|
Wada Test
The Wada test, also known as the intracarotid sodium amobarbital procedure (ISAP) or Wada-Milner Test, establishes cerebral language and memory representation of each hemisphere. Method Medical professionals conduct the test with the patient awake. A barbiturate, usually sodium amobarbital, is introduced into one of the internal carotid arteries via a cannula or intra-arterial catheter from the femoral artery. The drug is injected into one hemisphere at a time through the right or left internal carotid artery. If the right carotid is injected, the right side of the brain is inhibited and cannot communicate with the left side. The effect shuts down any language and/or memory function in that hemisphere in order to evaluate the other hemisphere. An EEG recording at the same time confirms that the injected side of the brain is inactive as a neurologist performs a neurological examination. The neurologist engages the patient in a series of language and memory related tests. They ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery , an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the brain
{{SIA ...
Carotid artery may refer to: * Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery * External carotid artery, an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the face, scalp, skull, neck and meninges * Internal carotid artery The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disinhibition
Disinhibition, also referred to as behavioral disinhibition, is medically recognized as an orientation towards immediate gratification, leading to impulsive behaviour driven by current thoughts, feelings, and external stimuli, without regard for past learning or consideration for future consequences. It is one of five pathological personality trait domains in certain psychiatric disorders. In psychology, it is defined as a lack of restraint manifested in disregard of social conventions, impulsivity, and poor risk assessment. Hypersexuality, hyperphagia, substance abuse, money mismanagement, frequent faux pas, and aggressive outbursts are indicative of disinhibited instinctual drives. Certain psychoactive substances that have effects on the limbic system of the brain may induce disinhibition. Clinical concept Disinhibition in psychology is defined as a lack of inhibitory control manifested in several ways, affecting motor, instinctual, emotional, cognitive, and perce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal Neurological Institute
The McGill University Health Centre (MUHC; ) is one of two major healthcare networks in the city of Montreal, Quebec. It is affiliated with McGill University and one of the largest medical complexes in Montreal. It is the largest hospital system in Canada by bed capacity. The majority of its funding comes from Quebec taxpayers through the Ministry of Health and Social Services. The centre provides inpatient and ambulatory care. History The centre announced that it would consolidate its services in a single facility in 2007; it was a long and troubled process. The project was budgeted at around $700 million but cost around $1.3 billion; it was meant to take only three years but took much longer. The project was completed in 2015. The facility replaced the existing facilities of the Royal Victoria Hospital (on April 26, 2015), the Montreal Children's Hospital (on May 24, 2015), and the Montreal Chest Institute (on June 14, 2015). It did not replace the Montreal General Hospital, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is the principal language of the Japonic languages, Japonic language family spoken by the Japanese people. It has around 123 million speakers, primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language, and within the Japanese diaspora worldwide. The Japonic family also includes the Ryukyuan languages and the variously classified Hachijō language. There have been many Classification of the Japonic languages, attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as Ainu languages, Ainu, Austronesian languages, Austronesian, Koreanic languages, Koreanic, and the now discredited Altaic languages, Altaic, but none of these proposals have gained any widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), extensive waves of Sino-Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the specialty (medicine), medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the Human brain, brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system, and cerebrovascular system. Neurosurgery as a medical specialty also includes non-surgical management of some neurological conditions. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United Kingdom In the United Kingdom, students must gain entry into medical school. The MBBS qualification (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) takes four to six years depending on the student's route. The newly qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a Public university, public research university with campuses near University of British Columbia Vancouver, Vancouver and University of British Columbia Okanagan, Kelowna, in British Columbia, Canada. With an annual research budget of $893million, UBC funds 9,992 projects annually in various fields of study within the industrial sector, as well as governmental and non-governmental organizations. The Vancouver campus is situated on the University of British Columbia Vancouver, Point Grey campus lands, an unincorporated area next to the City of Vancouver and the University Endowment Lands.Municipalities Enabling and Validating Act (No. 3)', S.B.C. 2001, c. 44. The university is located west of Downtown Vancouver. UBC is also home to TRIUMF, Canada's national Particle physics, particle and nuclear physics laboratory, which boasts the world's largest cyclotron. In addition to the Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies and the Stuart B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juhn Atsushi Wada
Juhn Atsushi Wada (March 28, 1924 – April 22, 2023) was a Japanese–Canadian neurologist known for research into epilepsy and human brain asymmetry, including his description of the Wada test for cerebral hemispheric dominance of language function. The Wada Test remains the gold standard for establishing cerebral dominance and is conducted worldwide prior to epilepsy surgery. Wada was a professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Neurosciences at the UBC Faculty of Medicine. He has edited 11 books and published over 300 papers on human brain asymmetry, the neurobiology of epilepsy, and kindling. Biography Juhn Wada studied medicine at Hokkaido University, qualifying as a Doctor of Medicine in 1946 and qualifying as a Doctor of Medical Science in 1951. He was an assistant professor of neurology and psychiatry at Hokkaido University after which he worked at the University of Minnesota and the Montreal Neurological Institute before settling at the University of British Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar, pulse oximetry, functional neuroimaging, sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics, rehabilitation, neonatal research, brain computer interface, urology (bladder contraction), and neurology (neurovascular coupling). There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical, food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry, combustion propagation. Theory Near-infrared spectroscopy is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. Overtones and combinations exhibit lower intensity compared to the fundamental, as a result, the molar absorptivity in the near-IR region is typically quite small. (NIR absorption bands are typically 10–100 times weaker than the corresponding fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
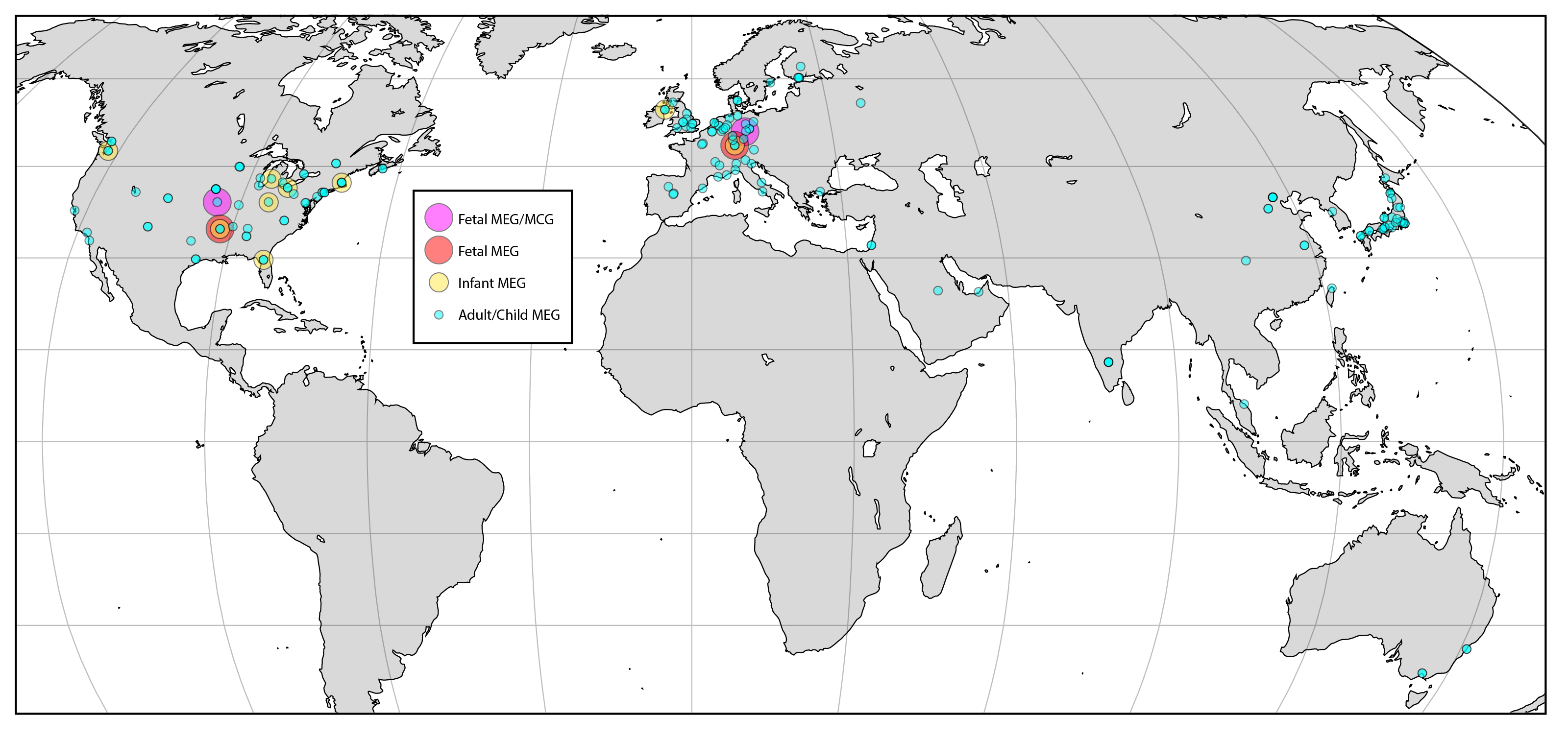
Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electric current, electrical currents occurring naturally in the human brain, brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen (physicist), David Cohen in 1968, before the availabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow ( hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. With time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance it is no longer necessary to use a contrast. The word itself comes from the Greek words ἀνγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |