|
Volkheimeria
''Volkheimeria'' is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now Argentina during the Early Jurassic, 178–179 million years ago. Its type and only species is ''Volkheimeria chubutensis''. Discovery and naming The only known specimen of ''Volkheimeria'' was discovered at the site of Cerro Cóndor Sur, roughly a kilometer west of the village of Cerro Cóndor in Chubut Province, Argentina. In 1979, José Bonaparte described it as representing a new genus and species, ''Volkheimeria chubutensis'', alongside two other species discovered in the same strata, ''Piatnitzkysaurus floresi'' and ''Patagosaurus fariasi''. The genus name ''Volkheimeria'' honors the Argentinean paleontologist Wolfgang Volkheimer. Fossil record Only a single specimen of ''Volkheimeria chubutensis'' is known: the holotype PVL 4077, a partial skeleton from the Cañadón Asfalto Formation of Argentina. This specimen consists of a partial cervical vertebra, two complete and two partial dorsa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagosaurus Fariasi
''Patagosaurus'' (meaning "Patagonia lizard") is an extinct genus of eusauropod dinosaur from the Middle-Late Toarcian of Patagonia, Argentina. It was first found in deposits of the Cañadón Asfalto Formation, which date to around 179 to 177 million years ago. Although originally twelve specimens were assigned to the taxon, at least one of them may belong to a different genus. ''Patagosaurus'' probably lived alongside genera as ''Piatnitzkysaurus'', ''Condorraptor'' and ''Volkheimeria''. Since ''Patagosaurus'' is known from many specimens, including at least one juvenile, its anatomy and growth are fairly well understood. Both ages exhibit the typical features of a sauropod, a long neck, small head, a long tail and being quadrupedal. The juvenile exhibits features different from the adult in regions like the mandible, pectoral girdle, pelvis and hindlimb, although overall their anatomy is quite similar. The many known specimens help fill in gaps in the anatomy of the genus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdalodon
''Amygdalodon'' (; "almond tooth" for its almond shaped teeth) was a genus of basal sauropod from the Middle Jurassic of Argentina. The type species is ''Amygdalodon patagonicus''. Fossils of ''Amygdalodon'' have been found in the Toarcian Cerro Carnerero Formation of the Jurassic (about 180-172 million years ago). Very little is known about it, but it is one of the few Jurassic dinosaurs from South America found thus far. Discovery The holotype (MLP 46-VIII-21-1) consists of some vertebrae, ribs, four complete and three partial teeth, and a partial pelvis and shoulder-blade, of which was discovered in 1936. The type species, ''Amygdalodon patagonicus'', was described by Cabrera in Argentina in 1947.A. Cabrera. 1947. Un saurópodo nuevo del Jurásico de Patagonia. Instituto del Museo de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata, ''Notas del Museo de La Plata, Paleontología'' 12(95):1–17 Until 1936 sauropod fossils from Argentina were completely unknown then, prompted by Piatnitzky' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
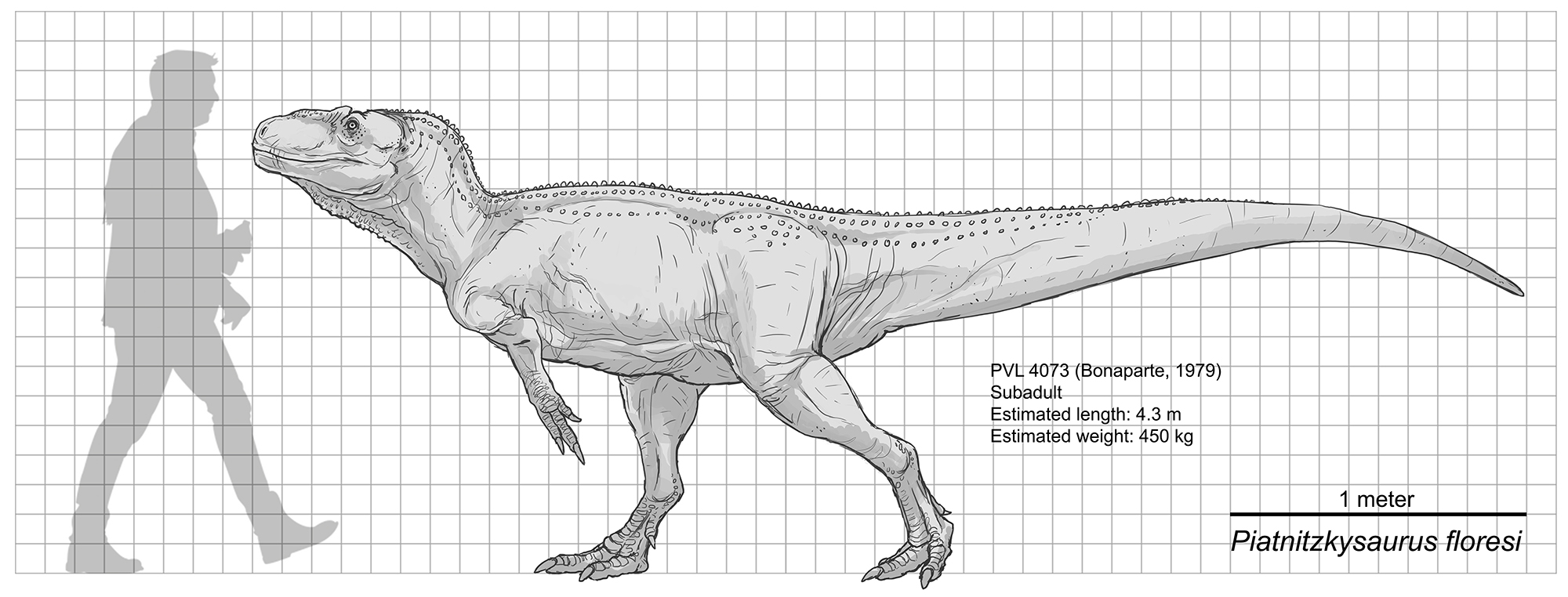
Piatnitzkysaurus Floresi
''Piatnitzkysaurus'' ( meaning "Piatnitzky's lizard") is a genus of megalosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 179 to 177 million years ago during the lower part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Argentina. ''Piatnitzkysaurus'' was a moderately large, lightly built, bipedal, ground-dwelling carnivore that could grow up to long. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen of ''Piatnitzkysaurus'', PVL 4073, was collected during expeditions in 1977, 1982, and 1983 at the Cañadón Asfalto Formation in sediments that were deposited during the Middle-Late Toarcian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 179 to 177 million years ago.Bonaparte, J. F. (1979)Dinosaurs: a Jurassic assemblage from Patagonia.''Science'', ''205''(4413), 1377-1379. The specimen was very complete and is one of the best known from a Megalosaur, including a partial skull and partial anterior postcranial skeleton of a subadult individual preserved in semi-articulation.Bonaparte, J. F., & L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cañadón Asfalto Formation
The Cañadón Asfalto Formation is a Lower Jurassic to Late Jurassic geologic formation, from the Jurassic period of the Mesozoic Era. Its age is controversial, uranium-lead dating of the volcanic tuff beds having given various different ages. A Recent work suggested that the base of the formation was formed around 171 Ma, during the upper Aalenian, while the main age for the Lower Las Chacritas Member being around 168 Ma, during the Bajocian, Bathonian and Callovian While the overlying Puesto Almada Member seems to be around 158 ma, or Oxfordian age, that changed thanks to the discovery of zircons near the location of discovery of '' Bagualia'', allowing a precise age of Las Charcitas Member as Middle-Late Toarcian, 178-179 million years, and a later study constrained the age of the formation as Middle Toarcian-Lower Bajocian, being contemporaneous to the Chon Aike volcanic activity, being a local equivalent to Antarctica's Mawson Formation. It is located in the Cañadón Asfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 In Paleontology
Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravisauria
Gravisauria is a clade of sauropod dinosaurs consisting of some genera, Vulcanodontidae and Eusauropoda.Allain, R. and Aquesbi, N. (2008). "Anatomy and phylogenetic relationships of ''Tazoudasaurus naimi'' (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) from the late Early Jurassic of Morocco." ''Geodiversitas'', 30(2): 345-424. Classification The clade Gravisauria was appointed by the French paleontologist Ronan Allain and Moroccan paleontologist Najat Aquesbi in 2008 when a cladistic analysis of the dinosaur found by Allain, ''Tazoudasaurus'', as the outcome was that the family Vulcanodontidae. The group includes ''Tazoudasaurus'' and ''Vulcanodon'', and the sister taxon Eusauropoda, but also certain species such as ''Antetonitrus'', ''Gongxianosaurus'' and ''Isanosaurus'' that do not belong in Vulcanodontidae but to an even more basic position occupied in Sauropoda. It made sense to have Sauropoda compared to this, more derived group that included Vulcanodontidae and Eusauropoda in a definition: Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Bonaparte
José Fernando Bonaparte (14 June 1928 – 18 February 2020) was an Argentine paleontologist who discovered a plethora of South American dinosaurs and mentored a new generation of Argentine paleontologists . One of the best-known Argentine paleontologists, he has been described by paleontologist Peter Dodson as "almost singlehandedly ... responsible for Argentina becoming the sixth country in the world in kinds of dinosaurs". Biography Bonaparte was the son of an Italian sailor, with no close connection to Napoleon's House of Bonaparte. He was born in Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina, and grew up in Mercedes, Buenos Aires. Despite a lack of formal training in paleontology, he started collecting fossils with many friends at an early age, and created a museum in their home town. He later became the curator of the National University of Tucumán, where he was named ''Doctor Honoris causa'' in 1976, and then in the late 1970s became a senior scientist at the Museo Argentino de Cienci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusauropod
Eusauropoda (meaning "true sauropods") is a derived clade of sauropod dinosaurs. Eusauropods represent the node-based group that includes all descendant sauropods starting with the basal eusauropods of ''Shunosaurus'', and possibly ''Barapasaurus'', and ''Amygdalodon'', but excluding ''Vulcanodon'' and ''Rhoetosaurus''. The Eusauropoda was coined in 1995 by Paul Upchurch to create a monophyletic new taxonomic group that would include all sauropods, except for the vulcanodontids. Eusauropoda are herbivorous, quadrupedal, and have long necks. They have been found in South America, Europe, North America, Asia, Australia, and Africa. The temporal range of Eusauropoda ranges from the early Jurassic to the Latest Cretaceous periods. The most basal forms of eusauropods are not well known and because the cranial material for the ''Vulcanodon'' is not available, and the distribution of some of these shared derived traits that distinguish Eusauropoda is still completely clear. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lessemsauridae
Lessemsauridae is a clade of early sauropodiform dinosaurs that lived in the Triassic and Jurassic of Argentina, South Africa and possibly Lesotho. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Apaldetti and colleagues in 2018 recovered a new clade of sauropodiforms uniting ''Lessemsaurus'', ''Antetonitrus'', and ''Ingentia'' which they named Lessemsauridae. It is a node-based taxon, defined as all descendants of the most recent common ancestor of ''Lessemsaurus sauropoides'' and ''Antetonitrus ingenipes''. Depending on the definition of Sauropoda, Lessemsauridae is either one of the most basal sauropod taxa, or a sister taxon of Sauropoda. An additional member of the clade was named later in 2018, ''Ledumahadi''. A 2021 study by Pol and colleagues also assigned the genera '' Kholumolumo'' and ''Meroktenos'' to the group. Lessemsaurids are recognised as very large quadrupeds that achieved giant sizes (up to 12 metric tons) independently of other giant sauropodomorphs. They had highly pne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lessemsaurus
''Lessemsaurus'' is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaur belonging to Lessemsauridae. Naming and description The type species, ''L. sauropoides'', was formally described by José Fernando Bonaparte in 1999 in honor of Don Lessem, a writer of popular science books. It was found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in La Rioja Province, Argentina.Weishampel, David B; ''et al.'', 2004. "Dinosaur distribution (Late Triassic, South America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 527–528. . This dinosaur was around long and was discovered in strata dating to the Norian stage, around 210 million years ago. It is estimated to have reached in maximum body mass. Classification A cladogram after Pol, Garrido & Cerda, 2011, illustrates a possible placing of ''Lessemsaurus'' and ''Antetonitrus'' in Sauropodomorpha: In 2018, Apaldetti ''et al.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antetonitrus
''Antetonitrus'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur found in the Early Jurassic Elliot Formation of South Africa. The only species is ''Antetonitrus ingenipes''. As one of the oldest known sauropods, it is crucial for the understanding of the origin and early evolution of this group. It was a quadrupedal herbivore, like all of its later relatives, but shows primitive adaptations to use the forelimbs for grasping, instead of purely for weight support. Discovery and naming Adam Yates (paleontologist), Adam Yates, an Australian expert on early sauropodomorphs, named ''Antetonitrus'' in a 2003 report co-authored by South African James Kitching. The name is derived from the Latin ''ante-'' ("before") and ''tonitrus'' ("thunder"), which refers to its existence, before other known sauropods, specifically ''Brontosaurus'' ("thunder lizard"). The one known species of ''Antetonitrus'' is called ''A. ingenipes'', from the Latin ''ingens'' ("massive") and ''pes'' ("foot"), because it shows the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toarcian
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma (million years ago) and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian. The Toarcian Age began with the Toarcian turnover, the extinction event that sets its fossil faunas apart from the previous Pliensbachian age. It is believed to have ended with a global cooling event known as the Comptum Cooling Event, although whether it represented a worldwide event is controversial. Stratigraphic definitions The Toarcian takes its name from the city of Thouars, just south of Saumur in the Loire Valley of France. The stage was introduced by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842, after examining rock strata of this age in a quarry near Thouars. In Europe this period is represented by the upper part of the Lias. The base of the Toarcian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the ammonite genus '' Eoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |