|
Visual Flight Rules
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e. in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft. If the weather is less than VMC, pilots are required to use instrument flight rules, and operation of the aircraft will be primarily through referencing the instruments rather than visual reference. In a control zone, a VFR flight may obtain a clearance from air traffic control to operate as Special VFR. Requirements VFR require a pilot to be able to see outside the cockpit, to control the aircraft's altitude, navigate, and avoid obstacles and other aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
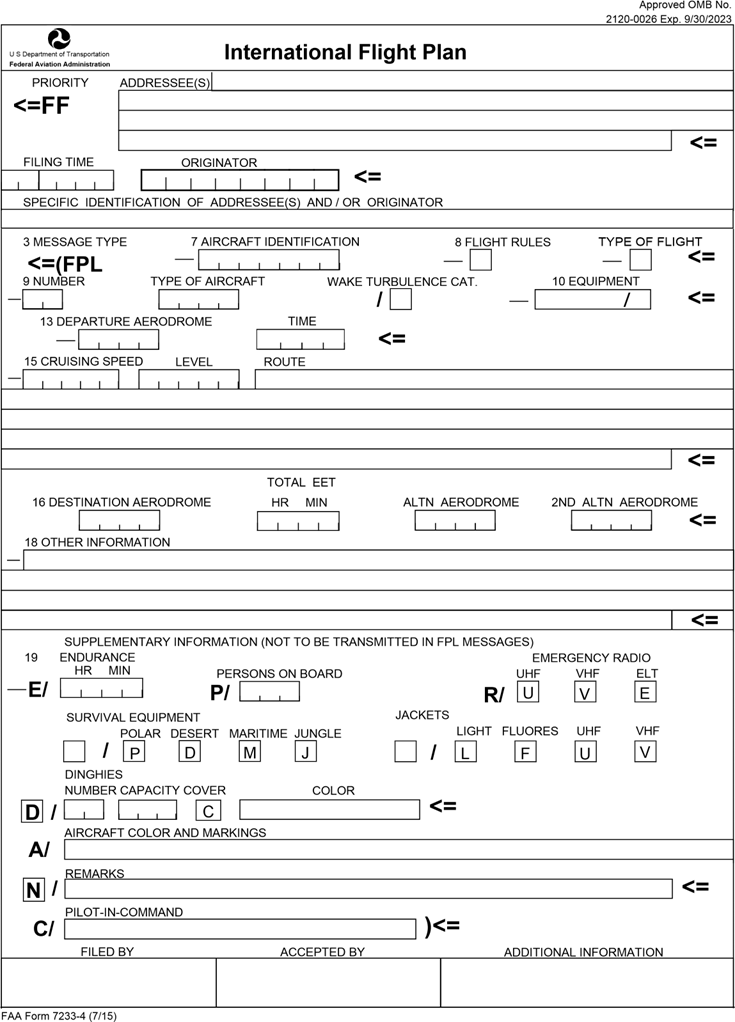
Flight Plan
Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider (e.g. the FAA in the United States) prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight (whether instrument flight rules FRor visual flight rules FR, the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an aircraft is crossing the Air Defense Identificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Course (navigation)
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be steered. The course is to be distinguished from the ''heading'', which is the direction where the watercraft's bow or the aircraft's nose is pointed. Course, track, route and heading The path that a vessel follows over the ground is called a ''ground track'', ''course made good'' or ''course over the ground''. For an aircraft it is simply its ''track''. The intended track is a ''route''. For ships and aircraft, routes are typically straight-line segments between waypoints. A navigator determines the ''bearing'' (the compass direction from the craft's current position) of the next waypoint. Because water currents or wind can cause a craft to drift off course, a navigator sets a ''course to steer'' that compensates for drift. The helmsman or pilot points the craft on a ''heading'' that corresponds to the course to steer. If the predicted drift is correct, then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Declination
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole). This angle varies depending on position on the Earth's surface and changes over time. Somewhat more formally, Bowditch defines variation as “the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west to indicate the direction of magnetic north from true north. The angle between magnetic and grid meridians is called grid magnetic angle, grid variation, or grivation.” By convention, declination is positive when magnetic north is east of true north, and negative when it is to the west. ''Isogonic lines'' are lines on the Earth's surface along which the declination has the same constant value, and line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airworthiness Directive
An Airworthiness Directive (commonly abbreviated as AD) is a notification to owners and operators of certified aircraft that a known safety deficiency with a particular model of aircraft, engine, avionics or other system exists and must be corrected. If a certified aircraft has outstanding airworthiness directives that have not been complied with, the aircraft is not considered airworthy. Thus, it is mandatory for an aircraft operator to comply with an AD. Purpose ADs usually result from service difficulty reporting by operators or from the results of aircraft accident investigations. They are issued either by the national civil aviation authority of the country of aircraft manufacture or of aircraft registration. When ADs are issued by the country of registration they are almost always coordinated with the civil aviation authority of the country of manufacture to ensure that conflicting ADs are not issued. In detail, the purpose of an AD is to notify aircraft owners: * that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Wave
In meteorology, lee waves are atmospheric stationary waves. The most common form is mountain waves, which are atmospheric internal gravity waves. These were discovered in 1933 by two German glider pilots, Hans Deutschmann and Wolf Hirth, above the Krkonoše. They are periodic changes of atmospheric pressure, temperature and orthometric height in a current of air caused by vertical displacement, for example orographic lift when the wind blows over a mountain or mountain range. They can also be caused by the surface wind blowing over an escarpment or plateau, or even by upper winds deflected over a thermal updraft or cloud street. The vertical motion forces periodic changes in speed and direction of the air within this air current. They always occur in groups on the lee side of the terrain that triggers them. Sometimes, mountain waves can help to enhance precipitation amounts downwind of mountain ranges. Usually a turbulent vortex, with its axis of rotation parallel to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailplane
A glider or sailplane is a type of glider aircraft used in the leisure activity and sport of gliding (also called soaring). This unpowered aircraft can use naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to gain altitude. Sailplanes are aerodynamically streamlined and so can fly a significant distance forward for a small decrease in altitude. In North America the term 'sailplane' is also used to describe this type of aircraft. In other parts of the English-speaking world, the word 'glider' is more common. Types Gliders benefit from producing the least drag for any given amount of lift, and this is best achieved with long, thin wings, a slender fuselage and smooth surfaces with an absence of protuberances. Aircraft with these features are able to soar – climb efficiently in rising air produced by thermals or hills. In still air, sailplanes can glide long distances at high speed with a minimum loss of height in between. Sailplanes have rigid wings and either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Level
In aviation and aviation meteorology, a flight level (FL) is an aircraft's altitude at standard air pressure, expressed in hundreds of feet. The air pressure is computed assuming an International Standard Atmosphere pressure of 1013.25 hPa (29.92 inHg) at sea level, and therefore is not necessarily the same as the aircraft's actual altitude, either above sea level or above ground level. Background Flight levels are used to ensure safe vertical separation between aircraft, despite natural local variations in atmospheric air pressure. Historically, altitude has been measured using a pressure altimeter, which is essentially a calibrated barometer. An altimeter measures ambient air pressure, which decreases with increasing altitude following the barometric formula. It then calculates and displays the corresponding altitude. If different aircraft's altimeters were not calibrated consistently, then two aircraft could be flying at the same altitude even though their altimeter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspace Class
The world's navigable airspace is divided into three-dimensional segments, each of which is assigned to a specific class. Most nations adhere to the classification specified by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and described below, though they might use only some of the classes defined below, and significantly alter the exact rules and requirements. Similarly, individual nations may also designate special use airspace (SUA) with further rules for reasons of national security or safety. Abbreviations used in this article ICAO definitions On March 12, 1990, ICAO adopted the current airspace classification scheme. The classes are fundamentally defined in terms of flight rules and interactions between aircraft and air traffic control (ATC). Generally speaking, the ICAO airspaces allocate the responsibility for avoiding other aircraft, namely either to ATC (if separation is provided) or to the aircraft commander (if not). Some key concepts are: * Separation: Mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special VFR
Special visual flight rules (also special VFR or SVFR) are a set of aviation regulations under which a pilot may operate an aircraft. It is a special case of operating under visual flight rules (VFR). Use in different regions The definition for SVFR may be different in different countries, depending on the local aviation regulations. ICAO definition The ICAO definition of Special VFR flight is a VFR flight cleared by air traffic control to operate within a control zone in meteorological conditions below visual meteorological conditions. United States According to Federal Aviation Regulations, SVFR operations can only be conducted in the controlled airspace around an airport where that controlled airspace extends down to the surface (so-called ''surface area''). SVFR can only be conducted below 10,000 feet MSL in such areas. SVFR at night requires an IFR-equipped aircraft and an IFR-rated pilot in command ("IFR" means Instrument flight rules). In helicopters, there is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Rating
Instrument rating refers to the qualifications that a pilot must have in order to fly under instrument flight rules (IFR). It requires specific training and instruction beyond what is required for a private pilot certificate or commercial pilot certificate, including rules and procedures specific to instrument flying, additional instruction in meteorology, and more intensive training in flight solely by reference to instruments. Training and testing Testing consists of a written exam and a practical test (also known as a check ride in the US, or a flight test in other countries). The check ride is divided into an oral component (certain countries only) to verify that the applicant understands the theory of instrument flying and an actual flight to ensure the pilot possesses the practical skills required for safe IFR flight. For most private pilots, the most significant value of flying under IFR is the ability to fly in instrument meteorological conditions (such as inside clouds or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Approach
In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as, "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply." There are three categories of instrument approach procedures: pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)