|
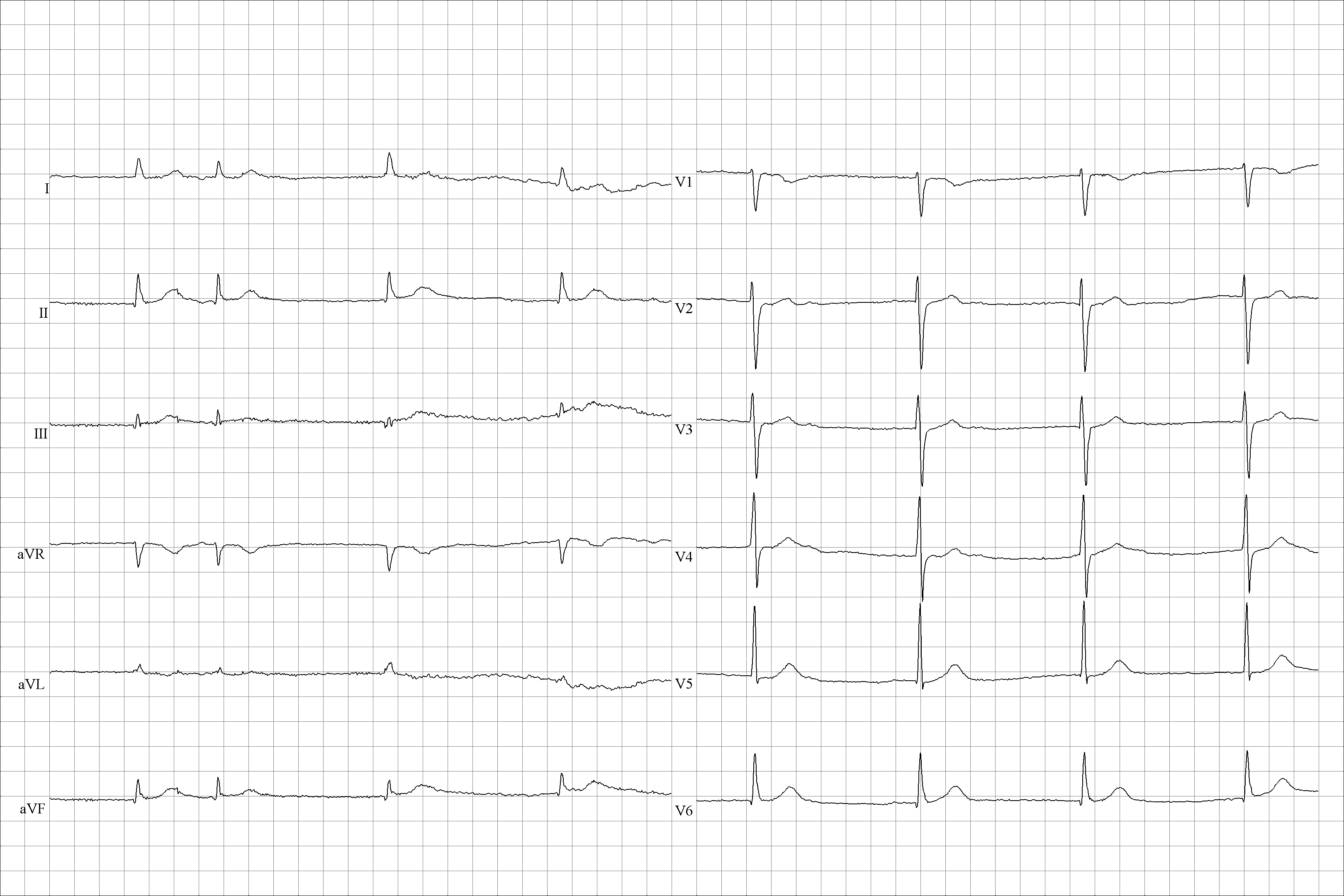
Wandering Pacemaker
Wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP) is an atrial rhythm where the pacemaking activity of the heart originates from different locations within the atria. This is different from normal pacemaking activity, where the sinoatrial node (SA node) is responsible for each heartbeat and keeps a steady rate and rhythm. Causes of wandering atrial pacemaker are unclear, but there may be factors leading to its development. It is often seen in the young, the old, and in athletes, and rarely causes symptoms or requires treatment. Diagnosis of wandering atrial pacemaker is made by an ECG. Pathophysiology The SA node is considered the primary pacemaker of the heart. In wandering atrial pacemaker, there are other locations within the atria besides the SA node that are responsible for each heartbeat. This is unusual because the SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers are the structures that have pacemaking capability. The atrial and ventricular muscle tissue do not have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier Science Direct
ScienceDirect is a website which provides access to a large bibliographic database of scientific and medical publications of the Dutch publisher Elsevier. It hosts over 18 million pieces of content from more than 4,000 academic journals and 30,000 e-books of this publisher. The access to the full-text requires subscription, while the bibliographic metadata is free to read. ScienceDirect is operated by Elsevier. It was launched in March 1997. Usage The journals are grouped into four main sections: ''Physical Sciences and Engineering'', ''Life Sciences'', ''Health Sciences'', and ''Social Sciences and Humanities''. Article abstracts are freely available, and access to their full texts (in PDF and, for newer publications, also HTML) generally requires a subscription or pay-per-view purchase unless the content is freely available in open access. Subscriptions to the overall offering hosted on ScienceDirect, rather than to specific titles it carries, are usually acquired through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Multifocal (or multiform) atrial tachycardia (MAT) is an cardiac arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm, specifically a type of supraventricular tachycardia, that is particularly common in older people and is associated with exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Normally, the heart rate is controlled by a cluster of cells called the sinoatrial node (SA node). When a number of different clusters of cells outside the SA node take over control of the heart rate, and the rate exceeds 100 beats per minute, this is called multifocal atrial tachycardia (if the heart rate is ≤100, this is technically not a tachycardia and it is then termed multifocal atrial rhythm). "Multiform" refers to the observation of variable P wave (electrocardiography), P wave shapes, while "multifocal" refers to the underlying cause. Although these terms are used interchangeably, some sources prefer "multiform" since it does not presume any underlying mechanism. Causes MAT usually arises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PR Interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization); it is normally between 120 and 200 ms in duration. The PR interval is sometimes termed the PQ interval. Interpretation Variations in the PQ interval can be associated with certain medical conditions: * Duration ** A long PR interval (of over 200 ms) indicates a slowing of conduction between the atria and ventricles, usually due to slow conduction through the atrioventricular node (AV node). This is known as first degree heart block. Prolongation can be associated with fibrosis of the AV node, high vagal tone, medications that slow the AV node such as beta-blockers, hypokalemia, acute rheumatic fever, or carditis associated with Lyme disease. ** A short PR interval (of less than 120ms) may be associated with a Pre-excitation syndromes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is characterised by the presence of correctly oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG). Sinus rhythm is necessary, but not sufficient, for normal electrical activity within the heart. The term normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is sometimes used to denote a specific type of sinus rhythm where all other measurements on the ECG also fall within designated normal limits, giving rise to the characteristic appearance of the ECG when the electrical conduction system of the heart is functioning normally; however, other sinus rhythms can be entirely normal in particular patient groups and clinical contexts, so the term is sometimes considered a misnomer and its use is sometimes discouraged. Other types of sinus rhythm that can be normal include sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, and sinus arrhythmia. Sinus rhythms may be present together with various other cardiac arrhythmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Wave (electrocardiography)
The P wave on the ECG represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Physiology The P wave is a summation wave generated by the depolarization front as it transits the atria. Normally the right atrium depolarizes slightly earlier than left atrium since the depolarization wave originates in the sinoatrial node, in the high right atrium and then travels to and through the left atrium. The depolarization front is carried through the atria along semi-specialized conduction pathways including Bachmann's bundle resulting in uniform shaped waves. Depolarization originating elsewhere in the atria (atrial ectopics) result in P waves with a different morphology from normal. Pathology Peaked P waves (> 0.25 mV) suggest right atrial enlargement, cor pulmonale, (''P pulmonale'' rhythm), but have a low predictive value (~20%). A P wave with increased amplitude can indicate hypokalemia. It can also indicate right atrial enlargement. A P wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rhythm
The cardiac conduction system (CCS) (also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through the body's circulatory system. The pacemaking signal travels through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node, along the bundle of His, and through the bundle branches to Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles. The Purkinje fibers transmit the signals more rapidly to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The conduction system consists of specialized heart muscle cells, situated within the myocardium. There is a skeleton of fibrous tissue that surrounds the conduction system which can be seen on an ECG. Dysfunction of the conduction system can cause irregular heart rhythms including rhythms that are too fast or too slow. Structure Electrical signals arising in the SA node (located in the right atrium) stimulate the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Family Physician
''American Family Physician'' (''AFP'') is the editorially independent, peer-reviewed and evidence-based medical journal published by the American Academy of Family Physicians. Published continuously since 1950, each issue delivers concise, easy-to-read clinical review articles for physicians and other health care professionals. The journal is published monthly in print, online, and app formats. It is mailed to an audience of more than 180,000 family medicine and other primary care physicians and health care professionals and viewed online by more than 2.5 million unique visitors monthly. The predecessor to ''American Family Physician'' was the journal ''GP'', an acronym for "General Practitioner". ''GP'' was first published in 1950 by the American Academy of General Practice, which was the predecessor organization to the American Academy of Family Physicians. See also *''JAMA'' *''The New England Journal of Medicine'' *''The BMJ'' *''Annals of Internal Medicine'' *''Canadian Fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxin Toxicity
Digoxin toxicity, also known as digoxin poisoning, is a type of poisoning that occurs in people who take too much of the medication digoxin or eat plants such as foxglove that contain a similar substance. Symptoms are typically vague. They may include vomiting, loss of appetite, confusion, blurred vision, changes in color perception, and decreased energy. Potential complications include an irregular heartbeat, which can be either too fast or too slow. Toxicity may occur over a short period of time following an overdose or gradually during long-term treatment. Risk factors include low potassium, low magnesium, and high calcium. Digoxin is a medication used for heart failure or atrial fibrillation. An electrocardiogram is a routine part of diagnosis. Blood levels are only useful more than six hours following the last dose. Activated charcoal may be used if it can be given within two hours of the person taking the medication. Atropine may be used if the heart rate is slow whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Node Dysfunction
Sinus node dysfunction (SND), also known as sick sinus syndrome (SSS), is a group of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) usually caused by a malfunction of the sinus node, the heart's primary pacemaker. Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome is a variant of sick sinus syndrome in which the arrhythmia alternates between fast and slow heart rates. Signs and symptoms Often sinus node dysfunction produces no symptoms, especially early in the disease course. Signs and symptoms usually appear in more advanced disease and more than 50% of patients will present with syncope or transient near-fainting spells as well as bradycardias that are accompanied by rapid heart rhythms, referred to as tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome Other presenting signs or symptoms can include confusion, fatigue, palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, and nausea. Patients can also present with symptoms of congestive heart failure, stroke or transient ischemic attacks due to the abnormal rhythm. Compli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |