|
Wilson's Disease
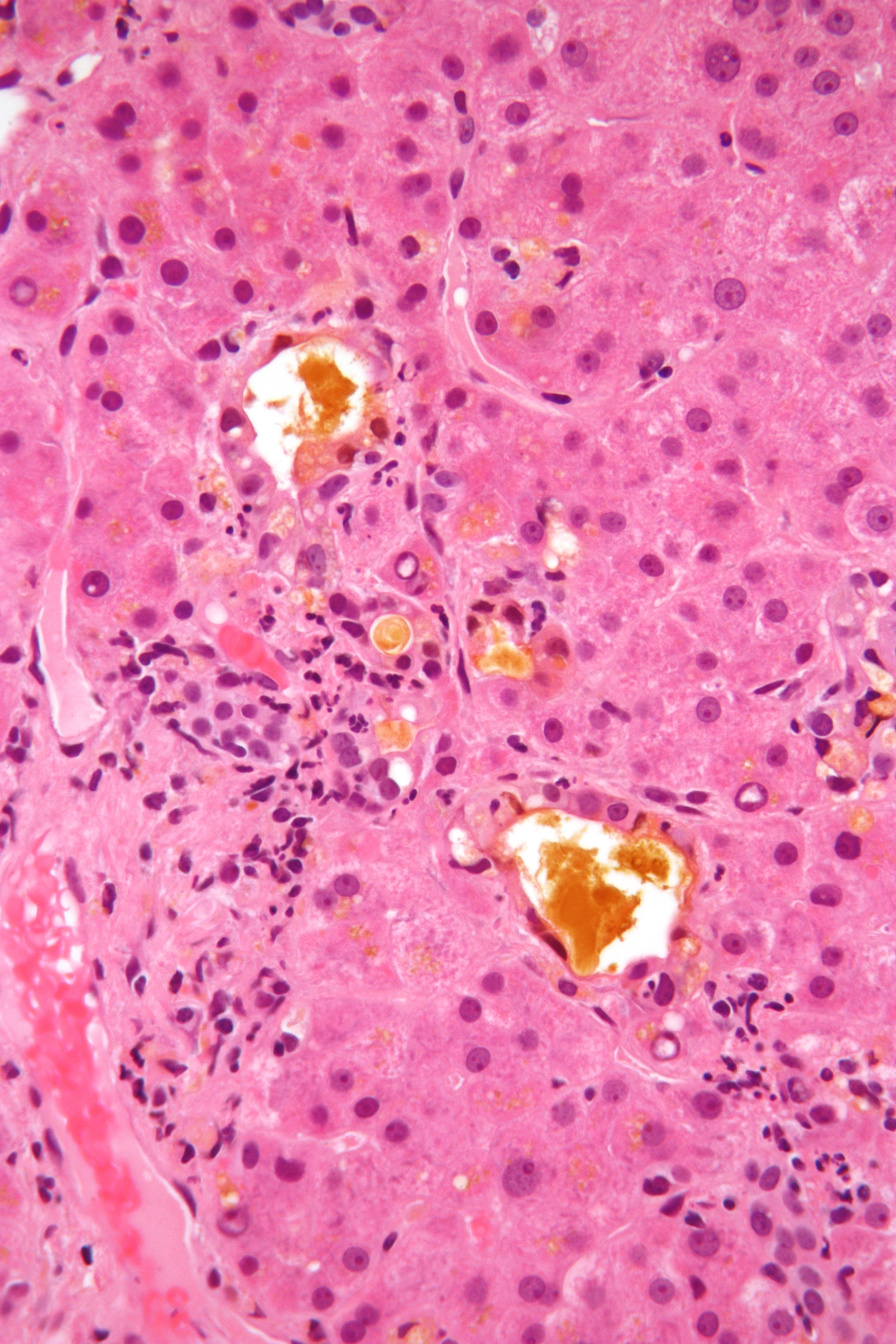
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for a person to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically treated with dietary changes and medication. Dietary changes invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson's Temperature Syndrome
Wilson's (temperature) syndrome, also called Wilson's thyroid syndrome or WTS, is a term used in alternative medicine to attribute various common and non-specific symptoms to abnormally low body temperature and impaired conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3), despite normal thyroid function tests. , a physician who invented the concept and named it after himself, treated these symptoms with sustained-release triiodothyronine (SR-T3) until one of his patients died and he was banned from prescribing this treatment any longer. Wilson's Syndrome is not an actual medical condition, and medical expert groups have warned against it as a potentially dangerous misunderstanding of physiology. The American Thyroid Association (ATA) released an official statement asserting that Wilson's syndrome is at odds with established knowledge of thyroid function and describing the diagnostic criteria for Wilson's syndrome as "imprecise" and "non-specific". After one of Wilson's pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pruritus
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itch leads to a scratch reflex. Unmyelinated nerve fibers for itch and pain both originate in the skin; however, information for them is conveyed centrally in two distinct systems that both use the same nerve bundle and spinothalamic tract. Classification Most commonly, an itch is felt in one place. If it is felt all over the body, then it is called ''generalized itch'' or ''generalized pruritus''. If the sensation of itching persists for six weeks or longer, then it is called ''chronic itch'' or ''chronic pruritus''. ''Chronic idiopathic pruritus'' or ''essential pruritus'' is a rare form of itch that persists for longer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-penicillamine
Penicillamine, sold under the brand name of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease. It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, and various heavy metal poisonings. It is taken by mouth. Penicillamine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1970. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses It is used as a chelating agent: * In Wilson's disease, a rare genetic disorder of copper metabolism, penicillamine treatment relies on its binding to accumulated copper and elimination through urine. * Penicillamine was the second line treatment for arsenic poisoning, after dimercaprol (BAL). It is no longer recommended. In cystinuria, a hereditary disorder in which high urine cystine levels lead to the formation of cystine stones, penicillamine binds with cysteine to yield a mixed disulfide which is more soluble than cystine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trientine
Triethylenetetramine (TETA and trien), also known as trientine (INN) when used medically, is an organic compound with the formula H2NHCH2CH2NH2sub>2. The pure freebase is a colorless oily liquid, but, like many amines, older samples assume a yellowish color due to impurities resulting from air-oxidation. It is soluble in polar solvents. The branched isomer tris(2-aminoethyl)amine and piperazine derivatives may also be present in commercial samples of TETA. The hydrochloride salts are used medically as a treatment for copper toxicity. Uses The reactivity and uses of TETA are similar to those for the related polyamines ethylenediamine and diethylenetriamine. It is primarily used as a crosslinker ("hardener") in epoxy curing. Medical uses The hydrochloride salt of TETA, referred to as ''trientine hydrochloride'', is a chelating agent that is used to bind and remove copper in the body to treat Wilson's disease, particularly in those who are intolerant to penicillamine. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Biopsy
Liver biopsy is the biopsy (removal of a small sample of tissue) from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment. Medical uses Liver biopsy is often required for the diagnosis of a liver problem (jaundice, abnormal blood tests) where blood tests, such as hepatitis A serology, have not been able to identify a cause. It is also required if hepatitis is possibly the result of medication, but the exact nature of the reaction is unclear. Alcoholic liver disease and tuberculosis of the liver may be diagnosed through biopsy. Direct biopsy of tumors of the liver may aid the diagnosis, although this may be avoided if the source is clear (e.g. spread from previously known colorectal cancer). Liver biopsy will likely remain particularly important in the diagnosis of unexplained liver disease. Non-invasive tests for liver fibrosis in alcoholic, nonalcoholic and viral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile) and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum. The composition of hepatic bile is (97–98)% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About 400 to 800 millilitres of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. Bile salt anions are hydrophilic on one side and hydrophobic on the other side; consequently, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Protein
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
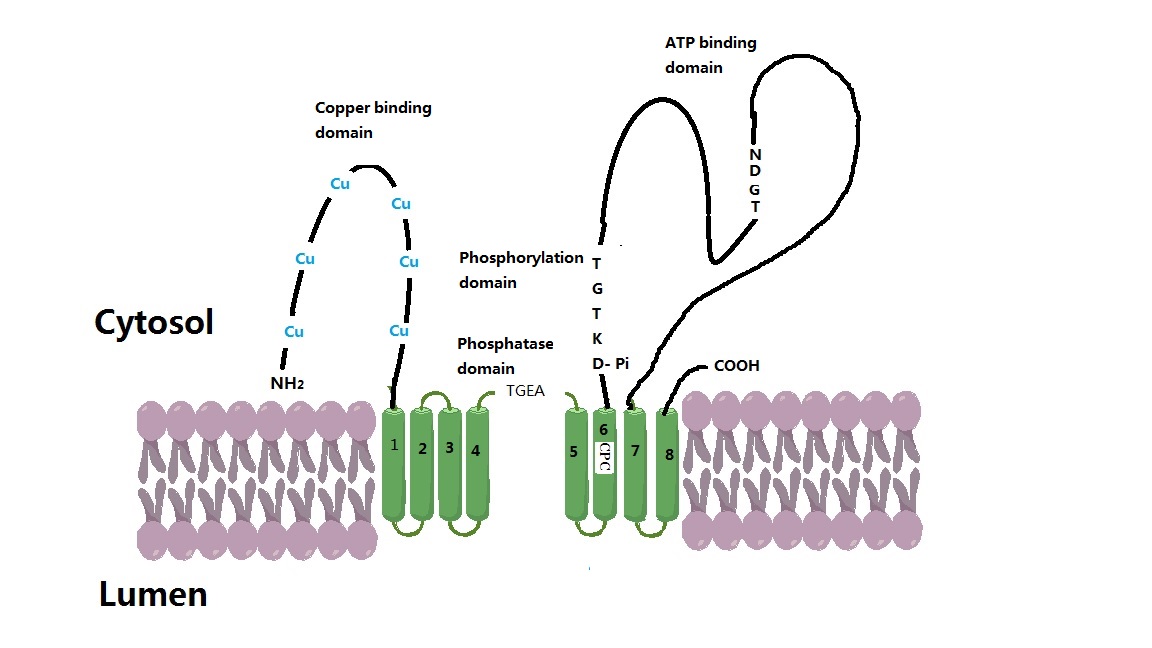
Wilson Disease Protein
Wilson disease protein (WND), also known as ATP7B protein, is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which is encoded by the ''ATP7B'' gene. The ATP7B protein is located in the trans-Golgi network of the liver and brain and balances the copper level in the body by excreting excess copper into bile and plasma. Genetic disorder of the ATP7B gene may cause Wilson's disease, a disease in which copper accumulates in tissues, leading to neurological or psychiatric issues and liver diseases. Gene Wilson disease protein is associated with ''ATP7B'' gene, approximately 80 Kb, located on human chromosome 13 and consists of 21 exons. The mRNA transcribed by ''ATP7B'' gene has a size of 7.5 Kb, and which encodes a protein of 1465 amino acids. The gene is a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family and encodes a protein with several membrane-spanning domains, an ATPase consensus sequence, a hinge domain, a phosphorylation site, and at least two putative copper-binding sites. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |