|
Wallenberg's Syndrome
Lateral medullary syndrome is a neurological disorder causing a range of symptoms due to ischemia in the lateral part of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The ischemia is a result of a blockage most commonly in the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Lateral medullary syndrome is also called Wallenberg's syndrome, posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) syndrome and vertebral artery syndrome. Signs and symptoms This syndrome is characterized by sensory deficits that affect the trunk and extremities contralaterally (opposite to the lesion), and sensory deficits of the face and cranial nerves ipsilaterally (same side as the lesion). Specifically a loss of pain and temperature sensation if the lateral spinothalamic tract is involved. The cross body finding is the chief symptom from which a diagnosis can be made. Patients often have difficulty walking or maintaining balance (ataxia), or difference in temperature of an object based on which side of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
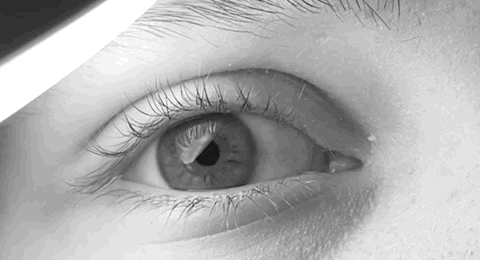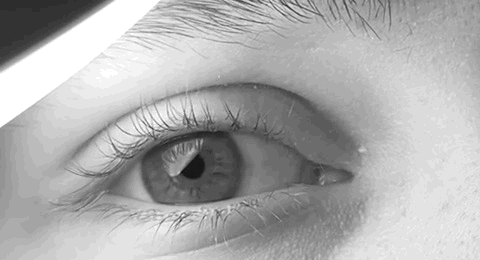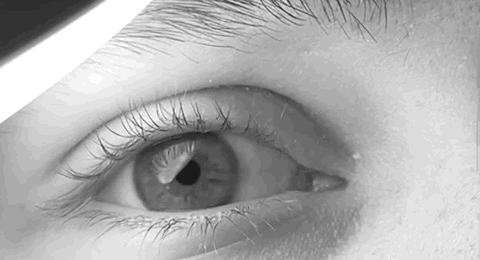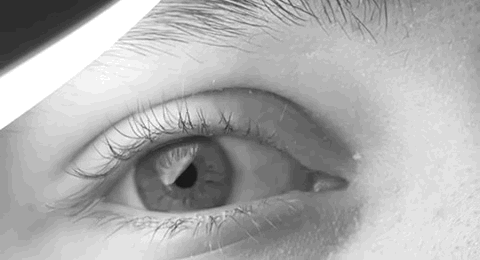
Horner's Syndrome
Horner's syndrome, also known as oculosympathetic paresis, is a combination of symptoms that arises when a group of nerves known as the sympathetic trunk is damaged. The signs and symptoms occur on the same side (ipsilateral) as it is a lesion of the sympathetic trunk. It is characterized by miosis (a constricted pupil), partial ptosis (a weak, droopy eyelid), apparent anhidrosis (decreased sweating), with apparent enophthalmos (inset eyeball). The nerves of the sympathetic trunk arise from the spinal cord in the chest, and from there ascend to the neck and face. The nerves are part of the sympathetic nervous system, a division of the autonomic (or involuntary) nervous system. Once the syndrome has been recognized, medical imaging and response to particular eye drops may be required to identify the location of the problem and the underlying cause. Signs and symptoms Signs that are found in people with Horner's syndrome on the affected side of the face include the following: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle, a thick rope-like strand situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle and the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with the cerebellum, and comprises the juxtarestiform body and restiform body. Important fibers running through the inferior cerebellar peduncle include the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and axons from the inferior olivary nucleus, among others. Function The inferior cerebellar peduncle carries many types of input and output fibers that are mainly concerned with integrating proprioceptive sensory input with motor vestibular functions such as balance and posture maintenance. It consists of the following fiber tracts entering cerebellum: * Posterior spinocerebellar tract: unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower part of trunk and lower limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologic Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. The most common disorders that result in vertigo are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière's disease, and labyrinthitis. Less common causes include stroke, brain tumors, brain injury, multiple sclerosis, migraines, trauma, and uneven pressures between the middle ears. Physiologic vertigo may occur following being exposed to motion for a prolonged period such as when on a ship or simply following spinning with the eyes closed. Other causes may include toxin exposures such as to carbon monoxide, alcohol, or aspirin. Vertigo typically indicates a problem in a part of the vestibular system. Other causes of dizziness include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to Alcoholic drink, alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia nervosa, bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular System
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. The brain uses information from the vestibular system in the head and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Nuclei
The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem. In Terminologia Anatomica they are grouped in both the pons and the medulla in the brainstem. Structure Path The fibers of the vestibular nerve enter the medulla oblongata on the medial side of those of the cochlear, and pass between the inferior peduncle and the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. They then divide into ascending and descending fibers. The latter end by arborizing around the cells of the medial nucleus, which is situated in the area acustica of the rhomboid fossa. The ascending fibers either end in the same manner or in the lateral nucleus, which is situated lateral to the area acustica and farther from the ventricular floor. Some of the axons of the cells of the lateral nucleus, and possibly also of the medial nucleus, are continued upward through the inferior peduncle to the roof nuclei of the opposite side of the cerebellum, to which also other fibers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, and in athletes. In some people, bradycardia below 60 BPM may be associated with fatigue, weakness, dizziness, sweating, and fainting. The term "relative bradycardia" is used to refer to a heart rate slower than an individual's typical resting heart rate. Athletes may have athletic heart syndrome, which includes bradycardia as part of the cardiovascular adaptations to training and participation. The word "bradycardia" is from the Greek βραδύς ''bradys'' "slow", and καρδία ''kardia'' "heart". Classification Sinus Atrial bradycardias are divided into three types. The first, respiratory sinus arrhythmia, is usually found in young and healthy adults. Heart rate increases during inhalation and decreases during exhalation. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tegmental Tract
The central tegmental tractKamali A, Kramer LA, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the somatosensory system in the human brainstem: initial findings using high isotropic spatial resolution at 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2009 19:1480-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1305-x. is a structure in the midbrain and pons. * The central tegmental tract includes ''ascending'' axonal fibers that arise from the rostral nucleus solitarius and terminate in the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) of thalamus. Information from the thalamus will go to cortical taste area, namely the insula and frontal operculum. * It also contains ''descending'' axonal fibers from the parvocellular red nucleus. The descending axons will project to the inferior olivary nucleus. This latter pathway (the rubro-olivary tract) will be used to connect the contralateral cerebellum. Lesion of the tract can cause palatal myoclonus Palatal myoclonus is a rare condition in which there are rhythmic jerky movements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatal Myoclonus
Palatal myoclonus is a rare condition in which there are rhythmic jerky movements or a rapid spasm of the palatal (roof of the mouth) muscles. Chronic clonus is often due to lesions of the central tegmental tract (which connects the red nucleus to the ipsilateral inferior olivary nucleus). When associated with eye movements, it is known as ''oculopalatal myoclonus''. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of Palatal Myoclonus include: - A rhythmic clicking sound in the ear due to the opening and closing of the Eustachian tube. - Rhythmic, jerky movements in the face, eyeballs, tongue, jaw, vocal cord In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speec ... or extremities (mostly hands). Diagnosis Classifications physiologic, essential, epileptic, and symptomatic Treatment Drugs Drug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |