|
Weaver's Cave
Weaver Cave ( sl, Tkalca jama), also known as Inlet Cave (), is a long ponor cave in southwest Slovenia. It runs from the west (downstream) side of the Rak Škocjan Valley, where it has two entrances, and continues into Planina Cave. It is traversed by Rak Creek, part of the Ljubljanica source system. It thus forms part of the hydrological connection between Cerknica Polje and Planina Polje. Due to sumps, the stream of the Rak is very difficult to follow and was explored by divers only in 1974, when the majority of the cave was discovered in the course of a rescue expedition, and in August 2012. The cave was named after a stalagmite reminiscent of a weaver. An old story says that he was turned to stone because he worked on Sunday, the Lord's Day. The first description of Weaver Cave was published in 1687 by Johann Weikhard von Valvasor in the ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society''. He also published an engraving of it. The cave has also been depicted by other arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Rak Going Underground
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as Stream#Creek, creek, Stream#Brook, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to Geographical feature, geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "Burn (landform), burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabbath In Christianity
Sabbath in Christianity is the inclusion in Christianity of a Sabbath, a day set aside for rest and worship, a practice that was mandated for the Israelites in the Ten Commandments in line with God's blessing of the seventh day (Saturday) making it holy, "because on it God rested from all his work that he had done in creation". The practice was associated with the assembly of the people to worship in synagogues on the day known as Shabbat. Early Christians, at first mainly Jewish, observed the seventh-day Sabbath with prayer and rest, but gathered on the seventh day, Saturday, reckoned in Jewish tradition as beginning, like the other days, at sunset on what would now be considered the Friday evening. At the beginning of the second century Ignatius of Antioch approved non-observance of the Sabbath. The now majority practice of Christians is to observe Sunday, called the Lord's Day, rather than the Jewish seventh-day Sabbath as a day of rest and worship. Possibly because of a move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljubljanica Basin
The Ljubljanica (), known in the Middle Ages as the ''Sava'', is a river in the southern part of the Ljubljana Basin in Slovenia. The capital of Slovenia, Ljubljana, lies on the river. The Ljubljanica rises south of the town of Vrhnika and flows into the Sava River about downstream from Ljubljana. Its largest affluent is the Mali Graben Canal. Including its source affluent the Little Ljubljanica ( sl, Mala Ljubljanica), the river is in length. The Little Ljubljanica joins the Big Ljubljanica ( sl, Velika Ljubljanica) after and the river continues its course as the Ljubljanica. The Ljubljanica is the continuation of several karst rivers that flow from the Prezid Karst Field ( sl, Prezidsko polje) to Vrhnika on the surface and underground in caves, and so the river is poetically said to have seven names (six name changes): Trbuhovica, Obrh, Stržen, Rak, Pivka, Unica, and Ljubljanica. Archaeological significance The Ljubljanica has become a popular site for archaeologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Inner Carniola
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime
QuickTime is an extensible multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. Created in 1991, the latest Mac version, QuickTime X, is available for Mac OS X Snow Leopard up to macOS Mojave. Apple ceased support for the Windows version of QuickTime in 2016, and ceased support for QuickTime 7 on macOS in 2018. As of Mac OS X Lion, the underlying media framework for QuickTime, QTKit, was deprecated in favor of a newer graphics framework, AVFoundation, and completely discontinued as of macOS Catalina. Overview QuickTime is bundled with macOS. QuickTime for Microsoft Windows is downloadable as a standalone installation, and was bundled with Apple's iTunes prior to iTunes 10.5, but is no longer supported and therefore security vulnerabilities will no longer be patched. Already, at the time of the Windows version's discontinuation, two such zero-day vulnerabilities (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Gallery Of Slovenia
The National Gallery of Slovenia ( sl, Narodna galerija) is the national art gallery of Slovenia. It is located in the capital Ljubljana. It was founded in 1918, after the dissolution of Austria-Hungary and the establishment of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. Initially, it was hosted in the Kresija Palace of Ljubljana, but moved to the present location in 1925. The building The present building was built in 1896, during the administration of Mayor Ivan Hribar, whose ambition was to transform Ljubljana into a representative capital of all the Slovene Lands. It was designed by the Czech architect František Škabrout and was first used as a Slovenian cultural center (''Narodni dom'') as the central seat of various cultural associations of national importance. The building stands near Tivoli Park and was completely renovated in 2013-2016. In the early 1990s, an extension to the main building was built by the Slovene architect Edvard Ravnikar. In 2001, a large t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Natural Bridge
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" *Artel Great (born 1981), American actor Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer instructed program that includes classroom instruction and various learning activities. Their intention is to teach the students to avoid gang ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'', a 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Kurz Zum Thurn Und Goldenstein
{{disambigu ...
Franz may refer to: People * Franz (given name) * Franz (surname) Places * Franz (crater), a lunar crater * Franz, Ontario, a railway junction and unorganized town in Canada * Franz Lake, in the state of Washington, United States – see Franz Lake National Wildlife Refuge Businesses * Franz Deuticke, a scientific publishing company based in Vienna, Austria * Franz Family Bakeries, a food processing company in Portland, Oregon * Franz-porcelains, a Taiwanese brand of pottery based in San Francisco Other uses * ''Franz'' (film), a 1971 Belgian film * Franz Lisp, a dialect of the Lisp programming language See also * Frantz (other) * Franzen (other) * Frantzen (other) Frantzen or Frantzén is a surname. It may refer to: * Allen Frantzen (born 1947/48), American medievalist * Björn Frantzén (born 1977), Swedish chef and owner of the Frantzén restaurant * Jean-Pierre Frantzen (1890–1957), Luxembourgian gym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the first journal in the world exclusively devoted to science, and therefore also the world's longest-running scientific journal. It became an official society publication in 1752. The use of the word ''philosophical'' in the title refers to natural philosophy, which was the equivalent of what would now be generally called ''science''. Current publication In 1887 the journal expanded and divided into two separate publications, one serving the physical sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'') and the other focusing on the life sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''). Both journals now publish themed issues and issues resulting from pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Weikhard Von Valvasor
Johann Weikhard Freiherr von Valvasor or Johann Weichard Freiherr von Valvasor ( sl, Janez Vajkard Valvasor, ) or simply Valvasor (baptised on 28 May 1641 – September or October 1693) was a natural historian and polymath from Carniola, present-day Slovenia, and a fellow of the Royal Society in London. He is known as a pioneer of study of karst studies. Together with his other writings, until the late 19th century his best-known work—the 1689 ''Glory of the Duchy of Carniola'', published in 15 books in four volumes—was the main source for older Slovenian history, making him one of the precursors of modern Slovenian historiography. Biography Valvasor was born in the town of Ljubljana, then Duchy of Carniola, now the capital of Slovenia. In the 16th century, it was Johann Baptist Valvasor who established the family Valvasor in the Duchy of Carniola in central Europe in a part of Austria that is now the Republic of Slovenia. In medieval Latin " Valvasor" or "Valvasore" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
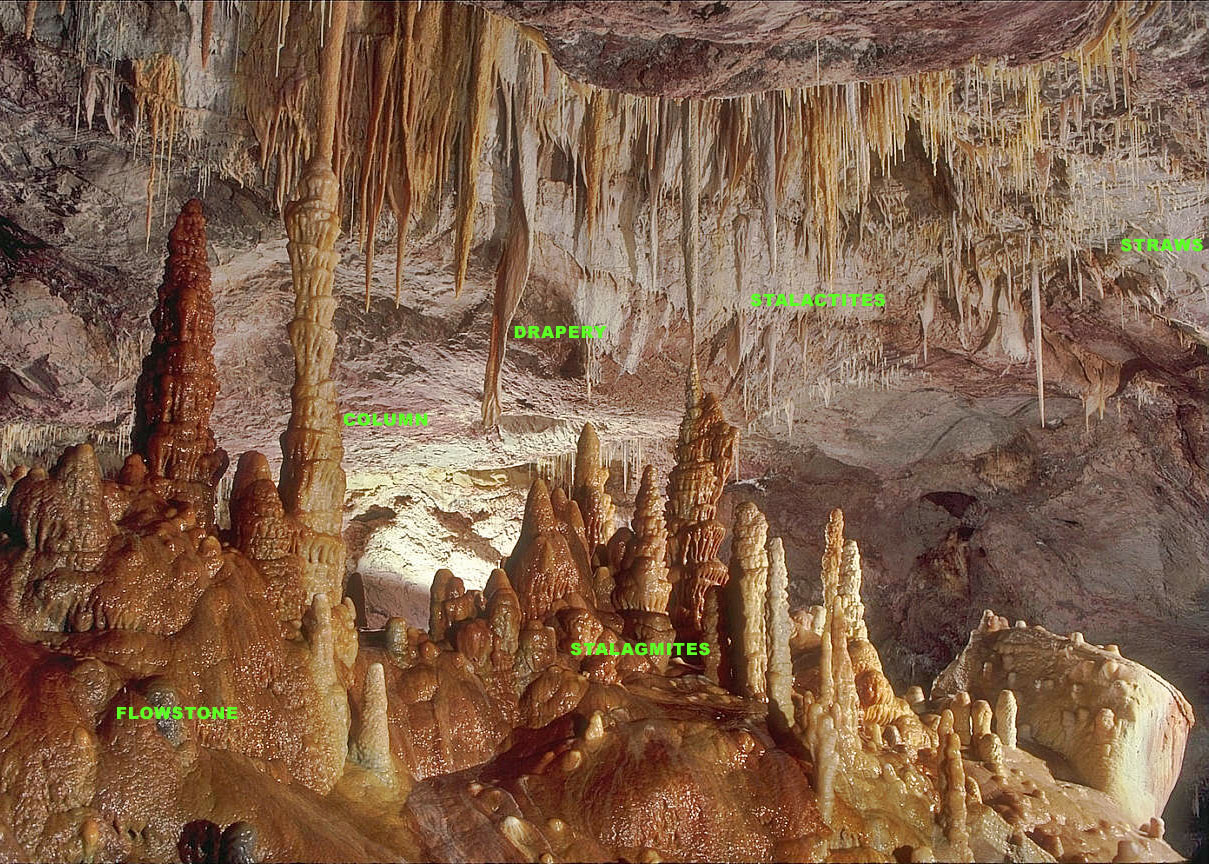
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)