|
Vika Oxygen Generator
Vika or TGK is an oxygen generating system for spaceflight. It is a SFOG, or solid-fuel oxygen generator, a kind of chemical oxygen generator. It has been used on the retired Mir space station and the International Space Station. It was originally developed by Roscosmos to supplement the ''Elektron'' oxygen system on ''Mir''. A Vika module, also known as a "candle", contains about one liter of lithium perchlorate and can provide oxygen for one person for 24 hours. After being adopted for use on the ISS, it had the NASA name SFOG, but they also sometimes use the Russian acronym TGK. Vika on Mir Vika was used on Mir when more than three people were on board. Vika needs a supply of canisters to work, which must be flown into space. An example of this is Progress M-34, which carried 60 canisters to Mir in 1997 along with other cargo. If ''Vika'' and ''Elektron'' stopped working, the station would have to rely on a limited supply of bottled oxygen. In February 1997 a Vika chemical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Oxygen Generator
A chemical oxygen generator is a device that releases oxygen via a chemical reaction. The oxygen source is usually an inorganic superoxide, chlorate, or perchlorate; ozonides are a promising group of oxygen sources. The generators are usually ignited by a firing pin, and the chemical reaction is usually exothermic, making the generator a potential fire hazard. Potassium superoxide was used as an oxygen source on early crewed missions of the Soviet space program, in submarines for use in emergency situations, for firefighters, and for mine rescue. In commercial airliners Commercial aircraft provide emergency oxygen to passengers to protect them in case of loss of cabin pressure. Chemical oxygen generators are not used for the cockpit crew, who are typically supplied using compressed oxygen canisters, also known as oxygen bottles. In narrow body airliners, for each row of seats there were overhead oxygen masks and oxygen generators. In some wide-body airliners, such as the DC-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roscosmos
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Perchlorate
Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a water of crystallization, trihydrate. Applications Inorganic chemistry Lithium perchlorate is used as a source of oxygen in some chemical oxygen generators. It decomposes at about 400 °C, yielding lithium chloride and oxygen: : LiClO4 → LiCl + 2 O2 Over 60% of the mass of the lithium perchlorate is released as oxygen. It has both the highest oxygen to weight and oxygen to volume ratio of all practical perchlorate salts. Organic chemistry LiClO4 is highly soluble in organic solvents, even diethyl ether. Such solutions are employed in Diels–Alder reaction, Diels–Alder reactions, where it is proposed that the Lewis acidic Li+ binds to Lewis basic sites on the dienophile, thereby accelerating the reaction. Lithium perchlorate is also used as a co-catalyst in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linenger In Respirator
Jerry Michael Linenger (born January 16, 1955) is a retired Captain in the United States Navy Medical Corps, and a former NASA astronaut who flew on the Space Shuttle and Space Station Mir. Background Born January 16, 1955, and raised in East Detroit, Michigan, he is married to the former Kathryn M. Bartmann of Arlington Heights, Illinois; they have four children. Linenger graduated from East Detroit High School 1973. He received a Bachelor of Science degree in bioscience from the United States Naval Academy in 1977, a doctorate in medicine from Wayne State University School of Medicine in 1981, a Master of Science degree in systems management from the University of Southern California in 1988, a Master of Public Health degree in health policy from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 1989 and a Doctor of Philosophy degree in epidemiology from the University of North Carolina in 1989. Linenger is a member of the Alumni Associations of the U.S. Naval Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-34
Progress M-34 (russian: Прогресс М-34, italic=yes) was a Russian uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1997 to resupply the Mir space station, and which subsequently collided with Mir during a docking attempt, resulting in significant damage to the space station. Spacecraft The 52nd of 64 Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 234. It carried supplies including food, water, and oxygen for the EO-23 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing maneuvers. Among its cargo were two new spacesuits, three fire extinguishers, oxygen candles, and equipment to facilitate repairs to Mir's life support system. Launch and docking Progress M-34 was launched at 16:04:05 UTC on 6 April 1997, atop a Soyuz-U carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Following two days of free flight, it docked with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-1
Kvant-1 (russian: Квант-1; English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet space station ''Mir''. It remained attached to ''Mir'' until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001. The Kvant-1 module contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments. It was used to conduct research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars and it was uniquely positioned for studies of the Supernova SN 1987A. Furthermore, it supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Some additions to Kvant-1 during its lifetime were solar arrays and the ''Sofora'' and ''Rapana'' girders. The Kvant-1 module was based on the TKS spacecraft and was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules. The 37K modules featured a jettisonable TKS-E type propulsion module, also called the Functional Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station is an artificial satellite (i.e. a type of orbital spaceflight). Stations must have docking ports to allow other spacecraft to dock to transfer crew and supplies. The purpose of maintaining an orbital outpost varies depending on the program. Space stations have most often been launched for scientific purposes, but military launches have also occurred. Space stations have harboured so far the only long-duration direct human presence in space. After the first station Salyut 1 (1971) and its tragic Soyuz 11 crew, space stations have been operated consecutively since Skylab (1973), having allowed a progression of long-duration direct human presence in space. Stations have been occupied by consecutive crews since 1987 with the Salyut successor M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
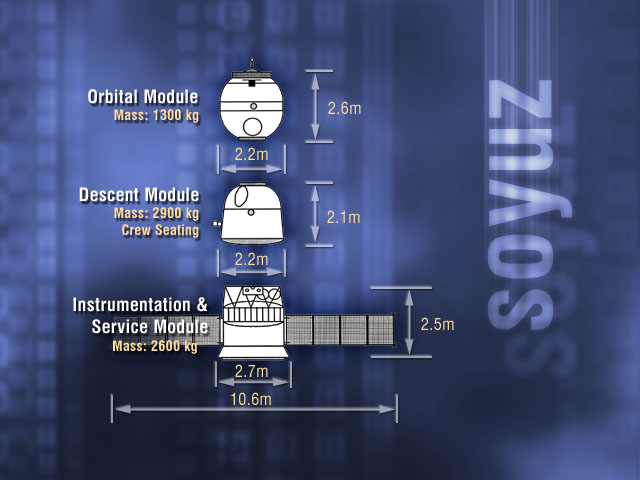
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igniter
In pyrotechnics, a pyrotechnic initiator (also initiator or igniter) is a device containing a pyrotechnic composition used primarily to ignite other, more difficult-to-ignite materials, such as thermites, gas generators, and solid-fuel rockets. The name is often used also for the compositions themselves. Pyrotechnic initiators are often controlled electrically (called electro-pyrotechnic initiators), e.g. using a heated bridgewire or a ''bridge resistor''. They are somewhat similar to blasting caps or other detonators, but they differ in that there is no intention to produce a shock wave. An example of such pyrotechnic initiator is an electric match. Composition The energetic material used, often called pyrogen, is usually a pyrotechnic composition made of a fuel and oxidizer, where the fuel produces a significant amount of hot particles that cause/promote the ignition of the desired material. Initiator compositions are similar to flash powders, but they differ in burning speed, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Support System
A life-support system is the combination of equipment that allows survival in an environment or situation that would not support that life in its absence. It is generally applied to systems supporting human life in situations where the outside environment is hostile, such as outer space or underwater, or medical situations where the health of the person is compromised to the extent that the risk of death would be high without the function of the equipment. In human spaceflight, a life-support system is a group of devices that allow a human being to survive in outer space. US government space agency NASA, and private spaceflight companies use the term environmental control and life-support system or the acronym ECLSS when describing these systems. The life-support system may supply air, water and food. It must also maintain the correct body temperature, an acceptable pressure on the body and deal with the body's waste products. Shielding against harmful external influences suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |