|
Weedon–Marton Junction Line
The Weedon–Marton Junction line (also known as the ''Weedon–Leamington line'') was a rural branch line in England that ran from the West Coast Main Line at Weedon, via Daventry to Marton Junction, where it joined the Rugby–Leamington line and thus connected to Leamington Spa. Opening in stages between 1888 and 1895, the line was closed to passengers in 1958, and to freight in 1963, however a short section of the line at the western end from Marton Junction to Southam, remained open for freight trains serving the cement works until 1985. Route and stations There were six stations on the line: * Weedon (which allowed interchange with the West Coast Main Line) * Daventry * Braunston * Flecknoe * Napton & Stockton * Southam & Long Itchington Trains to Leamington called at the now closed Leamington Spa (Avenue) station, and either terminated at the now closed Milverton station, or continued to . Weedon, Daventry and Braunston stations were in Northamptonshire, while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Line
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line. Industrial spur An industrial spur is a type of secondary track used by railroads to allow customers at a location to load and unload railcars without interfering with other railroad operations. Industrial spurs can vary greatly in length and railcar capacity depending on the requirements of the customer the spur is serving. In heavily industrialized areas, it is not uncommon for one industrial spur to have multiple sidings to several different customers. Typically, spurs are serviced by local trains responsible for collecting small numbers of railcars and delivering them to a larger yard, where these railcars are sorted and dispatched in larger trains with other cars destined to similar locations. Because industrial spurs generally have less capacity and traffic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-track Railway
A single-track railway is a railway where trains traveling in both directions share the same track. Single track is usually found on lesser-used rail lines, often branch lines, where the level of traffic is not high enough to justify the cost of constructing and maintaining a second track. Advantages and disadvantages Single track is significantly cheaper to build and maintain, but has operational and safety disadvantages. For example, a single-track line that takes 15 minutes to travel through would have capacity for only two trains per hour in each direction safely. By contrast, a double track with signal boxes four minutes apart can allow up to 15 trains per hour in each direction safely, provided all the trains travel at the same speed. This hindrance on the capacity of a single track may be partly overcome by making the track one-way on alternate days, if the single track is not used for public passenger transit. Long freight trains are a problem if the passing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuneaton Railway Station
Nuneaton railway station serves the large town of Nuneaton in Warwickshire, England. The station is managed by West Midlands Trains. It is served by three railway lines: the Trent Valley section of the West Coast Main Line (WCML), the Birmingham-Leicester-Peterborough line and the Nuneaton to Coventry branch line. It was known, during the period 1924–1969, as ''Nuneaton Trent Valley'', to distinguish it from the now closed Nuneaton Abbey Street station; many local people still refer to it as ''Trent Valley''. The station lies on the north-eastern edge of Nuneaton town centre, just outside the ring road. History 19th and 20th century The original Nuneaton station was opened on 15 September 1847, when the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) opened the Trent Valley Line; the branch line to Coventry opened in 1850. The original station, like many others on the line, had been designed by John William Livock. A simple two platform structure, it became inadequate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Train
Push–pull is a configuration for locomotive-hauled trains, allowing them to be driven from either end of the train, whether having a locomotive at each end or not. A push–pull train has a locomotive at one end of the train, connected via some form of remote control, such as multiple-unit train control, to a vehicle equipped with a control cab at the other end of the train. This second vehicle may be another locomotive, or an unpowered control car. In the UK and some other parts of Europe, the control car is referred to as a ''driving trailer'' (or driving van trailer/DVT where there is no passenger accommodation); in the US and Canada, they are called ''cab cars''. Train formation Locomotive at one end Historically, push–pull trains with steam power provided the driver with basic controls at the cab end along with a bell or other signalling code system to communicate with the fireman located in the engine itself in order to pass commands to adjust controls not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railmotor
Railmotor is a term used in the United Kingdom and elsewhere for a railway lightweight railcar, usually consisting of a railway carriage with a steam traction unit, or a diesel or petrol engine, integrated into it. Steam railcars Overview In the earliest days of railways, designers wished to produce a vehicle for passenger carrying that was economical to build and operate on routes where passenger numbers were light. A single coach with its own prime mover was a solution adopted in some cases; this may be thought of as the predecessor to the railcar, a term more associated with the use of internal combustion engines. William Bridges Adams started building railmotors in small numbers as early as 1848. The Bristol and Exeter Railway used a steam carriage. In most cases the early designs were unsuccessful technically, but in the early years of the twentieth century, street-running passenger tramways started to use small steam engines to draw tramcars, replacing the customary hors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1895 In The United Kingdom
Events from the year 1895 in the United Kingdom. Incumbents * Monarch – Victoria * Prime Minister – Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery (Liberal) (until 22 June); Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury ( Coalition) (starting 25 June) * Parliament – 25th (until 8 July), 26th (starting 12 August) Events * January–February – "Great Frost". * 3 January – première of Oscar Wilde's comedy '' An Ideal Husband'' at the Haymarket Theatre in London. * 5 January – première of Henry James's historical drama ''Guy Domville'' at the newly renovated St James's Theatre in London is booed. * 12 January – the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty is founded in England by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Canon Hardwicke Rawnsley. * 14 January – Diglake Colliery Disaster in the North Staffordshire Coalfield: a flood of water underground causes the deaths of 77 miners; only three bodies are recovered . * 25 January – first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marton, Warwickshire
Marton is a village and civil parish in Warwickshire, England. The parish is within the Borough of Rugby and in the 2011 Census' had a population of 484. The hamlet of Marton Moor lies south of the village. Marton is on the A423 road between Coventry and Southam. To the north of the village is the River Leam and just to the west the River Itchen joins the Leam. Due to its proximity from these two rivers, parts of the village have periodically suffered from flooding. Marton was mentioned in the Domesday Book as ''Mortone''. In the early Middle Ages it was a place of some importance, as it was the centre of a hundred named ''Meretone''. By the late 12th century this had become part of the hundred of Knightlow. Just north of Marton is a medieval bridge over the River Leam known as Marton Bridge, which was built in 1414 by a locally born merchant called John Middleton. In 1928 a modern bridge was effectively built over the top of the medieval one, and it was hidden from view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1888 In The United Kingdom
Events from the year 1888 in the United Kingdom. This year is noted for the first Whitechapel murders. Incumbents * Monarch – Victoria * Prime Minister – Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury (Conservative) * Parliament – 24th Events * 26 January – the Lawn Tennis Association is founded. * 13 February – the first issue of the ''Financial Times'' goes on sale (originally launched on 9 January by Horatio Bottomley as the ''London Financial Guide''). * 23 March – a meeting called by William McGregor to discuss establishment of The Football League is held in London. * 24 March – West Bromwich Albion F.C. beat Preston North End 2–1 to win the FA cup. * 27 March – "Goschen's Conversion" (National Debt (Conversion) Act): George Goschen, Chancellor of the Exchequer, consolidates Consolidated 3% Annuities ( consols) into a new bond, 2.75% Consolidated Stock, the first change in the coupon rate since 1757. * 3 April – London prostitute Emma Elizabeth Smith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways: the LNWR is effectively an ancestor of today's West Coast Main Line. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in part, by the Great Western Railway's plans for a railway north from Oxford to Birmingham. The company initially had a network of approximately , connecting London with Birmingham, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester. The headquarters were at Euston railway station. As traffic increased, it was greatly expanded with the opening in 1849 of the Great Hall, designed by P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And Birmingham Railway
The London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom, in operation from 1833 to 1846, when it became part of the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR). The railway line which the company opened in 1838, between London and Birmingham, was the first intercity line to be built into London. It is now the southern section of the West Coast Main Line. The line was engineered by Robert Stephenson. It started at Euston Station in London, went north-west to Rugby, where it turned west to Coventry and on to Birmingham. It terminated at Curzon Street Station, which it shared with the Grand Junction Railway (GJR), whose adjacent platforms gave an interchange with full connectivity (with through carriages) between Liverpool, Manchester and London. History Early plans The railway engineer John Rennie proposed a railway line from London to Birmingham in 1823, and formed a company to build it by a route through Oxford and Banbury, a route later taken by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



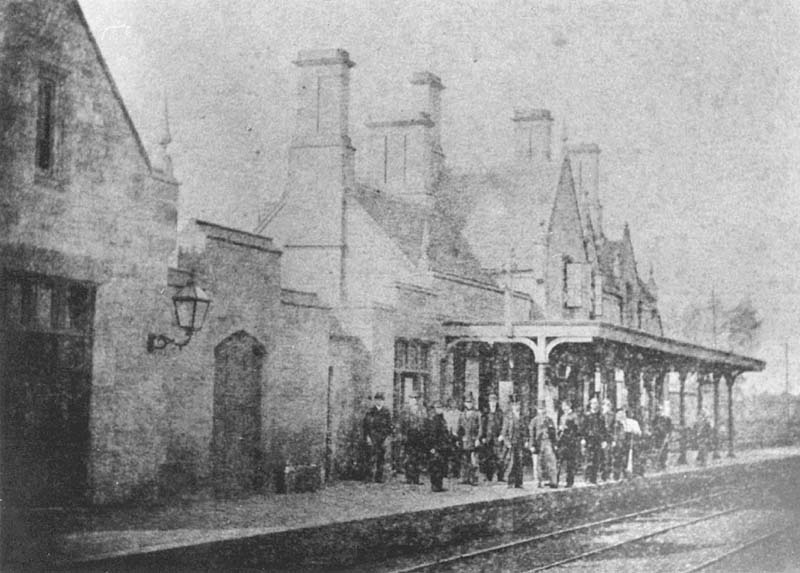
.jpg)

.jpg)

