|
Volgadraco
''Volgadraco'' ("Volga River dragon") is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of European Russia. ''Volgadraco'' was originally classified as an azhdarchid. However, recent studies have concluded that it may belong to either the family Nyctosauridae, or the family Pteranodontidae. ''Volgadraco'' is known from lower beak (holotype SGU, no. 46/104a) and postcranial fragments from the early Campanian-age Rybushka Formation of Saratov, Russia. The size of this animal, and the development of blood supply in the lower jaw are intermediate between older Santonian or Turonian azhdarchids like ''Azhdarcho'' and '' Bakonydraco'' and later Maastrichtian azhdarchids like '' Quetzalcoatlus''. ''Volgadraco'' was described in 2008 by Averianov, Arkhangelsky, and Pervushov. The type species is ''V. bogolubovi'', the specific name honouring Russian paleontologist Nikolai Nikolaevich Bogolubov. The authors consider the earlier named genus ''Bogolubovia'' to be a '' no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azhdarchid
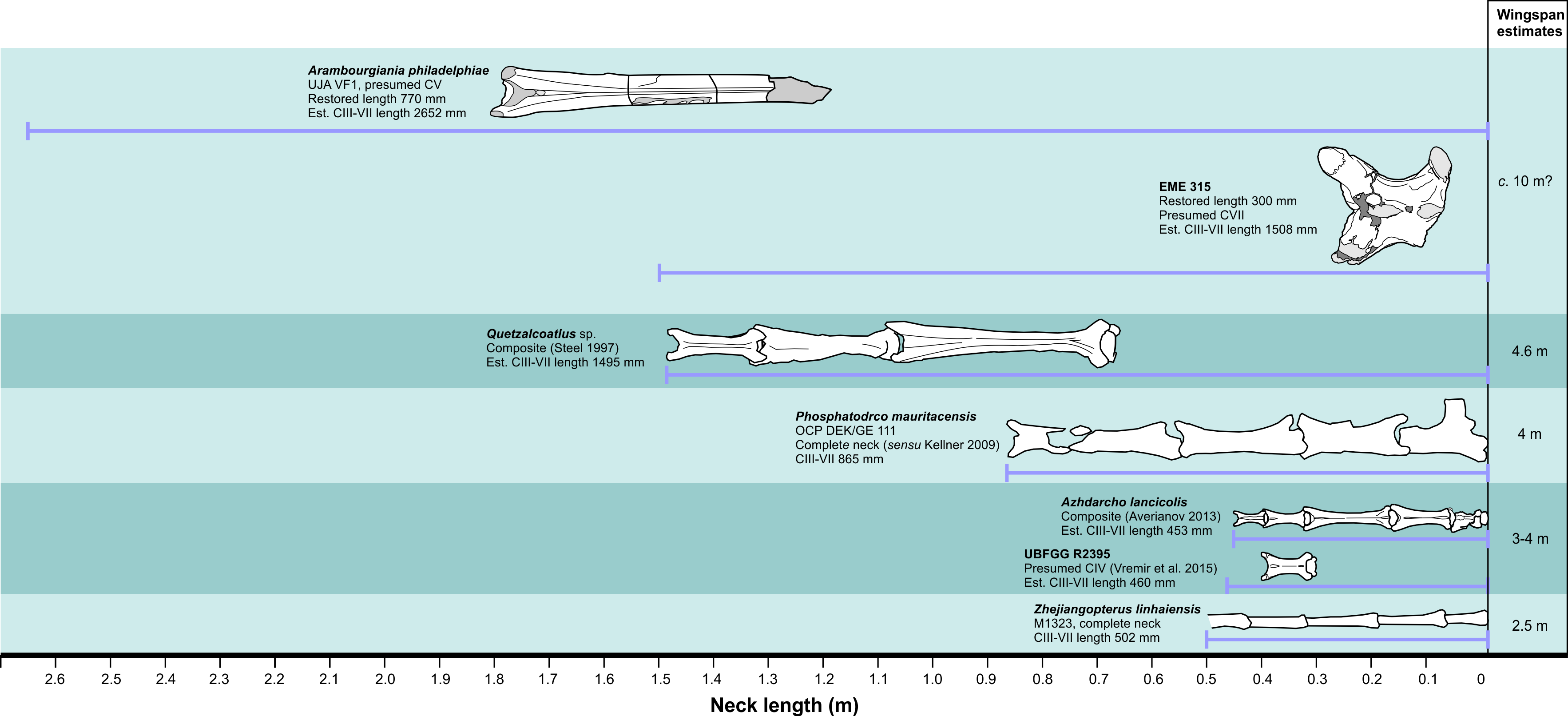
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cretaceous as well (late Berriasian age, about 140 million years ago). Azhdarchids included some of the largest known flying animals of all time, but smaller cat-size members have also been found. Originally considered a sub-family of Pteranodontidae, Nesov (1984) named the Azhdarchinae to include the pterosaurs ''Azhdarcho'', ''Quetzalcoatlus'', and ''Titanopteryx'' (now known as ''Arambourgiania''). They were among the last known surviving members of the pterosaurs, and were a rather successful group with a worldwide distribution. By the time of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction, most pterosaur families except for the Azhdarchidae disappear from the fossil record, but recent studies indicate a wealth of pterosaurian fauna, including pteran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteranodontidae
The Pteranodontidae are a family of large pterosaurs of the Cretaceous Period of North America and Africa. The family was named in 1876 by Othniel Charles Marsh. Pteranodontids had a distinctive, elongated crest jutting from the rear of the head (most famously seen in ''Pteranodon'' itself). The spectacularly-crested ''Nyctosaurus'' is sometimes included in this family, though usually placed in its own family, the Nyctosauridae (Nicholson & Lydekker, 1889). Modern researchers differ in their use of the concept. S. Christopher Bennett and Alexander Kellner have concluded that ''Nyctosaurus'' was not a pteranodontid. In 1994 Bennett defined a clade Pteranodontidae, also including species of the Anhangueridae. However, this definition has not been accepted by other workers. Alexander Kellner, for example, named several additional species for specimens previously classified as ''Pteranodon'', and placed ''P. sternbergi'' in a distinct genus, ''Geosternbergia''. Kellner re-defined Ptera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rybushka Formation
The Rybushka Formation is a Campanian geologic formation in the Penza and Saratov Oblasts of European Russia. Pterosaur, fish and invertebrate fossils have been recovered from the formation. Fossil content The following fossils have been reported from the formation: * '' Amylodon karamysh'' * '' Archaeolamna kopingensis'' * '' Bogolubovia orientalis'' * '' Cretolamna appendiculata'' * '' Ischyodus bifurcatus'' * ''Volgadraco bogolubovi'' * '' Pseudocorax laevis'' * '' Squalicorax kaupi'' * '' Squatina hasei'' * '' Chalmys sp.'' * '' Edaphodon sp.'' * '' Elasmodus sp.'' * '' Eostriatolamia sp.'' * '' Gryphaeostrea sp.'' * '' Heterodontus sp.'' * '' Monticulina sp.'' * '' Prognathodon sp.'' * '' Solariella sp.'' * '' Squatirhina sp.'' * '' ?Clidastes sp.'' * Chelospharginae indet. * Elasmobranchii indet. * Elasmosauridae indet. * Enchodontidae indet. * Mosasauridae indet. * Plesiosauria indet. * Polycotylidae indet. * Testudinata indet. * ?Thoracosaurinae indet. See al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogolubovia
''Bogolubovia'' is a genus of pterosaur from the Upper Cretaceous (early Campanian) Rybushka Formation of Petrovsk, Saratov Oblast, Russia. It is named for Nikolai Nikolaevich Bogolubov, the paleontologist who discovered the remains in 1914. It was in 1991 assigned to the Azhdarchidae. Wellnhofer (1991) however, retained it in the Pteranodontidae. Bogolubov had initially assigned the specimen, consisting of a single partial large cervical vertebra, as a new species of ''Ornithostoma'', ''O. orientalis''. It was later reclassified as a species of '' Pteranodon'', before being assigned its own genus by Lev Nesov and Alexander Yarkov in 1989.Bogolubov, N.N. (1914). "O pozvonkŌĆÖ pterodaktilya uzŌĆÖ vyerkhnyemŌĆÖlovyikhŌĆÖ otlozhyenii Saratovskoi gubyernii (A propos d'une vert├©bre de Pterodactyle des depots cretac├®s superieurs du gouvernment de Sartoff). n a pterodactyle vertebra from Upper Cretaceous deposits of the Government of Saratoff" ''Annuaire geologique et mineralogique d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteranodontia
Pteranodontia is an extinct group of ornithocheiroid pterodactyloid pterosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (Coniacian to Maastrichtian stages) of North America and Africa. They were some of the most advanced pterosaurs, and possessed highly specialized cranial crests that may have served as sexual attraction, with males having a much larger crest. Classification Pteranodontia was originally named by Marsh in 1876. In 2003, it was given a phylogenetic definition by David Unwin as the common ancestor of ''Pteranodon'' and ''Nyctosaurus'' plus all its descendants. Though Marsh had originally named this group based on the shared absence of teeth in those species, most analyses show that all of the traditional "ornithocheiroid" pterosaurs are also members of this clade. Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic placement of this group from Andres and Myers (2013). In 2018, Longrich, Martill, and Andres revisited the classification, and made a different phylogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyctosauridae
Nyctosauridae (meaning "night lizards" or "bat lizards") is a family of specialized soaring pterosaurs of the late Cretaceous Period of North America, Africa, and possibly Europe. It was named in 1889 by Henry Alleyne Nicholson and Richard Lydekker.Nicholson, H.A. and Lydekker, R. (1889). ''A manual of palaeontology for the use of students: with a general introduction on the principles of pal├”ontology, Volume II''. Blackwood, 1889. Nyctosaurids are characterized by their lack of all but the wing finger. In most pterosaurs, the hand has four fingers, with the fourth elongated to support the wing, and the remaining three are usually small, clawed, and used in walking or climbing. The lack of functional fingers in nyctosaurids may suggest that they spent almost all of their time in the air, rarely walking on the ground. Nyctosaurids also possessed a distinctively enlarged crest for muscle attachment on their upper arm bone, or humerus, the ''deltopectoral crest'', hatchet shaped li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The CretaceousŌĆōPaleogene extinction event (formerly known as the CretaceousŌĆōTertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist Andr├® Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the Chalk Group c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quetzalcoatlus
''Quetzalcoatlus'' is a genus of pterosaur known from the Late Cretaceous period of North America (Maastrichtian stage); its members were among the largest known flying animals of all time. ''Quetzalcoatlus'' is a member of the Azhdarchidae, a family of advanced toothless pterosaurs with unusually long, stiffened necks. Its name comes from the Aztec feathered serpent god Quetzalcoatl. The type species is ''Q. northropi'', named by Douglas Lawson in 1975; the genus also includes the smaller species ''Q. lawsoni'', which was known for many years as an unnamed species before being named by Brian Andres and Wann Langston Jr. (posthumously) in 2021. Discovery and species The first ''Quetzalcoatlus'' fossils were discovered in Texas, United States, from the Maastrichtian Javelina Formation at Big Bend National Park (dated to around 68 million years ago) in 1971 by Douglas A. Lawson, then a geology graduate student from the Jackson School of Geosciences at the University of Texas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Nikolaevich Bogolubov
Nikolay Nikolayevich Bogolyubov (russian: ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░╠üą╣ ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░╠üąĄą▓ąĖčć ąæąŠą│ąŠą╗čÄ╠üą▒ąŠą▓; 21 August 1909 ŌĆō 13 February 1992), also transliterated as Bogoliubov and Bogolubov, was a Soviet and Russian mathematician and theoretical physicist known for a significant contribution to quantum field theory, classical and quantum statistical mechanics, and the theory of dynamical systems; he was the recipient of the 1992 Dirac Medal. Biography Early life (1909ŌĆō1921) Nikolay Bogolyubov was born on 21 August 1909 in Nizhny Novgorod, Russian Empire to Russian Orthodox Church priest and seminary teacher of theology, psychology and philosophy Nikolay Mikhaylovich Bogolyubov, and Olga Nikolayevna Bogolyubova, a teacher of music. The Bogolyubovs relocated to the village of Velikaya Krucha in the Poltava Governorate (now in Poltava Oblast, Ukraine) in 1919, where the young Nikolay Bogolyubov began to study physics and mathematics. The family soon moved to Kiev in 1921, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azhdarcho
''Azhdarcho'' is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Bissekty Formation (middle Turonian stage, about 92 million years ago) of Uzbekistan, as well as the Zhirkindek Formation of Kazakhstan. It is known from fragmentary remains including the distinctive, elongated neck vertebrae that characterizes members of the family Azhdarchidae, a family that includes many giant pterosaurs such as ''Quetzalcoatlus''. The name ''Azhdarcho'' comes from the Persian word '' azhdar'' (), a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology. The type species is ''Azhdarcho lancicollis''. The specific epithet ''lancicollis'' is derived from the Latin words ''lancea'' (meaning "lance" or "spear") and ''collum'' ("neck"). History The fossil remains of ''Azhdarcho'' were recovered in the Kyzyl Kum desert (from the Taykarshinskaya unit of the Bissekty Formation) by Lev A. Nesov during expeditions to Central Asia in 1974ŌĆō1981. The type specimen, given the catalog number ą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(2).jpg)