separate MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows products into a single product and featured significant improvements over its predecessor, most notably in the graphical user interface (GUI) and in its simplified " plug-and-play" features. There were also major changes made to the core components of the operating system, such as moving from a mainly cooperatively multitasked 16-bit architecture of its predecessor Windows 3.1 to a 32-bit preemptive multitasking architecture. Windows 95 introduced numerous functions and features that were featured in later Windows versions, and continue in modern variations to this day, such as the taskbar, the notification area, file shortcuts on the desktop, plug and play driver integration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Mode
In the x86-64 computer architecture, long mode is the mode where a 64-bit operating system can access 64-bit instructions and registers. 64-bit programs are run in a sub-mode called 64-bit mode, while 32-bit programs and 16-bit protected mode programs are executed in a sub-mode called compatibility mode. Real mode or virtual 8086 mode programs cannot be natively run in long mode. Overview An x86-64 processor acts identically to an IA-32 processor when running in real mode or protected mode, which are supported modes when the processor is ''not'' in long mode. A bit in the CPUID extended attributes field informs programs in real or protected modes if the processor can go to long mode, which allows a program to detect an x86-64 processor. This is similar to the CPUID attributes bit that Intel IA-64 processors use to allow programs to detect if they are running under IA-32 emulation. With a computer running legacy BIOS, the BIOS and the boot loader run in real mode. After ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set architecture, instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new four-level paging mechanism. In 64-bit mode, x86-64 supports significantly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory compared to its 32-bit computing, 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to utilize more memory for data storage. The architecture expands the number of general-purpose registers from 8 to 16, all fully general-purpose, and extends their width to 64 bits. Floating-point arithmetic is supported through mandatory SSE2 instructions in 64-bit mode. While the older x87 FPU and MMX registers are still available, they are generally superseded by a set of sixteen 128-bit Processor register, vector registers (XMM registers). Each of these vector registers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2, codenamed "Windows Server 7" or "Windows Server 2008 Release 2", is the eighth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009, the same respective release dates of Windows 7. It is the successor to the Windows Vista-based Windows Server 2008, released the previous year, and was succeeded by the Windows 8-based Windows Server 2012. Enhancements in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new functionality for Active Directory, new virtualization and management features, version 7.5 of the Internet Information Services web server and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is built on the same kernel used with the client-oriented Windows 7, and is the first server operating system released by Microsoft which dropped support for 32-bit processors, an addition which carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |