|
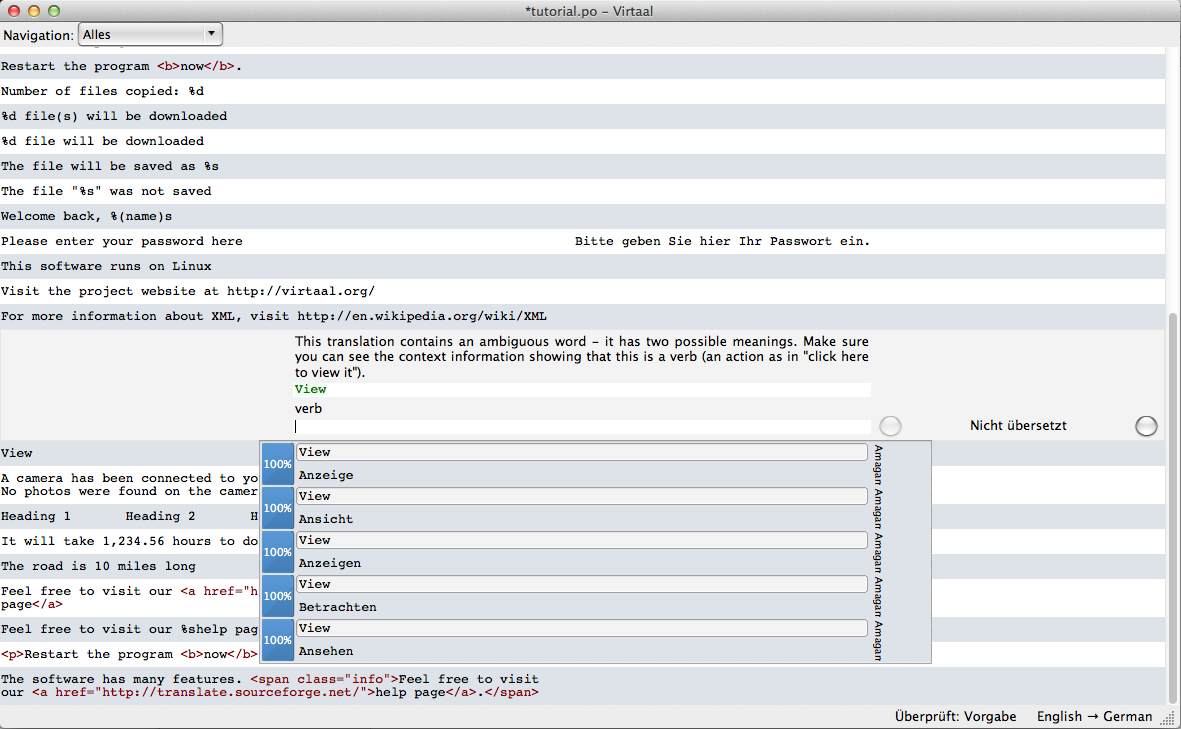
Virtaal
Virtaal is a computer-assisted translation tool written in the Python programming language. It is free software developed and maintained by Translate.org.za. Virtaal is built using the Translate Toolkit allowing it to process a number of translation and localisation formats. Design Philosophy The key principle behind the design of Virtaal is the optimisation of the interface for the localiser. This includes ensuring that all relevant functionality is keyboard accessible and that needed information is always optimally displayed. History Work on Virtaal began in 2007 with an initial 0.1 release made to a small number of open-source localisers. Version 0.2, released in October 2008, became the first official release. Name The name Virtaal, pronounced , is a play on words. In Afrikaans, an official language of South Africa where Translate.org.za is located, the expression "vir taal" means "for language", while the word "vertaal" (pronounced the same as "vir taal") means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtaal 0
Virtaal is a computer-assisted translation tool written in the Python programming language. It is free software developed and maintained by Translate.org.za. Virtaal is built using the Translate Toolkit allowing it to process a number of translation and localisation formats. Design Philosophy The key principle behind the design of Virtaal is the optimisation of the interface for the localiser. This includes ensuring that all relevant functionality is keyboard accessible and that needed information is always optimally displayed. History Work on Virtaal began in 2007 with an initial 0.1 release made to a small number of open-source localisers. Version 0.2, released in October 2008, became the first official release. Name The name Virtaal, pronounced , is a play on words. In Afrikaans, an official language of South Africa where Translate.org.za is located, the expression "vir taal" means "for language", while the word "vertaal" (pronounced the same as "vir taal") means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translate Toolkit
The Translate Toolkit is a localization and translation toolkit. It provides a set of tools for working with localization file formats and files that might need localization. The toolkit also provides an API on which to develop other localization tools. The toolkit is written in the Python programming language. It is free software originally developed and released by Translate.org.za in 2002 and is now maintained by Translate.org.za and community developers. Translate Toolkit uses Enchant as spellchecker. History The toolkit was originally developed as the mozpotools by David Fraser for Translate.org.za. Translate.org.za had focused on translating KDE which used Gettext PO files for localization. With an internal change to focus on end-user, cross-platform, OSS software, the organisation decided to localize the Mozilla Suite. This required using new tools and new formats that were not as rich as Gettext PO. Thus mozpotools was created to convert the Mozilla DTD and .prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Gettext
In computing, gettext is an internationalization and localization (i18n and l10n) system commonly used for writing multilingual programs on Unix-like computer operating systems. One of the main benefits of gettext is that it separates programming from translating. The most commonly used implementation of gettext is GNU gettext, released by the GNU Project in 1995. The runtime library is libintl. gettext provides an option to use different strings for any number of plural forms of nouns, but this feature has no support for grammatical gender. History Initially, POSIX provided no means of localizing messages. Two proposals were raised in the late 1980s, the 1988 Uniforum gettext and the 1989 X/Open catgets (XPG-3 § 5). Sun Microsystems implemented the first gettext in 1993. The Unix and POSIX developers never really agreed on what kind of interface to use (the other option is the X/Open catgets), so many C libraries, including glibc, implemented both. , whether gettext should be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation Memory EXchange
Translation Memory eXchange (TMX) is an XML specification for the exchange of translation memory (TM) data between computer-aided translation and localization tools with little or no loss of critical data. TMX was originally developed and maintained by OSCAR (Open Standards for Container/Content Allowing Re-use), a special interest group of LISA (Localization Industry Standards Association), and first released in 1997. Specification 1.4b of 2005 remained current . It allows the original source and target documents to be recreated from the TMX data. A working draft of TMX 2.0 was released for public comment in March 2007 but no work was done on the new version; in March 2011 LISA was declared insolvent and as a result its standards were moved under a Creative Commons license and the standards specification relocated. TMX forms part of the Open Architecture for XML Authoring and Localization (OAXAL OAXAL: Open Architecture for XML Authoring and Localization is an Organization for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moses (machine Translation)
Moses is a free software, statistical machine translation engine that can be used to train statistical models of text translation from a source language to a target language, developed by the University of Edinburgh. Moses then allows new source-language text to be decoded using these models to produce automatic translations in the target language. Training requires a parallel corpus of passages in the two languages, typically manually translated sentence pairs. Moses is released under the LGPL licence and available both as source code and binaries for Windows and Linux. Its development is primarily supported by the EuroMatrix project, with funding by the European Commission. Among its features are: * A beam search algorithm that quickly finds the highest probability translation within a number of choices * Phrase-based translation of short text chunks * Handles words with multiple factored representations to enable the integration of linguistic and other information (e.g., surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Translator
Microsoft Translator is a multilingual machine translation cloud service provided by Microsoft. Microsoft Translator is a part of Microsoft Cognitive Services and integrated across multiple consumer, developer, and enterprise products; including Bing, Microsoft Office, SharePoint, Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Lync, Yammer, Skype Translator, Visual Studio, and Microsoft Translator apps for Windows, Windows Phone, iPhone and Apple Watch, and Android phone and Android Wear. Microsoft Translator also offers text and speech translation through cloud services for businesses. Service for text translation via the Translator Text API ranges from a free tier supporting two million characters per month to paid tiers supporting billions of characters per month. Speech translation via Microsoft Speech services is offered based on time of the audio stream. The service supports text translation between languages and language varieties as of . It also supports several speech translation system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Translate
Google Translate is a multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google to translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, and an API that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. As of , Google Translate supports languages at various levels, and , claimed over 500 million total users, with more than 100 billion words translated daily, after the company stated in May 2013 that it served over 200 million people daily. Launched in April 2006 as a statistical machine translation service, it used United Nations and European Parliament documents and transcripts to gather linguistic data. Rather than translating languages directly, it first translates text to English and then pivots to the target language in most of the language combinations it posits in its grid, with a few exceptions including Catalan-Spanish. During a translation, it looks for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apertium
Apertium is a free/open-source rule-based machine translation platform. It is free software and released under the terms of the GNU General Public License. Overview Apertium is a shallow-transfer machine translation system, which uses finite state transducers for all of its lexical transformations, and hidden Markov models for part-of-speech tagging or word category disambiguation. Constraint Grammar taggers are also used for some language pairs (e.g. Breton– French). Existing machine translation systems available at present are mostly commercial or use proprietary technologies, which makes them very hard to adapt to new usages; furthermore, they use different technologies across language pairs, which makes it very difficult, for instance, to integrate them in a single multilingual content management system. Apertium uses a language-independent specification, to allow for the ease of contributing to Apertium, more efficient development, and enhancing the project's overall g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Translation
Machine translation, sometimes referred to by the abbreviation MT (not to be confused with computer-aided translation, machine-aided human translation or interactive translation), is a sub-field of computational linguistics that investigates the use of software to translate text or speech from one language to another. On a basic level, MT performs mechanical substitution of words in one language for words in another, but that alone rarely produces a good translation because recognition of whole phrases and their closest counterparts in the target language is needed. Not all words in one language have equivalent words in another language, and many words have more than one meaning. Solving this problem with corpus statistical and neural techniques is a rapidly growing field that is leading to better translations, handling differences in linguistic typology, translation of idioms, and the isolation of anomalies. Current machine translation software often allows for customizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Equivalence
Unicode equivalence is the specification by the Unicode character encoding standard that some sequences of code points represent essentially the same character. This feature was introduced in the standard to allow compatibility with preexisting standard character sets, which often included similar or identical characters. Unicode provides two such notions, canonical equivalence and compatibility. Code point sequences that are defined as canonically equivalent are assumed to have the same appearance and meaning when printed or displayed. For example, the code point U+006E (the Latin lowercase "n") followed by U+0303 (the combining tilde "◌̃") is defined by Unicode to be canonically equivalent to the single code point U+00F1 (the lowercase letter " ñ" of the Spanish alphabet). Therefore, those sequences should be displayed in the same manner, should be treated in the same way by applications such as alphabetizing names or searching, and may be substituted for each other. Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Expression
A regular expression (shortened as regex or regexp; sometimes referred to as rational expression) is a sequence of characters that specifies a search pattern in text. Usually such patterns are used by string-searching algorithms for "find" or "find and replace" operations on strings, or for input validation. Regular expression techniques are developed in theoretical computer science and formal language theory. The concept of regular expressions began in the 1950s, when the American mathematician Stephen Cole Kleene formalized the concept of a regular language. They came into common use with Unix text-processing utilities. Different syntaxes for writing regular expressions have existed since the 1980s, one being the POSIX standard and another, widely used, being the Perl syntax. Regular expressions are used in search engines, in search and replace dialogs of word processors and text editors, in text processing utilities such as sed and AWK, and in lexical analysis. Most gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Insensitive
In computers, case sensitivity defines whether uppercase and lowercase letters are treated as distinct (case-sensitive) or equivalent (case-insensitive). For instance, when users interested in learning about dogs search an e-book, "dog" and "Dog" are of the same significance to them. Thus, they request a case-insensitive search. But when they search an online encyclopedia for information about the United Nations, for example, or something with no ambiguity regarding capitalization and ambiguity between two or more terms cut down by capitalization, they may prefer a case-sensitive search. Areas of significance Case sensitivity may differ depending on the situation: * Searching: Users expect information retrieval systems to be able to have correct case sensitivity depending on the nature of an operation. Users looking for the word "dog" in an online journal probably do not wish to differentiate between "dog" or "Dog", as this is a writing distinction; the word should be matched wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |