|
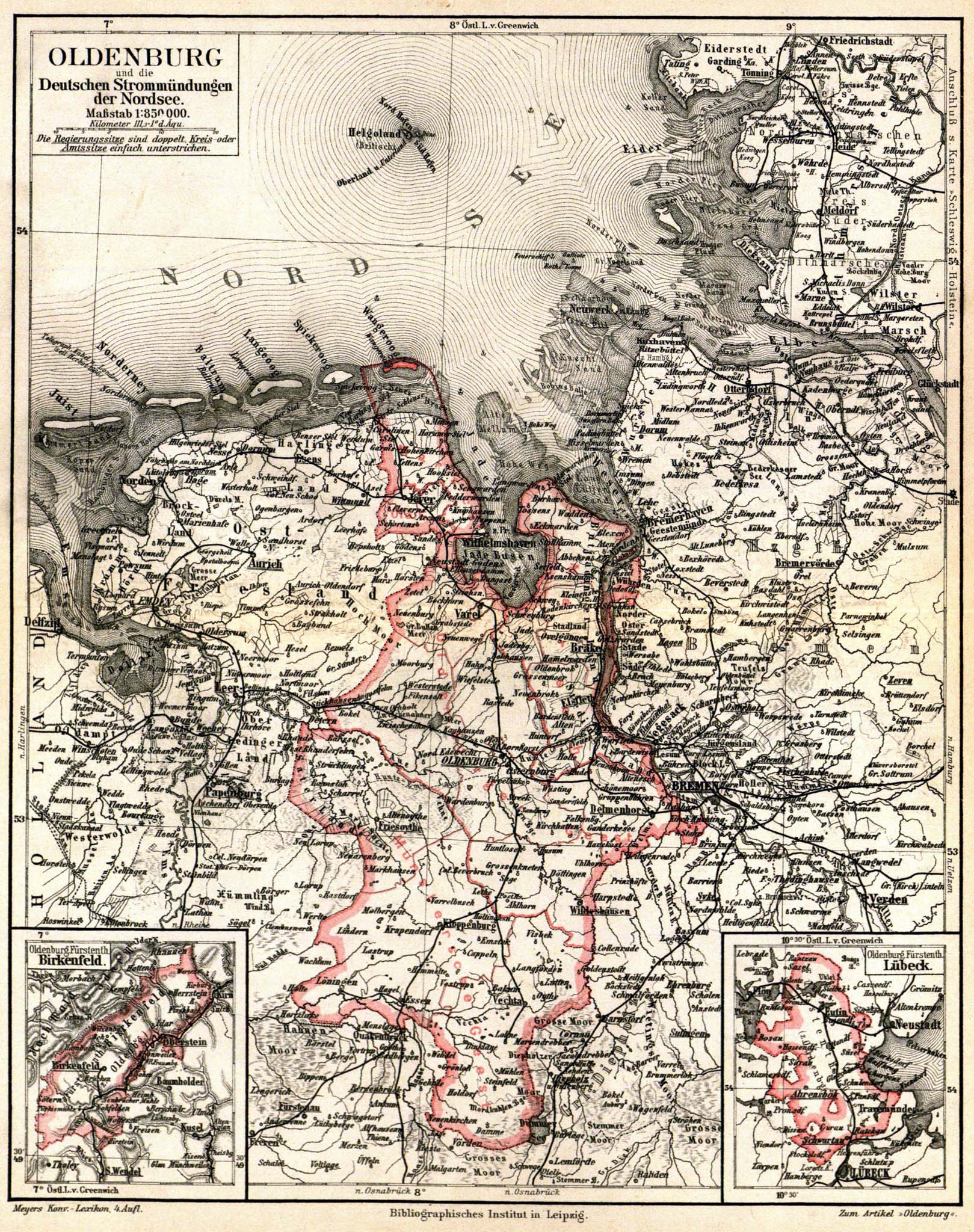
Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg Railway
The Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg railway is a predominantly double-track, non-electrified main line in the northwest in the German state of Lower Saxony. It runs to the south from the port city of Wilhelmshaven to Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg. The line is being upgraded in connection with the construction of JadeWeserPort so that it will be continuously duplicated and electrified. Route The Oldenburg–Wilhelmshaven line (VzG 1522) is currently duplicated with the exception of two sections, Varel–Jaderberg and Hahn–Rastede, and is designed for a top speed of 120 km/h. History The track was a joint project of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways and the Prussian state railways and was built together with the Oldenburg–Bremen railway, Oldenburg–Bremen line. It linked the Prussian naval base in Wilhelmshaven (then called Heppens) and opened up the north of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg, Grand Duchy. It was officially opened on 18 July 1867, but scheduled services s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-enclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Lüneburg, Osnabrück, Oldenburg, Hildesheim, Salzgitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldenburg–Osnabrück Railway
The Oldenburg–Osnabrück railway is a single-track, non-electrified railway line from Oldenburg to Osnabrück, both in the German state of Lower Saxony. The line was opened in two stages between 1875 and 1876. The first section from Oldenburg to Quakenbrück was built between 1870 and 1875 by the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways (GOE). The opening of the first section took place on 15 October 1875. The section from Quakenbrück to Osnabrück-Eversburg, then passing through Prussian territory, opened only a year later, on 30 June 1876. The official opening took place on 15 November 1876. Until the mid-1990s there was a modest long distance train connection over the line. There was a daily express train from Koblenz and Cologne to Wilhelmshaven and a train from Mönchengladbach to Wilhelmshaven. Since 2000, the infrastructure was expanded to introduce a train service with shorter journey times and better connections. Part of the development was to increase the maximum li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Oldenburg
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (, also known as Holstein-Oldenburg) was a grand duchy within the German Confederation, North German Confederation and German Empire that consisted of three widely separated territories: Oldenburg, Eutin and Birkenfeld. It ranked tenth among the German states and had one vote in the Bundesrat and three members in the Reichstag. Its ruling family, the House of Oldenburg, also came to rule in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Greece and Russia. History The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg came into existence in 1815 combining the territory of the old Duchy of Oldenburg with the Principality of Birkenfeld. Whilst Oldenburg was elevated to a Grand Duchy at the Congress of Vienna, the first two Grand Dukes continued to style themselves as merely Dukes and it wasn't until 1829 that the newly acceded Augustus used the title of Grand Duke. Although paternalist, the early Grand Dukes did not grant a constitution until events overtook them in 1848. The European Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldenburg–Bremen Railway
The Bremen–Oldenburg railway is a long mainline railway that connects Oldenburg in the northwest of the German states of Lower Saxony and Bremen. It is served by a daily Intercity Express service between Oldenburg and Munich, InterCity trains between Norddeich Mole, Oldenburg and Leipzig, as well as freight and regional trains. The Bremen S-Bahn also operates over the line. Route The line leaves Bremen Hauptbahnhof at its western exit and snakes through several tight bends through the former main freight yard and the "northwest node" to highway 6 passing the junctions of many freight lines to the bridge over the Weser. Until the construction of the Weser tunnel, this was the northernmost permanent crossing of the river. The line continues through Bremen-Neustadt in a westerly direction to Delmenhorst, where a busy line branches off to Vechta and Osnabrück (operated by NordWestBahn). From there it runs in a northwesterly direction towards Hude. There it connects with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian State Railways
The term Prussian state railways (German: ''Preußische Staatseisenbahnen'') encompasses those railway organisations that were owned or managed by the State of Prussia. The words "state railways" are not capitalized because Prussia did not have an independent railway administration; rather the individual railway organisations were under the control of the Ministry for Trade and Commerce or its later offshoot, the Ministry for Public Works. The official name of the Prussian rail network was ''Königlich Preußische Staatseisenbahnen'' (K.P.St.E., "Royal Prussian State Railways") until 1896, ''Königlich Preußische und Großherzoglich Hessische Staatseisenbahn'' (K.P.u.G.H.St.E., " Royal Prussian and Grand-Ducal Hessian State Railways") until the end of the First World War, and ''Preußische Staatsbahn'' (P.St.B., "Prussian State Railway") until its nationalization in 1920. A common mistake is the use of the abbreviation K.P.E.V. in supposed reference to a mythical "Royal Prussian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Oldenburg State Railways
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (''Großherzogtum Oldenburg''), part of the German Empire. History Compared with the other states in the German Empire, Oldenburg's first railway line arrived relatively late. In this sparsely populated and economically poor area, the construction of railways appeared for a long while to be unsustainable due to the financial costs. In addition, the various ideas of its neighboring states, Hanover and Prussia prevented railway projects from coming to fruition for a long time. Finally in 1864 a treaty was agreed between Prussia and Oldenburg over the construction of a railway line from Bremen to Oldenburg. At the same time Prussia committed itself to building a railway line from Heppens – later Wilhelmshaven – to Oldenburg (the Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg line). The Grand Ducal Railway Commission, set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastede
Rastede (Low German: ''Raastäe/Raas'') is a municipality in the Ammerland district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately 12 km north of Oldenburg. It is the site of the Schloss Rastede. The Rastede railway station is located at the Oldenburg–Wilhelmshaven railway. Sons and daughters * Hermann Schussler Hermann Schüssler or Schussler (August 4, 1842 – April 27, 1919) was a German civil engineer and designer of dams, famous for designing the Crystal Springs Dam and Comstock water system. Early years Hermann Schussler was born in what is ... (1842-1919), German water-systems engineer and architect of dams * Augustus, Grand Duke of Oldenburg (1783-1853), Grand Duke of Oldenburg * Christian, Duke of Oldenburg (born 1955), Duke of Oldenburg * Lenn Kuck (born 2001) References Ammerland {{Ammerland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varel
Varel () is a town in the district of Friesland, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated near the Jade River and the Jade Bight, approximately south of Wilhelmshaven and north of Oldenburg. With a population of 23,984 (2020) it is the biggest town in the district of Friesland. Geography Varel is located south of the Jade Bight at the North Sea on the Geest. Over time, the city expanded into lower areas as the construction of dykes helped to secure these areas from floods. The environment of Varel is shaped by agriculture, forests and the sea. Neighbour municipalities Jade in the district of Wesermarsch is the Eastern neighbour municipality of Varel. In the South of Varel one will find the municipalities Rastede and Wiefelstede which are part of the district of Ammerland. The municipality of Bockhorn is located in the West of Varel. Bockhorn is also part of the district of Friesland. Segmentation of the city Varel is segmented into 21 localities. Besides the down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varel 2010 PD 033
Varel () is a town in the district of Friesland, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated near the Jade River and the Jade Bight, approximately south of Wilhelmshaven and north of Oldenburg. With a population of 23,984 (2020) it is the biggest town in the district of Friesland. Geography Varel is located south of the Jade Bight at the North Sea on the Geest. Over time, the city expanded into lower areas as the construction of dykes helped to secure these areas from floods. The environment of Varel is shaped by agriculture, forests and the sea. Neighbour municipalities Jade in the district of Wesermarsch is the Eastern neighbour municipality of Varel. In the South of Varel one will find the municipalities Rastede and Wiefelstede which are part of the district of Ammerland. The municipality of Bockhorn is located in the West of Varel. Bockhorn is also part of the district of Friesland. Segmentation of the city Varel is segmented into 21 localities. Besides the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NordWestBahn2
The NordWestBahn GmbH is a private railway company providing regional train services on several routes in northern and western Germany. It is a joint venture of Stadtwerke Osnabrück AG, Verkehr und Wasser GmbH in Oldenburg and Transdev Germany, Berlin. The head office of the company is in Osnabrück. NWB claims to be Germany's largest regional railway company. Since 5 November 2000, NordWestBahn operates, on behalf of the public transport company of Lower Saxony (Landesnahverkehrsgesellschaft Niedersachsen - LNVG), the Weser-Ems-Network in Lower Saxony. In March 2008, NordWestBahn won the tender for the regional S-Bahn Bremen/Lower Saxony, defeating German National railway operator DB Regio DB Regio AG is a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn which operates regional and commuter train services in Germany. DB Regio AG, headquartered in Frankfurt am Main. It is a 100% subsidiary of the Deutsche Bahn Group and there part of the DB Regio bus .... Operation of these routes start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |