|
Vijlen
Vijlen ( li, Viele) is a village in the South-East part of the Dutch province of Limburg. The village is constituted of a number of hamlets, among which Mamelis, Camerig, Harles and Cottessen. Including these hamlets, Vijlen has around 1,500 inhabitants (in 2005) and is part of the municipality of Vaals. Located at 200 meters above Normaal Amsterdams Peil, on top of the Vijlenerberg (Vijlener hill), it is the highest situated town in the Netherlands. The neo-gothic and Catholic St. Martinus church, which is located in the center of the village, is known as the highest located church in the country. The area around the village is well known for its natural environment and landscapes. The ' Mergelland Route', a touristic route through the South-Limburg area, leads through the village and its surroundings. With lodging and camping facilities available, tourism related business is a key source of income for the village. The origin of the village is most likely Roman. The name Vijl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaals
Vaals (; Ripuarian: ) is a town in the extreme southeastern part of the Dutch province of Limburg, which is in the southeastern part of the Netherlands. The municipality covers an area of in the foothills of the Ardennes–Eifelrange and is located about east of Maastricht and west of the city centre of Aachen. It borders on both Belgium and Germany. The three borders meet on the Drielandenpunt, a few meters from the highest point in the European part of the Netherlands, the Vaalserberg. The Vaalserberg used to be called "Hubertusberg". History Its occupation in ancient Roman times might be recorded by its name itself which comes from Latin 'vallis'. It is one of the few places in the Netherlands with a name deriving from Latin. In Roman times, the south of the Dutch province of Limburg was a densely populated part of the Roman empire, with its regional focus on Cologne (Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium), for a while even capital of the Western Roman Empire. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
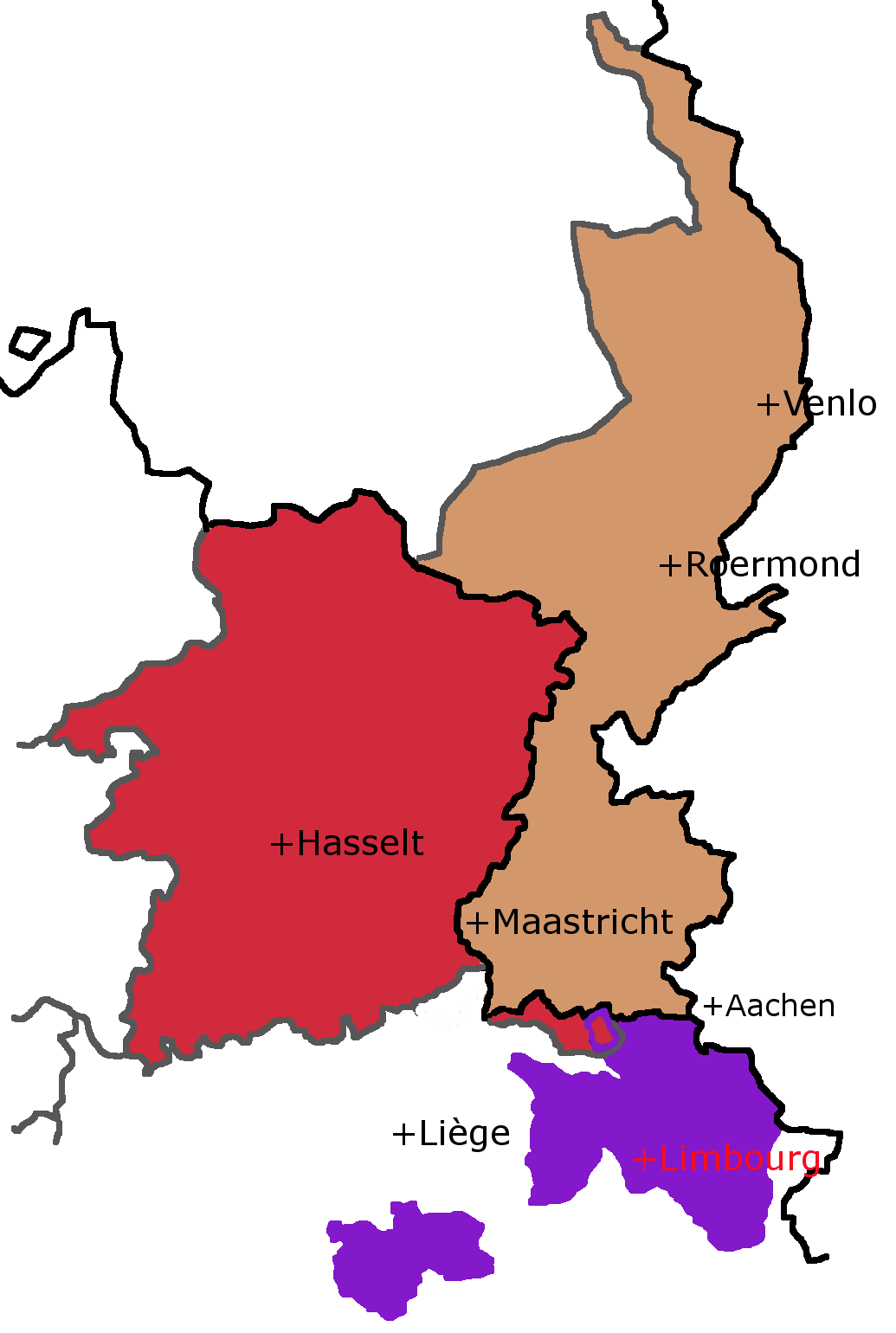
Limburg (Netherlands)
Limburg (, ) is the southernmost of the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. It is bordered by Gelderland to the north and by North Brabant to its west. Its long eastern boundary forms the international border with the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. To the west is the international border with the similarly named Belgian province of Limburg, part of which is delineated by the river Meuse. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme southeastern point, marking the tripoint of the Netherlands, Germany and Belgium. Limburg's main municipalities are the provincial capital Maastricht (population 120,837 as of January 2022), Venlo (population 102,176) in the northeast, as well as Sittard-Geleen (population 91,760, bordering both Belgium and Germany) and Heerlen (population 86,874) in the south. More than half of the population, approximately 650,000 people, live in the south of Limburg, which corresponds to roughly one-third of the province's area proper. In South Limburg, most peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of cities with surrounding urbanized areas. Settlements may include hamlets, villages, towns and cities. A settlement may have known historical properties such as the date or era in which it was first settled, or first settled by particular people. In the field of geospatial predictive modeling, settlements are "a city, town, village or other agglomeration of buildings where people live and work". A settlement conventionally includes its constructed facilities such as roads, enclosures, field systems, boundary banks and ditches, ponds, parks and woods, wind and water mills, manor houses, moats and churches. History The earliest geographical evidence of a human settlement was Jebel Irhoud, where early modern human remains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Pottery Culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Incised Ware culture, falling within the Danubian I culture of V. Gordon Childe. Most cultural evidence has been found on the middle Danube, the upper and middle Elbe, and the upper and middle Rhine. It represents a major event in the initial spread of agriculture in Europe. The pottery consists of simple cups, bowls, vases, jugs without handles and, in a later phase, with pierced lugs, bases, and necks.Hibben, page 121. Important sites include Vrable and Nitra in Slovakia; Bylany in the Czech Republic; Langweiler and Zwenkau (Eythra) in Germany; Brunn am Gebirge in Austria; Elsloo, Sittard, Köln-Lindenthal, Aldenhoven, Flomborn, and Rixheim on the Rhine; Lautereck and Hienheim on the upper Danube; and Rössen and Sonderhaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave (burial)
A grave is a location where a cadaver, dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is burial, buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as graveyards or cemetery, cemeteries. Certain details of a grave, such as the state of the body found within it and any objects found with the body, may provide information for archaeology, archaeologists about how the body may have lived before its death, including the time period in which it lived and the culture that it had been a part of. In some religions, it is believed that the body must be burned or cremated for the soul to survive; in others, the complete decomposition of the body is considered to be important for the rest of the soul (see Grief, bereavement). Description The formal use of a grave involves several steps with associated terminology. ;Grave cut The excavation that forms the grave.Ghamidi (2001)Customs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Document
Historical documents are original documents that contain important historical information about a person, place, or event and can thus serve as primary sources as important ingredients of the historical methodology. Significant historical documents can be deeds, laws, accounts of battles (often given by the victors or persons sharing their viewpoint), or the exploits of the powerful. Though these documents are of historical interest, they do not detail the daily lives of ordinary people, or the way society functioned. Anthropologists, historians and archeologists generally are more interested in documents that describe the day-to-day lives of ordinary people, indicating what they ate, their interaction with other members of their households and social groups, and their states of mind. It is this information that allows them to try to understand and describe the way society was functioning at any particular time in history. Greek ostraka provide good examples of historical docum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions. Typology and distribution Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas near Rome: the ''villa urbana'', a country seat that could easily be reached from Rome (or another city) for a night or two; and the ''villa rustica'', the farmhouse estate permanently occupied by the servants who generally had charge of the estate. The Roman Empire contained many kinds of villas, not all of them lavishly appointed with mosaic floors and frescoes. In the provinces, any country house with some decorative features in the Roman style may be called a "villa" by modern scholars. Some were pleasure houses, like Hadrian's Villa at Tivoli, that were sited in the cool hills within easy reach of Rome or, like the Villa of the Papyri at Herculaneum, on picturesque sites overlooking the Bay of Naples. Some villas were more like the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





