|
Vulture Bee
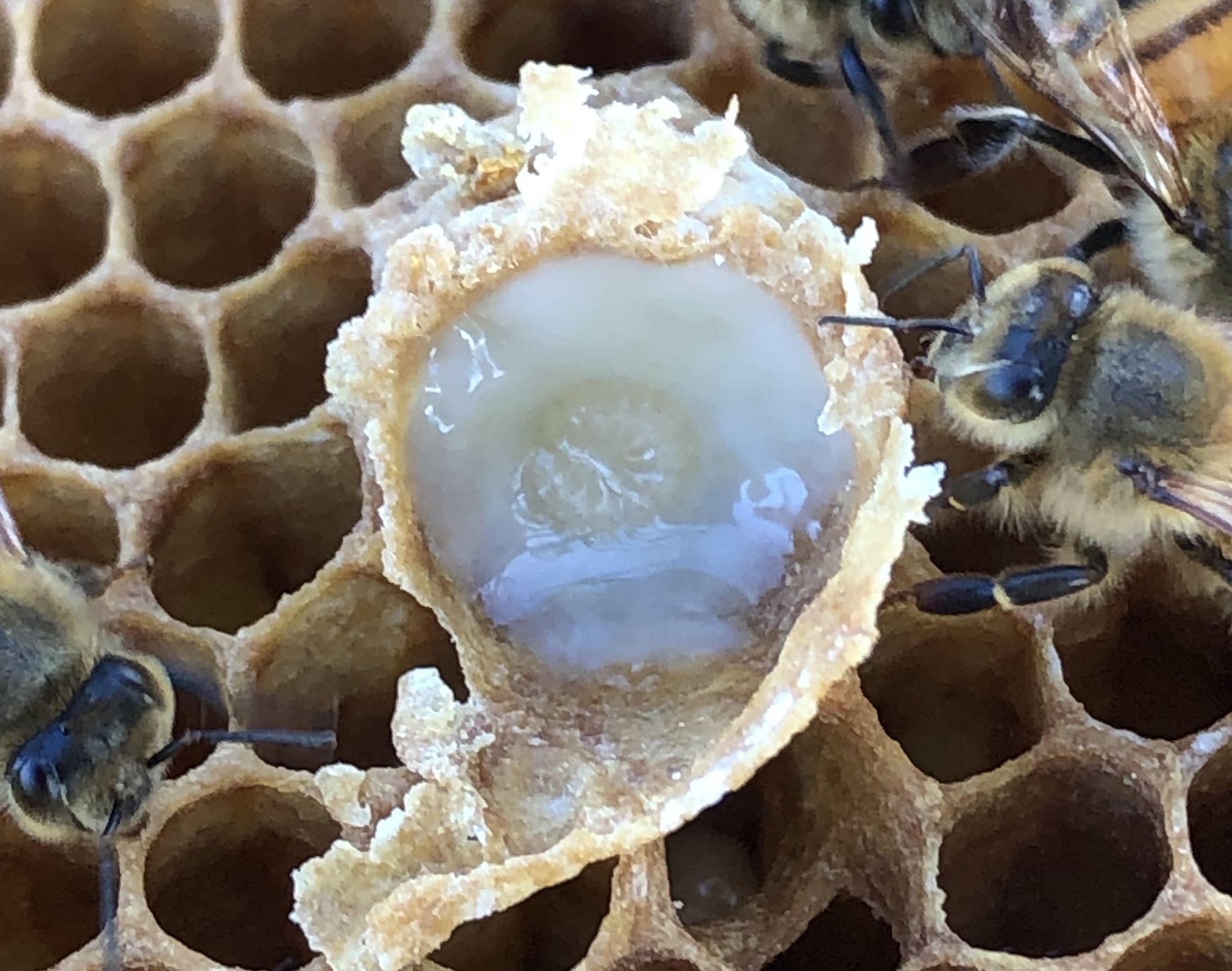
Vulture bees, also known as carrion bees, are a small group of three closely related South American stingless bee species in the genus ''Trigona'' which feed on rotting meat. Vulture bees produce a honey-like substance which is not derived from nectar, but rather from protein-rich secretions of the bees' hypopharyngeal glands. These secretions are likely derived from the bees' diet, which consists of carrion eaten outside the nest.Laura L. Figueroa, Jessica J. Maccaro, Erin Krichilsky, Douglas Yanega, Quinn S. McFrederickWhy Did the Bee Eat the Chicken? Symbiont Gain, Loss, and Retention in the Vulture Bee Microbiome In: ASM mBio, vol. 12, no. 6, e02317-12, 23 November 2021, doi:10.1128/mBio.02317-21 This unusual behavior was only discovered in 1982, nearly two centuries after the bees were first classified.Roubik, D.W. (1982)"Obligate Necrophagy in a Social Bee" ''Science'' 217 (4564): 1059–60. Taxonomy The three species in this group are: * ''Trigona crassipes'' (Fabricius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigona Crassipes
''Trigona'' is one of the largest genera of stingless bees, comprising about 32 species, exclusively occurring in the New World, and formerly including many more subgenera than the present assemblage; many of these former subgenera have been elevated to generic status.Michener, C.D. (2000). The Bees of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press Range ''Trigona'' species occur throughout the Neotropical region, including South and Central America, the Mexican lowlands, and the Caribbean islands. They can occur in forests, savannas, and man made environments. ''Trigona'' bees are active all year round, although they are less active in cool environments. Nesting ''Trigona'' nests are constructed from wax they produce and plant resins they collect. They usually nest in tree cavities and underground. Vulture bees Vulture bees comprise three ''Trigona'' species, and are the only bees known to be scavengers. These bees collect and feed on dead animal flesh. Communication Some spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigona Necrophaga
''Trigona'' is one of the largest genera of stingless bees, comprising about 32 species, exclusively occurring in the New World, and formerly including many more subgenera than the present assemblage; many of these former subgenera have been elevated to generic status.Michener, C.D. (2000). The Bees of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press Range ''Trigona'' species occur throughout the Neotropical region, including South and Central America, the Mexican lowlands, and the Caribbean islands. They can occur in forests, savannas, and man made environments. ''Trigona'' bees are active all year round, although they are less active in cool environments. Nesting ''Trigona'' nests are constructed from wax they produce and plant resins they collect. They usually nest in tree cavities and underground. Vulture bees Vulture bees comprise three ''Trigona'' species, and are the only bees known to be scavengers. These bees collect and feed on dead animal flesh. Communication Some spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigona Hypogea
''Trigona hypogea'' is a species of stingless bee from the Neotropics; it is unusual in that it is one of only three known species of bee that exclusively uses carrion as a protein source, rather than pollen,Roubik, D.W. (1982)"Obligate Necrophagy in a Social Bee" ''Science'' 217 (4564): 1059–60. earning it the nickname "vulture bee". These bees consume flesh, carry it internally back to the colony, and regurgitate it along with other secretions into storage pots similar to those used by the colonies to store honey; the larvae are fed on this substance, while the adult bees consume the honey. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q5601325 hypogea A hypogeum or hypogaeum (plural hypogea or hypogaea, pronounced ; literally meaning "underground", from Greek language, Greek ''hypo'' (under) and ''ghê'' (earth)) is an underground temple or tomb. Hypogea will often contain niche (archite ... Insects described in 1902 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stingless Bee
Stingless bees, sometimes called stingless honey bees or simply meliponines, are a large group of bees (about 550 described species), comprising the tribe Meliponini (or subtribe Meliponina according to other authors). They belong in the family Apidae, and are closely related to common honey bees, carpenter bees, orchid bees, and bumblebees. Meliponines have stingers, but they are highly reduced and cannot be used for defense, though these bees exhibit other defensive behaviors and mechanisms. Meliponines are not the only type of bee incapable of stinging: all male bees and many female bees of several other families, such as Andrenidae, also cannot sting. Some stingless bees have powerful mandibles and can inflict painful bites. Geographical distribution Stingless bees can be found in most tropical or subtropical regions of the world, such as Australia, Africa, Southeast Asia, and tropical America.Michener, C D. ''The bees of the World''. Johns Hopkins University Press, 972 pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigona (genus)
''Trigona'' is one of the largest genera of stingless bees, comprising about 32 species, exclusively occurring in the New World, and formerly including many more subgenera than the present assemblage; many of these former subgenera have been elevated to generic status.Michener, C.D. (2000). The Bees of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press Range ''Trigona'' species occur throughout the Neotropical region, including South and Central America, the Mexican lowlands, and the Caribbean islands. They can occur in forests, savannas, and man made environments. ''Trigona'' bees are active all year round, although they are less active in cool environments. Nesting ''Trigona'' nests are constructed from wax they produce and plant resins they collect. They usually nest in tree cavities and underground. Vulture bees Vulture bees comprise three ''Trigona'' species, and are the only bees known to be scavengers. These bees collect and feed on dead animal flesh. Communication Some spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
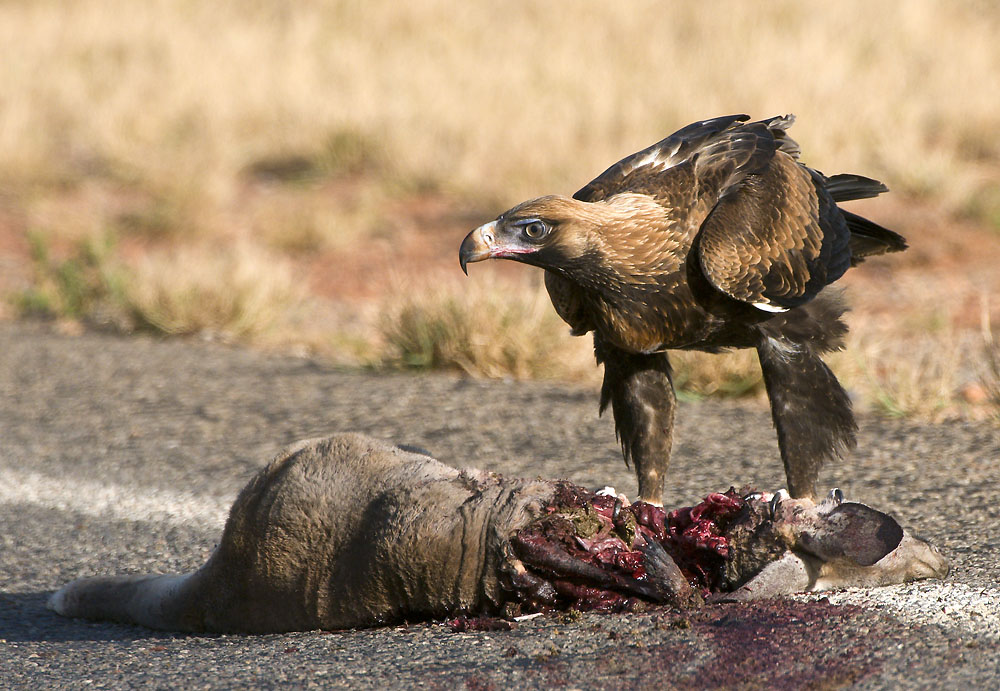
Carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh. Overview Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, condors, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia opossum, Tasmanian devils, coyotes and Komodo dragons. Many invertebrates, such as the carrion and burying beetles, as well as maggots of calliphorid flies (such as one of the most important species in '' Calliphora vomitoria'') and flesh-flies, also eat carrion, playing an important role in recycling nitrogen and carbon in animal remains. Carrion begins to decay at the moment of the animal's death, and it will increasingly attract insects and breed bacteria. Not long after the animal has died, its body will begin to exude a foul odor caused by the presence of bacteria and the emission of cadaverine and putrescine. Some plants and fungi smell like decomposing carrion and attract insects that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primarily floral nectar) or the secretions of other insects, like the honeydew of aphids. This refinement takes place both within individual bees, through regurgitation and enzymatic activity, as well as during storage in the hive, through water evaporation that concentrates the honey's sugars until it is thick and viscous. Honey bees stockpile honey in the hive. Within the hive is a structure made from wax called honeycomb. The honeycomb is made up of hundreds or thousands of hexagonal cells, into which the bees regurgitate honey for storage. Other honey-producing species of bee store the substance in different structures, such as the pots made of wax and resin used by the stingless bee. Honey for human consumption is collected from wild ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar plays a crucial role in the foraging economics and evolution of nectar-eating species; for example, nectar foraging behavior is largely responsible for the divergent evolution of the African honey bee, ''A. m. scutellata'' and the western honey bee. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of parasitoid wasps (e.g. the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
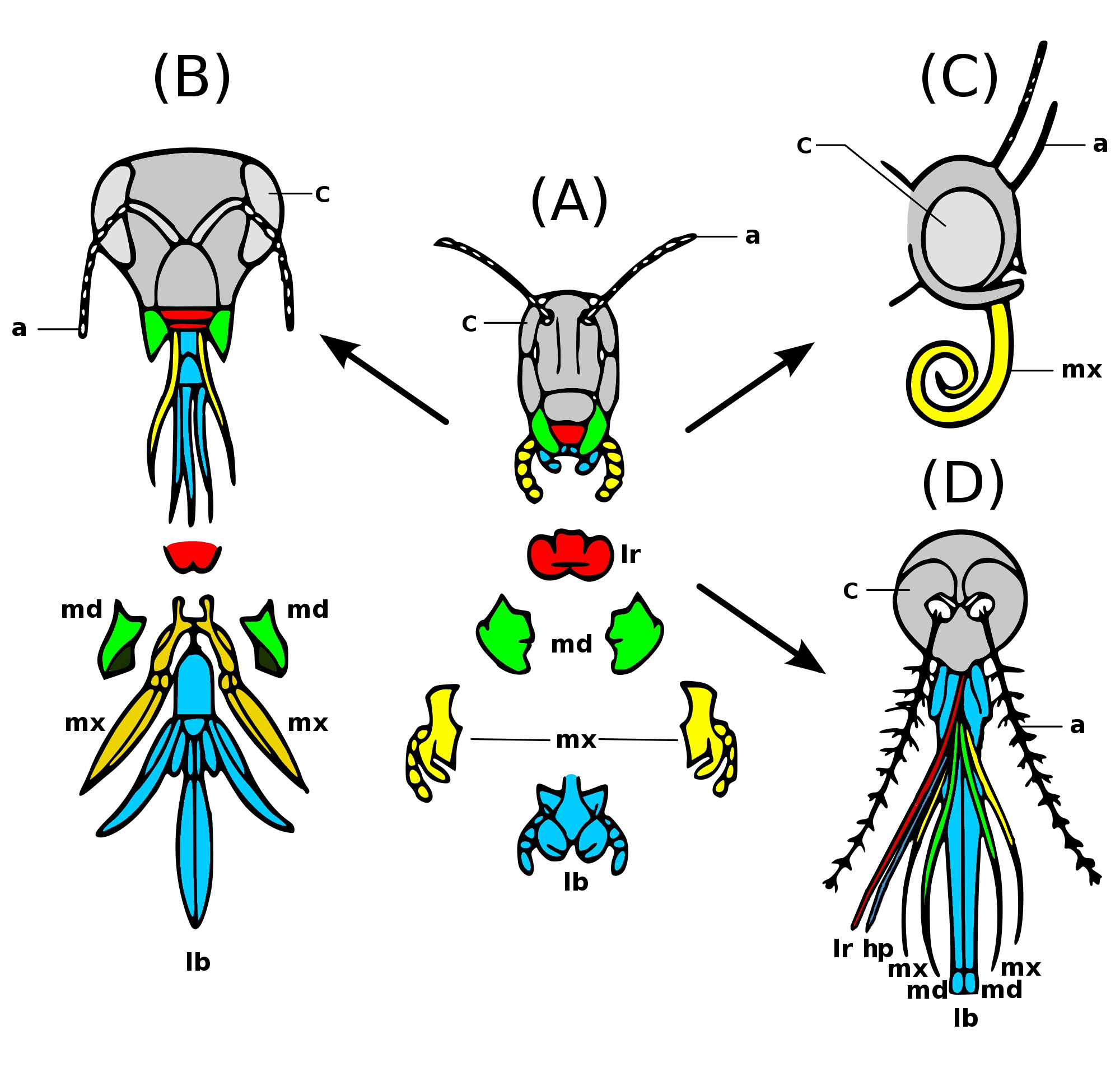
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times idependently. For example, mosquitoes and aphids (which are true bugs) both pierce and suck, however female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identical, they may not be homologous; their analogous functions and appearance might be the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeybees
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of perennial colonial nests from wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only eight surviving species of honey bee are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees. The best known honey bee is the western honey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is a honey bee secretion that is used in the nutrition of larvae and adult queens. It is secreted from the glands in the hypopharynx of nurse bees, and fed to all larvae in the colony, regardless of sex or caste.Graham, J. (ed.) (1992) ''The Hive and the Honey Bee'' (Revised Edition). Dadant & Sons. During the process of creating new queens, the workers construct special queen cells. The larvae in these cells are fed with copious amounts of royal jelly. This type of feeding triggers the development of queen morphology, including the fully developed ovaries needed to lay eggs. Royal jelly is sometimes used in alternative medicine under the category apitherapy. It is often sold as a dietary supplement for humans, but the European Food Safety Authority has concluded that current evidence does not support the claim that consuming royal jelly offers health benefits to humans. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration has taken legal action against companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop (anatomy)
A crop (sometimes also called a croup or a craw, ingluvies, or sublingual pouch) is a thin-walled expanded portion of the alimentary tract used for the storage of food prior to digestion. This anatomical structure is found in a wide variety of animals. It has been found in birds, and in invertebrate animals including gastropods (snails and slugs), earthworms, leeches, and insects. Insects Cropping is used by bees to temporarily store nectar of flowers. When bees "suck" nectar, it is stored in their crops. Other Hymenoptera also use crops to store liquid food. The crop in eusocial insects, such as ants, has specialized to be distensible, and this specialization enables important communication between colonial insects through trophallaxis. The crop can be found in the foregut of insects. Birds In a bird's digestive system, the crop is an expanded, muscular pouch near the gullet or throat. It is a part of the digestive tract, essentially an enlarged part of the esophagus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |