|
Vinoviloth
Vinoviloth are one of the tribes in ''Scandza'' (Scandinavia) mentioned by Jordanes in '' De origine actibusque Getarum'' in the 6th century CE.''De origine actibusque Getarum'' See als by C. C. Mierow. It has been suggested that they would have been the same as the Winnili. Sometimes is also mentioned. Jordanes writes: And there are beyond these the Ostrogoths, Raumarici, ... |
Vinoviloth
Vinoviloth are one of the tribes in ''Scandza'' (Scandinavia) mentioned by Jordanes in '' De origine actibusque Getarum'' in the 6th century CE.''De origine actibusque Getarum'' See als by C. C. Mierow. It has been suggested that they would have been the same as the Winnili. Sometimes is also mentioned. Jordanes writes: And there are beyond these the Ostrogoths, Raumarici, ... |
List Of Germanic Tribes
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, beginning in the 2nd century BC and extending into late antiquity. By the Early Middle Ages, early forms of kingship began to have a historical impact across Europe, with the exception of Northern Europe, where the Vendel Period from AD 550 to 800 and the subsequent Viking Age until AD 1050 are still seen in the Germanic context. The associations and locations of the numerous peoples and groups in ancient sources are often subject to heavy uncertainty and speculation, and classifications of ethnicity regarding a common culture or a temporary alliance of heterogeneous groups are disputed. Sometimes, it is uncertain that the groups are Germanic in the broader linguistic sense or, in other words, they consisted of speakers of a Germanic language. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandza
Scandza was described as a "great island" by Gothic-Byzantine historian Jordanes in his work ''Getica''. The island was located in the Arctic regions of the sea that surrounded the world. The location is usually identified with Scandinavia. Jordanes was a Roman citizen living in Constantinople but described himself as being of Gothic descent. His ''Getica'', written in 551 AD, gives a history of the Goths, beginning in Scandza from where they later migrated to Gothiscandza, near the mouth of the Vistula River. The Swedish archaeologist Göran Burenhult describes this account as a unique glimpse into the tribes of Scandinavia in the 6th century. Geographical description through history Early Greek and Roman geographers used the name ''Scandia'' for various uncharted islands in Northern Europe. The name originated in Greek sources, which used it for a long time for different islands in the Mediterranean region. In the Iliad the name denotes an ancient city in Kythira, Greece. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
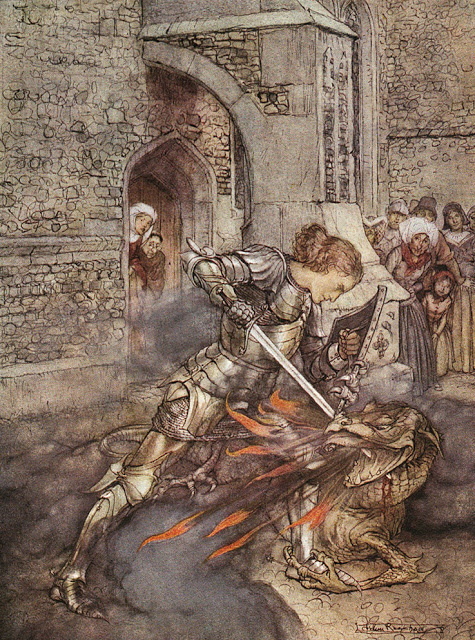
Lancelot
Lancelot du Lac (French for Lancelot of the Lake), also written as Launcelot and other variants (such as early German ''Lanzelet'', early French ''Lanselos'', early Welsh ''Lanslod Lak'', Italian ''Lancillotto'', Spanish ''Lanzarote del Lago'', and Welsh ''Lawnslot y Llyn''), is a character in some versions of Arthurian legend, where he is typically depicted as King Arthur's close companion and one of the greatest Knights of the Round Table. In the French-inspired Arthurian chivalric romance tradition, Lancelot is an orphaned son of King Ban of the lost Kingdom of Benoic, raised in the fairy realm by the Lady of the Lake. A hero of many battles, quests and tournaments, and famed as a nearly unrivalled swordsman and jouster, Lancelot becomes the lord of the castle Joyous Gard and personal champion of Arthur's wife, Queen Guinevere, despite suffering from frequent and sometimes prolonged fits of madness. But when his adulterous affair with Guinevere is discovered, it causes a ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Germanic Peoples
Early Germanic culture refers to the culture of the early Germanic peoples. Largely derived from a synthesis of Proto-Indo-European and indigenous Northern European elements, the Germanic culture started to exist in the Jastorf culture that developed out of the Nordic Bronze Age. It came under significant external influence during the Migration Period, particularly from ancient Rome. The Germanic peoples eventually overwhelmed the Western Roman Empire, which by the Middle Ages facilitated their conversion from paganism to Christianity and the abandonment of their tribal way of life. Certain traces of early Germanic culture have survived among the Germanic peoples up to the present day. Languages Linguists postulate that an early Proto-Germanic language existed and was distinguishable from the other Indo-European languages as far back as 500 BCE. From what is known, the early Germanic tribes may have spoken mutually intelligible dialects derived from a common parent lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binchester
Binchester is a small village in County Durham, England. It has a population of 271. It is situated between Bishop Auckland, which is to the south, and a short distance to the west of Spennymoor. It has a community centre, swing park and football field, and is surrounded by countryside. Granville Terrace, the main road through the village, was relaid and renovated in 1991 for the BBC television series ''Challenge Anneka''. Nearby is Binchester Roman Fort. Etymology Binchester almost certainly takes the first element of its name from the first element of the earlier Roman name ''Vinovia Vinovia or Vinovium was a Roman fort and settlement situated just over to the north of the town of Bishop Auckland on the banks of the River Wear in County Durham, England. The fort was the site of a hamlet until the late Middle Ages, but t ...''. This was Anglicised with the addition of the Old English word ''ceaster'' '(Roman) fortification' and perhaps through identification with the Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, Æthelberht and Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of northern England, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom against the Viking attempt at conquest, becoming the dominant ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinovia
Vinovia or Vinovium was a Roman fort and settlement situated just over to the north of the town of Bishop Auckland on the banks of the River Wear in County Durham, England. The fort was the site of a hamlet until the late Middle Ages, but the modern-day village of Binchester is about to the east, near Spennymoor. The ruins are now known as the . History of the fort and vicus The fort Not much is yet known about pre-Roman settlement in the immediate area. The fort was probably established around AD 79 to guard the crossing of the River Wear by Dere Street, the main Roman road between York, Hadrian's Wall and Scotland, and also the fort's ''via principalis''. Sitting atop a hill above the Wear, Binchester was the largest Roman fort in County Durham. The land was cleared of trees and brush and a huge levelling fill laid down on the plateau before construction of the fort began. Archaeologists found four coins of Vespasian that seem to corroborate that initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asser
Asser (; ; died 909) was a Welsh monk from St David's, Dyfed, who became Bishop of Sherborne in the 890s. About 885 he was asked by Alfred the Great to leave St David's and join the circle of learned men whom Alfred was recruiting for his court. After spending a year at Caerwent because of illness, Asser accepted. In 893, Asser wrote a biography of Alfred, called the ''Life of King Alfred''. The manuscript survived to modern times in only one copy, which was part of the Cotton library. That copy was destroyed in a fire in 1731, but transcriptions that had been made earlier, together with material from Asser's work which was included by other early writers, have enabled the work to be reconstructed. The biography is the main source of information about Alfred's life and provides far more information about Alfred than is known about any other early English ruler. Asser assisted Alfred in his translation of Gregory the Great's '' Pastoral Care'', and possibly with other works. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vingulmark
Vingulmark (Old Norse ''Vingulmörk'') is the old name for the area in Norway which today makes up the counties of Østfold, western parts of Akershus (excluding Romerike), and eastern parts of Buskerud (Hurum and Røyken municipalities), and includes the site of Norway's capital, Oslo. During the Middle Ages, Vingulmark was an administrative unit limited to Oslo, Bærum and Asker. Etymology The Old Norse form of the name was ''Vingulmǫrk''. The first part of the name, Vingul, is the accusative case of Vingull, "fescue", or "fool". The last element of the name, ''mark'' or plural ''mǫrk'', "forest" or "March", i.e. ''the forest of fescues/fools''. History According to medieval kings' sagas, it was a Viking Age petty kingdom. Vingulmark was one of the four counties under the Court of Law, which together constituted the ancient landscape of Viken. Archaeologists have made finds of richly endowed burials in the area around the estuary of the river Glomma, at Onsøy, Rolvsøy and Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
