|
Vorombe
''Vorombe'' is one of three genera of elephant birds, an extinct family of large ratite birds endemic to Madagascar. Originally considered to be large '' Aepyornis'' specimens, it is now thought ''Vorombe'' are the largest and heaviest birds known to have existed. The genus was erected in 2018 after a detailed morphometric analysis. Taxonomy and naming ''Vorombe titan'' was first described by Charles William Andrews as ''Aepyornis titan'' in 1894, though it was later synonymized with the type species of ''Aepyornis'', ''A. maximus'', by American paleontologist Pierce Brodkorb in 1963. In 2018, James Hansford and Samuel Turvey, two researchers from the Zoological Society of London, found that it was sufficiently distinct from ''Aepyornis'' based on genetic and morphological evidence and allocated the species to a new genus, ''Vorombe''. They also recognized ''Aepyornis ingens'' as a synonym of ''Vorombe titan''. The study by Hansford and Turvey is the first taxonomic reassess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorombe Titan Tibiotarsus
''Vorombe'' is one of three genera of elephant birds, an extinct family of large ratite birds endemic to Madagascar. Originally considered to be large ''Aepyornis'' specimens, it is now thought ''Vorombe'' are the largest and heaviest birds known to have existed. The genus was erected in 2018 after a detailed morphometric analysis. Taxonomy and naming ''Vorombe titan'' was first described by Charles William Andrews as ''Aepyornis titan'' in 1894, though it was later synonymized with the type species of ''Aepyornis'', ''A. maximus'', by American paleontologist Pierce Brodkorb in 1963. In 2018, James Hansford and Samuel Turvey, two researchers from the Zoological Society of London, found that it was sufficiently distinct from ''Aepyornis'' based on genetic and morphological evidence and allocated the species to a new genus, ''Vorombe''. They also recognized ''Aepyornis ingens'' as a synonym of ''Vorombe titan''. The study by Hansford and Turvey is the first taxonomic reasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorombe Titan
''Vorombe'' is one of three genera of elephant birds, an extinct family of large ratite birds endemic to Madagascar. Originally considered to be large ''Aepyornis'' specimens, it is now thought ''Vorombe'' are the largest and heaviest birds known to have existed. The genus was erected in 2018 after a detailed morphometric analysis. Taxonomy and naming ''Vorombe titan'' was first described by Charles William Andrews as ''Aepyornis titan'' in 1894, though it was later synonymized with the type species of ''Aepyornis'', ''A. maximus'', by American paleontologist Pierce Brodkorb in 1963. In 2018, James Hansford and Samuel Turvey, two researchers from the Zoological Society of London, found that it was sufficiently distinct from ''Aepyornis'' based on genetic and morphological evidence and allocated the species to a new genus, ''Vorombe''. They also recognized ''Aepyornis ingens'' as a synonym of ''Vorombe titan''. The study by Hansford and Turvey is the first taxonomic reasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
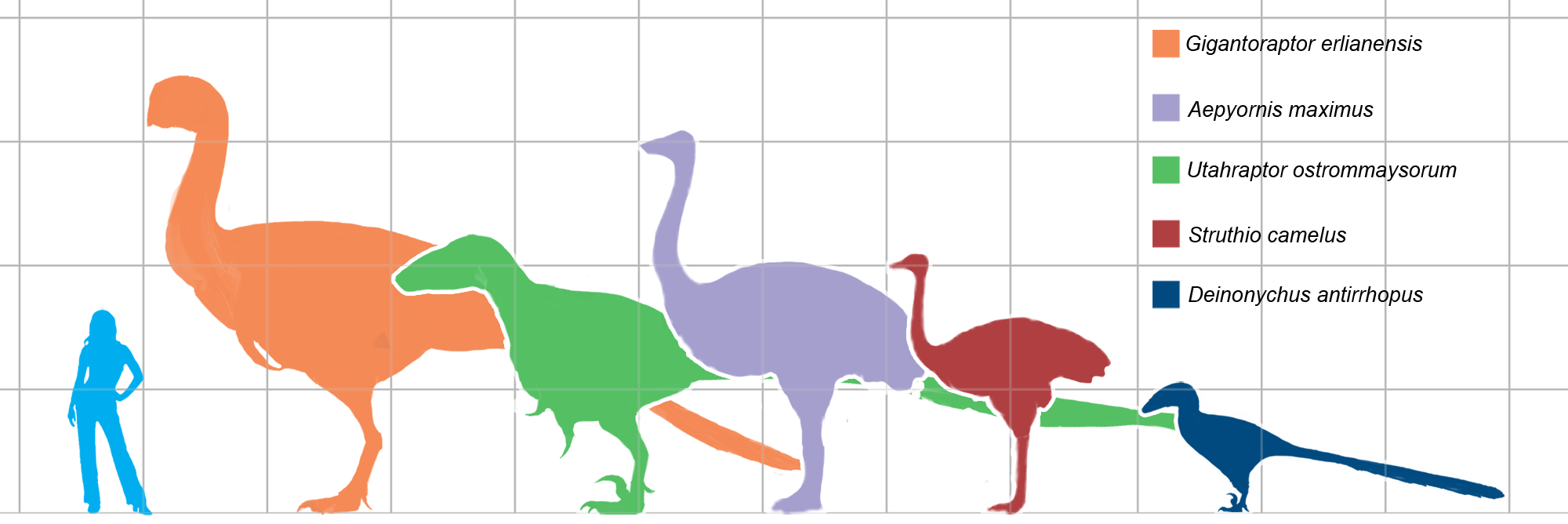
Elephant Bird
Elephant birds are members of the extinct ratite family Aepyornithidae, made up of flightless birds that once lived on the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct around 1000-1200 CE, probably as a result of human activity. Elephant birds comprised the genera '' Mullerornis'', '' Vorombe'' and '' Aepyornis''. While they were in close geographical proximity to the ostrich, their closest living relatives are kiwi (found only in New Zealand), suggesting that ratites did not diversify by vicariance during the breakup of Gondwana but instead evolved from ancestors that dispersed more recently by flying. In September 2018, scientists determined that ''Vorombe titan'' reached weights of and stood tall, making it the world's largest and heaviest bird, slightly larger than the much older '' Dromornis stirtoni''. Other members of the family were also very large, exhibiting the phenomenon of island gigantism. Description Elephant birds have been extinct since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aepyornis
''Aepyornis'' is a genus of aepyornithid, one of three genera of ratite birds endemic to Madagascar until their extinction sometime around 1000 CE. The species ''A. maximus'' weighed up to , and until recently was regarded as the largest known bird of all time. However, in 2018 the largest aepyornithid specimens, weighing up to , were moved to the related genus '' Vorombe''. Its closest living relative is the New Zealand kiwi. Taxonomy Brodkorb (1963) listed four species of ''Aepyornis'' as valid: ''A. hildebrandti'', ''A. gracilis'', ''A. medius'' and ''A. maximus''. However, Hume and Walters (2012) listed only one species, ''A. maximus''. Most recently, Hansford and Turvey (2018) recognized only ''A. hildebrandti'' and ''A. maximus''. * ?''A. grandidieri'' Rowley 1867 nomen dubium * ''Aepyornis hildebrandti'' Burckhardt, 1893 (Hildebrandt's elephant-bird) ** ''Aepyornis gracilis'' Monnier, 1913 ** ''Aepyornis lentus'' Milne-Edwards & Grandidier, 1894 ** ?''Aepyornis minimus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntype
In biological nomenclature, a syntype is any one of two or more biological types that is listed in a description of a taxon where no holotype was designated. Precise definitions of this and related terms for types have been established as part of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. In zoology In zoological nomenclature, a syntype is defined as "Each specimen of a type series (q.v.) from which neither a holotype nor a lectotype has been designated rts. 72.1.2, 73.2, 74 The syntypes collectively constitute the name-bearing type." (Glossary of the zoological Code ). Historically, syntypes were often explicitly designated as such, and under the present ICZN this is a requirement (Art. 72.3), but modern attempts to publish species or subspecies descriptions based on syntypes are generally frowned upon by practicing taxonomists, and most are gradually being replaced by lectotypes. Those that still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Homo sapiens''. ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is likely the most widely known binomial. The ''formal'' introduction of this system of naming species is credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its aftermath became part of the oral tradition of Homer's epic poems, the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey''. Two poems by Homer's near contemporary Hesiod, the ''Theogony'' and the '' Works and Days'', contain accounts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Society Of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity devoted to the worldwide conservation of animals and their habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained the London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Park. History On 29 November 1822, the birthday of John Ray, "the father of modern zoology", a meeting held in the Linnean Society in Soho Square led by Rev. William Kirby, resolved to form a "Zoological Club of the Linnean Society of London". Between 1816 and 1826, discussions between Stamford Raffles, Humphry Davy, Joseph Banks and others led to the idea that London should have an establishment similar to the Jardin des Plantes in Paris. It would house a zoological collection "which should interest and amuse the public." The society was founded in April 1826 by Sir Stamford Raffles, the Marquess of Lansdowne, Lord Auckland, Sir Humphry Davy, Robert Peel, Joseph Sabine, Nicholas Aylward Vigors along with various other nobility, clergy, and natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |