|
Wayland The Smith
In Germanic mythology, Wayland the Smith ( ang, Wēland; , ; Old Frisian: Wela(n)du; german: Wieland der Schmied; goh, Wiolant; ''Galans'' (''Galant'') in Old French; gem-x-proto, Wēlandaz, italic=no from ', lit. "crafting one") is a master blacksmith originating in Germanic heroic legend, described by Jessie Weston as "the weird and malicious craftsman, Weyland".Weston, J. (1929). 'Legendary Cycles of the Middle Age', in Tanner, J.R. (ed.), ''The Cambridge Medieval History'' Vol. VI, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, p. 841f. Wayland's story is most clearly told in the Old Norse sources ''Völundarkviða'' (a poem in the ''Poetic Edda'') and ''Þiðreks saga''. In them, Wayland is a smith who is enslaved by a king. Wayland takes revenge by killing the king's sons and then escapes by crafting a winged cloak and flying away. A number of other visual and textual sources clearly allude to similar stories, most prominently the Old English poem ''Deor'' and the Franks C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ed0026
Ed, ed or ED may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Ed (film), ''Ed'' (film), a 1996 film starring Matt LeBlanc * Ed (Fullmetal Alchemist), Ed (''Fullmetal Alchemist'') or Edward Elric, a character in ''Fullmetal Alchemist'' media * Ed (TV series), ''Ed'' (TV series), a TV series that ran from 2000 to 2004 Businesses and organizations * Ed (supermarket), a French brand of discount stores founded in 1978 * Consolidated Edison, from their NYSE stock symbol * United States Department of Education, a department of the United States government * Enforcement Directorate, a law enforcement and economic intelligence agency in India * European Democrats, a loose association of conservative political parties in Europe * Airblue (IATA code ED), a private Pakistani airline * Eagle Dynamics, a Swiss software company Places * Ed, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in the United States * Ed, Sweden, a town in Dals-Ed, Sweden * Erode Junction railway station, station code ED Health and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtana
Curtana, also known as the Sword of Mercy, is a ceremonial sword used at the coronation of British kings and queens. One of the Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom, its end is blunt and squared to symbolise mercy. Description The sword measures long and wide at the handle. About of the steel blade's tip is missing. The blade features a decorative "running wolf" mark which originated in the town of Passau, Lower Bavaria, Germany. It has a gilt-iron hilt, a wooden grip bound in wire, and a leather sheath bound in crimson velvet with gold embroidery. The sheath has been remade several times since the 17th century, and the current one was made in 1937. The Curtana has a squared tip. It is used in the procession alongside two other pointed swords. The Curtana once had a jagged edge like a naturally broken tip, but this was squared off at some time. At one time, the other two could be distinguished by their points: the sharply-pointed Sword of Temporal Justice, and the more ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie ("chooser of the slain") is one of a host of female figures who guide souls of the dead to the god Odin's hall Valhalla. There, the deceased warriors become (Old Norse "single (or once) fighters"Orchard (1997:36) and Lindow (2001:104).). When the are not preparing for the events of Ragnarök, the valkyries bear them mead. Valkyries also appear as lovers of heroes and other mortals, where they are sometimes described as the daughters of royalty, sometimes accompanied by ravens and sometimes connected to swans or horses. Valkyries are attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' (a book of poems compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources), the ''Prose Edda'', the (both by Snorri Sturluson) and the (one of the Sagas of Icelanders), all written—or compiled—in the 13th century. They appear throughout the poetry of skalds, in a 14th-century charm, and in various runic inscriptions. The Old English cognate term appears in several Old E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slagfiðr
In Norse mythology, Slagfiðr (Old Norse "beating- Finn")Orchard (1997:151). is one of a trio of brothers along with Völundr and Egil. In the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''Völundarkviða'', Slagfiðr is attested as the seven-year husband of the valkyrie Hlaðguðr svanhvít In Norse mythology, Hlaðguðr svanhvít (Old Norse ''Hlaðguðr'' " swan-white"Simek (2007:151).) is a valkyrie. Hlaðguðr svanhvít is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''Völundarkviða'' as the sister of the valkyrie Hervör alvitr (both d .... Notes References * Orchard, Andy (1997). ''Dictionary of Norse Myth and Legend''. Cassell. {{DEFAULTSORT:Slagfidr Characters in Norse mythology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agilaz
Egil is a legendary hero of the ''Völundarkviða'' and the '' Thidreks saga''. The name is from Proto-Germanic *Agilaz,https://web.archive.org/web/20110225031159/http://www.sofi.se/servlet/GetDoc?meta_id=1472 (archived link, 25 February 2011) and the same legend is reflected in Old English Ægil of the Franks Casket and Alamannic Aigil of the Pforzen buckle. The Proto-Germanic form of the legend may only be guessed at, but it appears likely that Egil was a renowned archer who defended a keep together with his wife Aliruna, against numerous attackers. The testimony of the Pforzen buckle is uncertain beyond naming ''Aigil'' and ''Ailrun'', possibly adding that they fought a battle at the Ilz river. The Franks Casket shows the scene of Aegil and his wife enclosed in the keep, with Aegil shooting arrows against attacking troops. ''Völundarkviða'' In the ''Völundarkviða'', Egil is a son of a Finn king, his elder brother being Slagfiðr, his younger one Völund. The three broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saami People
The Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers' Institute (SAAMI, pronounced "Sammy") is an association of American manufacturers of firearms, ammunition, and components. SAAMI is an accredited standards developer that publishes several American National Standards that provide safety, reliability, and interchangeability standards for commercial manufacturers of firearms, ammunition, and components. In addition, SAAMI publishes information on the safe and responsible transportation, storage, and use of those products. History The origins of SAAMI date back to World War I and the Society of American Manufacturers of Small Arms and Ammunition (SAMSAA). In 1913, the US War Department encouraged the firearms and ammunition industry to establish an organization to share new technology and establish common standards for small arms and ammunition. SAMSAA was officially formed in 1918, however became inactive by the early 1920s. By the mid-1920s the United States was still suffering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
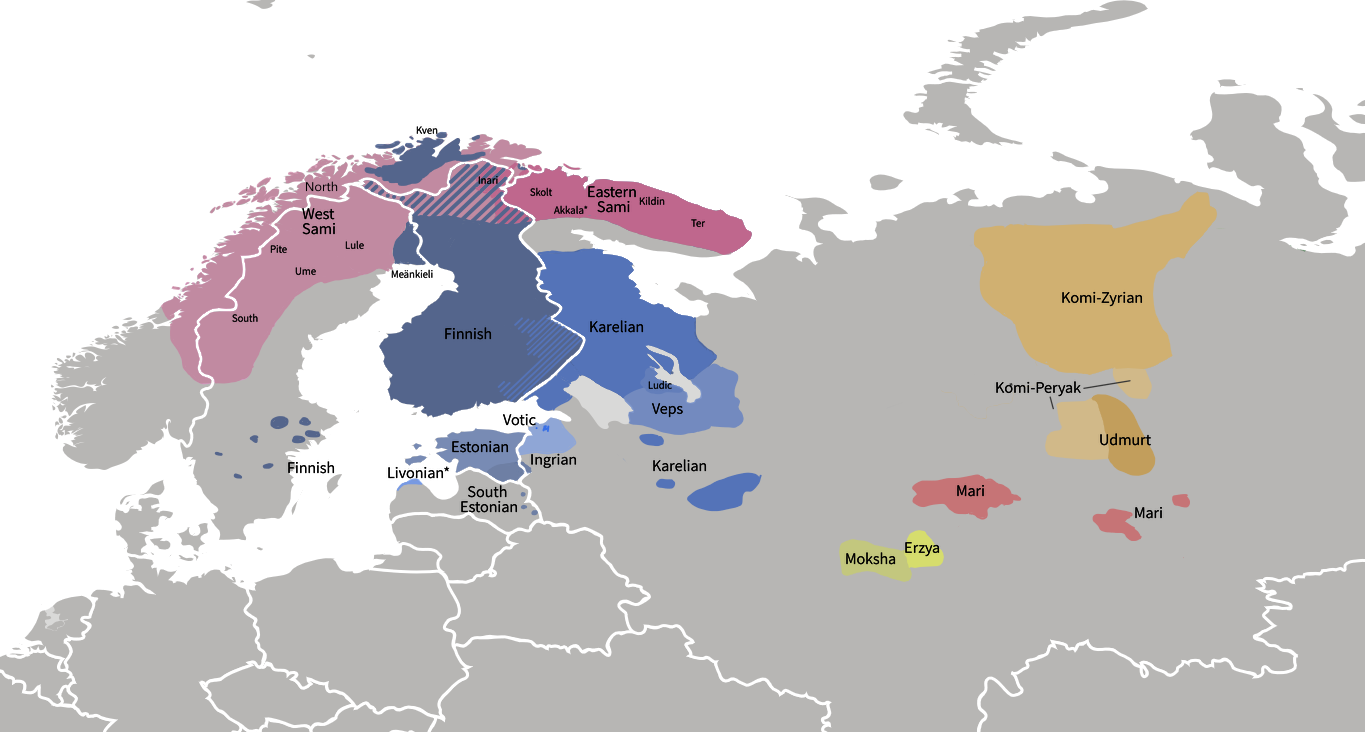
Finnic Peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns (or more precisely the Suomi, 6 million), the Estonians (1 million), the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000). The scope of the name "Finn" and "Finnic" varies by country. Today, Finnish and Estonian scholars restrict the term "Finnic" to the Baltic Finns, who include the Western Finns of Finland and their closest relatives but not the Sami. In Russia, however, where the Eastern Finns live, the word continues to be used in the broad sense, and sometimes implies the Volga Finns who have their own national republics. Three groups of people are covered by the names "Finn" and "Finnic" in the broad se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardre Image Stones
The Ardre image stones are a collection of ten rune and image stones, dated to the 8th to 11th centuries, that were discovered at Ardre Church, in Ardre, Gotland, Sweden. The principal edition is by Sune Lindqvist. Description The Ardre image stones were re-used as paving under the wooden floors of the local church in the Ardre parish of Gotland. Before the historical significance of rune and image stones was understood or appreciated, they were often used as materials in the construction of roads, bridges, and buildings. The image stones were re-discovered when the church was being restored around 1900. The stones are now preserved in the Swedish Museum of National Antiquities in Stockholm. Ardre VIII The largest and most noted of the stones is the Ardre VIII stone, dated to the 8th or 9th century, depicts scenes from Norse mythology, notably the Lay of Weyland the smith, Thor fishing for Jörmungandr, the punishment of Loki for the death of Baldr, and Odin riding to Valhall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Völund On Ardre 01
In Germanic mythology, Wayland the Smith ( ang, Wēland; , ; Old Frisian: Wela(n)du; german: Wieland der Schmied; goh, Wiolant; ''Galans'' (''Galant'') in Old French; gem-x-proto, Wēlandaz, italic=no from ', lit. "crafting one") is a master blacksmith originating in Germanic heroic legend, described by Jessie Weston as "the weird and malicious craftsman, Weyland".Weston, J. (1929). 'Legendary Cycles of the Middle Age', in Tanner, J.R. (ed.), ''The Cambridge Medieval History'' Vol. VI, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, p. 841f. Wayland's story is most clearly told in the Old Norse sources ''Völundarkviða'' (a poem in the ''Poetic Edda'') and ''Þiðreks saga''. In them, Wayland is a smith who is enslaved by a king. Wayland takes revenge by killing the king's sons and then escapes by crafting a winged cloak and flying away. A number of other visual and textual sources clearly allude to similar stories, most prominently the Old English poem ''Deor'' and the Franks C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland. Administratively, East Frisia consists of the districts Aurich, Leer and Wittmund and the city of Emden. It has a population of approximately 469,000 people and an area of . There is a chain of islands off the coast, called the East Frisian Islands (''Ostfriesische Inseln''). From west to east, these islands are: Borkum, Juist, Norderney, Baltrum, Langeoog and Spiekeroog. History The geographical region of East Frisia was inhabited in Paleolithic times by reindeer hunters of the Hamburg culture. Later there were Mesolithic and Neolithic settlements of various cultures. The period after prehistory can only be reconstructed from archaeological evidence. Access to the early history of East Fris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schweindorf
Schweindorf is a municipality in the district of Wittmund, in Lower Saxony, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Towns and villages in East Frisia Wittmund (district) {{Wittmund-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; ''solidi'') or nomisma ( grc-gre, νόμισμα, ''nómisma'', 'coin') was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Late Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. Constantine I, Constantine introduced the coin, and its weight of about 4.5 grams remained relatively constant for seven centuries. In the Byzantine Empire, the solidus or nomisma remained a highly pure gold coin until the 11th century, when several Byzantine Empire, Byzantine list of Byzantine emperors, emperors began to strike the coin with less and less gold. The nomisma was finally abolished by Alexius I in 1092, who replaced it with the hyperpyron, which also came to be known as a "bezant". The Byzantine solidus also inspired the originally slightly less pure Dinar (coin), dinar issued by the Muslim Caliphate. In Western Europe, the solidus was the main gold coin of commerce from late Roman times to Pepin the Short's Carolingian Renaissance#Carolingian currency, currency reform, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





du.jpg)

