|
Von Baeyer Nomenclature
The von Baeyer nomenclature is a system for describing polycyclic hydrocarbons. The system was originally developed in 1900 by Adolf von Baeyer for bicyclic systemsAdolf Baeyer: ''Systematik und Nomenclatur bicyclischer Kohlenwasserstoffe.'' and in 1913 expanded by Eduard Buchner and Wilhelm Weigand for tricyclic systems. The system has been adopted and extended by the IUPAC as part of its nomenclature for organic chemistry. The modern version has been extended to cover more cases of compounds including an arbitrary number of cycles, heterocyclic compounds A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and ... and unsaturated compounds. Extensive errata to this book has published online as: Extended Von Baeyer See also * Clar's Rule: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon#Physicochemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decahydronaphthalene
Decalin (decahydronaphthalene, also known as bicyclo .4.0ecane and sometimes decaline), a bicyclic organic compound, is an industrial solvent. A colorless liquid with an aromatic odor, it is used as a solvent for many resins or fuel additives. Isomers Decalin occurs in ''cis'' and ''trans'' forms. The ''trans'' form is energetically more stable because of fewer steric interactions. ''cis''-Decalin is a chiral molecule without a chiral center; it has a two-fold rotational symmetry axis, but no reflective symmetry. However, the chirality is canceled through a chair-flipping process that turns the molecule into its mirror image. Image:Cis-trans isomerism of decahydronaphthalene.svg, Image:cis-decalin double chair.png, 2: Image:trans-decalin double chair.png, 3: File:Cisdecalin conformations.png, 4: ''trans''-Decalin The only possible way to join the two six-membered rings in the ''trans'' position means the second ring needs to start from two equatorial bonds (blue) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer (; 31 October 1835 – 20 August 1917) was a German chemist who synthesised indigo and developed a nomenclature for cyclic compounds (that was subsequently extended and adopted as part of the IUPAC organic nomenclature). He was ennobled in the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1885 and was the 1905 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.''Adolf von Baeyer: Winner of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry 1905 '' Armin de Meijere Angewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 44, Issue 48, Pages 7836 – 7840 2005''Abstract/ref> Family and education Baeyer was born in Berlin as the son of the noted geodesist and captain of the Royal Prussian Army Johann Jacob Baeyer and his wife Eugenie Baeyer née Hitzig (1807–1843). Both his parents were Lutherans at the time of his birth and he was raised in the Lutheran religion. His mother was the daughter of Julius Eduard Hitzig and a member of the originally Jewish Itzig family, and had converted to Christianity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Buchner
Eduard Buchner (; 20 May 1860 – 13 August 1917) was a German chemist and zymologist, awarded the 1907 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on fermentation. Biography Early years Buchner was born in Munich to a physician and Doctor Extraordinary of Forensic Medicine. His older brother was Hans Ernst August Buchner. In 1884, he began studies of chemistry with Adolf von Baeyer and of botany with Carl Nägeli, at the Botanic Institute in Munich. After a period working with Otto Fischer (cousin of Emil Fischer) at the University of Erlangen, Buchner was awarded a doctorate from the University of Munich in 1888 under Theodor Curtius. Academics Buchner was appointed assistant lecturer in the organic laboratory of Adolf von Baeyer in 1889 at the University of Munich. In 1891, he was promoted to lecturer at the same university. In the autumn of 1893, Buchner moved to University of Kiel and appointed professor in 1895. In the next year he was appointed Professor Extraordinary for A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Weigand
Wilhelm Weigand (13 March 1862, in Gissigheim, Baden-Württemberg – 20 December 1949, in Munich) was a German Neoromanticism and Realism Realism, Realistic, or Realists may refer to: In the arts *Realism (arts), the general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts Arts movements related to realism include: *Classical Realism *Literary realism, a move ... period poet and writer. He was born Wilhelm Schnarrenberger, but on 2 May 1888 he took the maiden name of his grandmother. Distinctions * Johann-Peter-Hebel Prize (1942) * Honorary Citizen of the Community of Gissigheim Selected works * ''Der Frankenthaler'', novel (Leipzig, 1889) * ''Sommer'', poems (1894) * ''Der zwiefache Eros'', short stories (1896) * ''Die Löffelstelze'', novel (Tübingen, 1919) * ''Der Hof Ludwigs XIV. Nach den Denkwürdigkeiten des Herzogs von Saint-Simon'', history (c. 1922) * ''Der graue Bote'', short stories (Prague 1924) * ''Die Fahrt zur Liebesinsel'', novel (1928 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
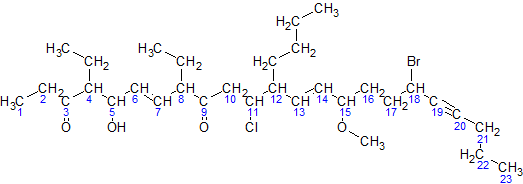
IUPAC Nomenclature Of Organic Chemistry
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the ''Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry'' (informally called the Blue Book). Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry. To avoid long and tedious names in normal communication, the official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice, except when it is necessary to give an unambiguous and absolute definition to a compound. IUPAC names can sometimes be simpler than older names, as with ethanol, instead of ethyl alcohol. For relatively simple molecules they can be more easily understood than non-systematic names, which must be learnt or looked over. However, the common or trivial name is often substantially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compounds
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quinol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon are also used for this concept. By definition, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons have multiple rings, precluding benzene from being considered a PAH. Some sources, such as the US EPA and CDC, consider naphthalene to be the simplest PAH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |