|
Vilkitsky Strait
: Vilkitsky Strait (russian: link=no, пролив Вилькицкого) is a strait between the Taimyr Peninsula and Bolshevik Island in the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. The strait connects the Kara and Laptev Seas. The length of the Vilkitsky Strait is 128 km, the width approx. 55 km and the depth between 32 m and 210 m. It is covered with drifting ice all year round. The strait was discovered in 1913 by a Russian hydrographic expedition led by Boris Vilkitsky and then named after him in 1918. The Geiberg Islands cover the entrance to the Vilkitsky Strait from the east, and the Firnley Islands do so from the west. The shores on the side of the Taymyr Peninsula are covered with tundra In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless moun ... vegetation and scattered stones. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and sea ice, ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. Ultimately the Kara, Barents and Laptev Seas are all extensions of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. The Kara Sea's northern limit is marked geographically by a line running from Cape Kohlsaat in Graham Bell Island, Franz Josef Land, to Cape Molotov (Arctic Cape), the northernmost point of Komsomolets Island in Severnaya Zemlya. The Kara Sea is roughly long and wide with an area of around and a mean depth of . Its main ports are Novy Port and Dikson and it is important as a fishing ground although the sea is ice-bound for all but two months of the year. The Kara Sea contains the East-Prinovozemelsky field (an extension of the West Siberian Oil Basin), containing significant undeveloped petroleum and natural gas. In 2014, US gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east. The sea is named after the Russian explorers Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev; formerly, it had been known under various names, the last being Nordenskiöld Sea (russian: link=no, мо́ре Норденшёльда), after explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The sea has a severe climate with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) over more than nine months per year, low water salinity, scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, and low depths (mostly less than 50 meters) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Terminology The terms ''channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, ''firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically important. Straits can be important shipping routes and wars have been fought for control of them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taimyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia. Geography The Taymyr Peninsula lies between the Yenisei Gulf of the Kara Sea and the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Afro-Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula. Population The Nenets people, also known as ''Samoyeds'', are an indigenous people in northern arctic Russia, and some live at the Taymyr Peninsula. The Nganasan people are an indigenous Samoyedic people inhabiting central Siberia, including the Taymyr Peninsula. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as being one of the Indigenous p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik Island
__NOTOC__ Bolshevik Island (russian: о́стров Большеви́к, ) is an island in Severnaya Zemlya, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russian Arctic. The island is named after the political faction of the same name. History The island, together with the eastern coast of what was named Emperor Nicholas II Land, was discovered by Boris Vilkitsky at the time of the 1913 Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition. Its insularity, however, wasn't proven until 1931, when Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev charted the archipelago during their 1930–32 expedition. Prima Polar Station, currently the only Polar station operating in Severnaya Zemlya, is located in this island near Cape Baranov. Geography It is the southernmost island and the second largest island in the group. The area of this island has been estimated at . The island is mountainous reaching a height of 935 m. About 31% of Bolshevik Island, totaling over , is covered by glaciers, the largest are Leningrad Glacier, Semyonov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severnaya Zemlya
Severnaya Zemlya (russian: link=no, Сéверная Земля́ (Northern Land), ) is a archipelago in the Russian high Arctic. It lies off Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula, separated from the mainland by the Vilkitsky Strait. This archipelago separates two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Kara Sea in the west and the Laptev Sea in the east. Severnaya Zemlya was first noted in 1913 and first charted in 1930–32, making it the last sizeable archipelago on Earth to be explored. Administratively, the islands form part of Russia's Krasnoyarsk Krai. In Soviet times there were a number of research stations in different locations, but currently there are no human inhabitants in Severnaya Zemlya, except for the Prima Polar Station near Cape Baranov. The largest glacier in the Russian Federation, the Academy of Sciences Glacier, is located in Severnaya Zemlya. The archipelago is notable as well in connection with the ongoing multiyear Arctic sea ice decline. Until recently, ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection. History The origins of hydrography lay in the making of charts to aid navigation, by individual mariners as they navigated into new waters. These were usually the private property, even closely held secrets, of individuals who used them for commercial or military advantage. As transoceanic trade and exploration increased, hydrographic surveys started to be carried out as an exercise in their own right, and the commissioning of surveys was increasingly done by governments and special hydrographic offices. National organizations, particularly navies, realized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
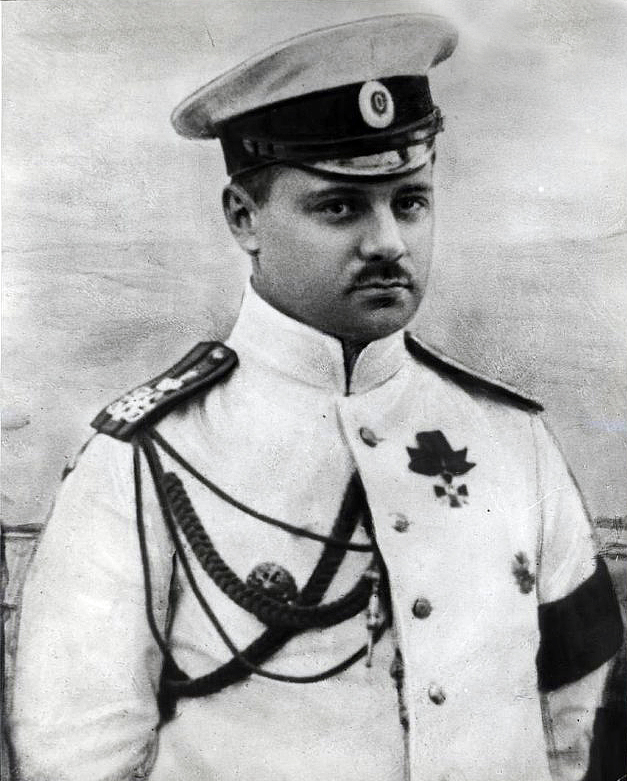
Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky (russian: Бори́с Андре́евич Вильки́цкий) (22 March (3 April N.S.) 1885, Pulkovo – 6 March 1961) was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky. Career Born in Pulkovo, Tsarskoselsky Uyezd (now part of Saint Petersburg), Vilkitsky graduated from the Naval Academy in Saint Petersburg in 1908. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. In 1913—1915 he led the Arctic hydrographic expedition on the ships ''"Taimyr"'' and ''"Vaigach"'' with the purpose of further exploration of the Northern Sea Route. In 1913, Vilkitsky's expedition discovered Emperor Nicholas II Land (russian: Земля Императора Николая II, ''Zemlya Imperatora Nikolaya II'') —later renamed 'Severnaya Zemlya', perhaps one of the most important Russian discoveries in the Arctic at the time. Other discoveries were an island that now bears his name ( Vilkitsky Island), as well as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geiberg Islands
The Heiberg Islands, spelt ''Geyberg'', ''Gejberg'' or ''Geiberg'' (Russian: ''острова Гейберга''; ''ostrova Geyberga'' or also ''острова Акселя Гейберга'') is a group of four small islands covered with tundra vegetation and with scattered stones on their shores. They lie in the Kara Sea, between the bleak coast of Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula and Severnaya Zemlya. These islands are between from the continental shore. The Heiberg Islands are covering the entrance to the Vilkitsky Strait from the west. The latitude of this group is 77° 40' N and the longitude 101° 27' E. The largest island of the group is only about in length. The sea surrounding the Heiberg Islands is covered with fast ice in the winter, which is long and bitter, and the climate is severe. The surrounding sea is obstructed by pack ice even in the summer, so that these islands are connected with the mainland for most of the year. The Heiberg Islands were named by Fridtjof Nan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firnley Islands
The Firnley Islands ( rus, острова Фирнлея; ''Ostrova Firnleya'', nn, Firnleyøyane) is a group of three small islands covered with tundra vegetation and with scattered stones on their shores. They lie in the Kara Sea, close to the bleak coast of Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula, not far east of the Nordenskjold Archipelago. These islands lie about 35 km from the continental shore. The Firnley Islands were named by Fridtjof Nansen after Thomas Fearnley?, a Norwegian merchant who was one of the main financiers of the ''Fram'' expedition. They were also explored later by the Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition. Geography The Firnley Islands are covering the entrance to the Vilkitsky Strait from the west. They are all relatively small islands, Dlinnyy, the largest of the group, is only about 5 km in length. The sea surrounding the islands is covered with fast ice in the winter, which is long and bitter, and the climate is exceptionally severe. The surrounding se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia. Geography The Taymyr Peninsula lies between the Yenisei Gulf of the Kara Sea and the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Afro-Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula. Population The Nenets people, also known as ''Samoyeds'', are an indigenous people in northern arctic Russia, and some live at the Taymyr Peninsula. The Nganasan people are an indigenous Samoyedic people inhabiting central Siberia, including the Taymyr Peninsula. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as being one of the Indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)