|
Vietnam People's Air Force Museum, Hanoi
The Vietnam People's Air Force Museum, Hanoi or ''Bảo Tàng Phòng Không - Không Quân'' is located on Truong Chinh Street in the ''Bach Mai'' District of Hanoi. The museum is on the edge of the disused Bach Mai Airfield. The museum tells the history of the Vietnam People's Air Force (VPAF) from its formation in 1954 through to the present day. There is a heavy emphasis on its role in the Second Indochina War and the Cambodian-Vietnamese War. The museum comprises one main building with displays on the history of the VPAF, biographies of VPAF aces, uniforms and flightsuits, aircraft weaponry and engines, items from downed US aircraft and the forward fuselage of a MiG-21. Outside is a static park with aircraft of the VPAF and the Republic of Vietnam Air Force. The museum is open Mon.-Thurs. and Sat.-Sun. from 08:00 to 11:00 and 13:00 to 16:00. Entry fee is 20,000 VND Aircraft on display Aircraft on outside display include: *Aero L-29 Delfin *Antonov An-2 ::Plaque states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is the cultural and political centre of Vietnam. Hanoi can trace its history back to the third century BCE, when a portion of the modern-day city served as the capital of the historic Vietnamese nation of Âu Lạc. Following the collapse of Âu Lạc, the city was part of Han China. In 1010, Vietnamese emperor Lý Thái Tổ established the capital of the imperial Vietnamese nation Đại Việt in modern-day central Hanoi, naming the city Thăng Long (literally 'Ascending Dragon'). Thăng Long remained Đại Việt's political centre until 1802, when the Nguyễn dynasty, the last imperial Vietnamese dynasty, moved the capital to Huế. The city was renamed Hanoi in 1831, and served as the capital of French Indochina from 1902 to 1945. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin (northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern coastline of Vietnam down to the Hòn La Island, in the north by China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and to the east by the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island. Etymology The name ''Tonkin'', written "" in Hán-Nôm characters and in the Vietnamese alphabet, means "eastern capital", and is the former toponym for Hanoi, the present capital of Vietnam. It should not to be confused with Tokyo, which is also written "" and also means "eastern capital". During the French colonial era, the northern region of today’s Vietnam was called ''Tonkin''. ''Bắc Bộ'' is the native Vietnamese name of Tonkin. The bay's Vietnamese and Chinese names – and , respectively – both mean "Northern Bay". History Gulf of Tonkin incident On 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
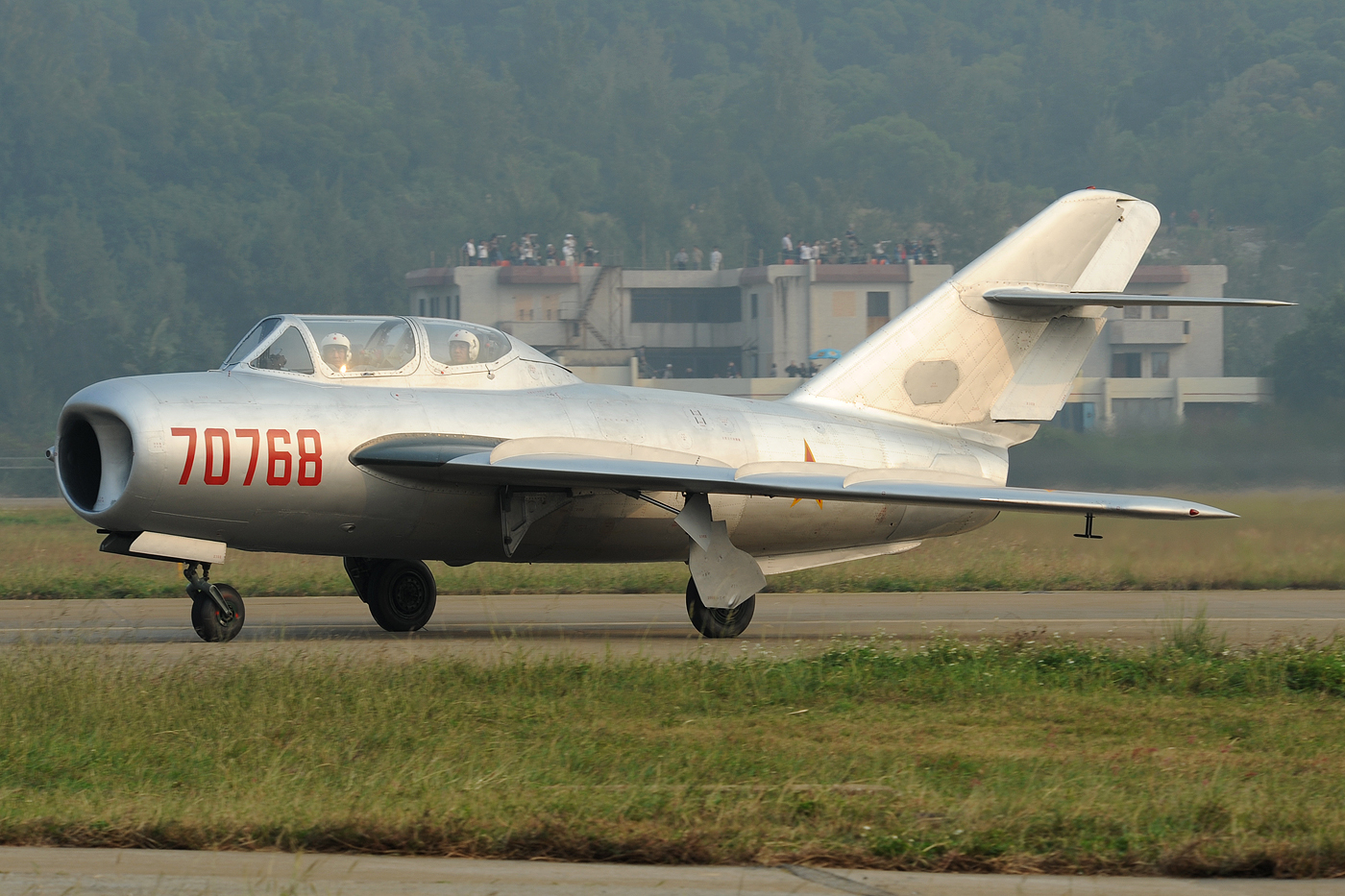
Shenyang J-5
The Shenyang J-5 (Chinese: 歼-5) (NATO reporting name ''Fresco'') is a Chinese-built single-seat jet interceptor and fighter aircraft derived from the Soviet Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17. The J-5 was exported as the F-5 and was originally designated Dongfeng-101 (East Wind-101) and also Type 56 before being designated J-5 in 1964. The MiG-17 was license-built in China and Poland into the 1960s. The People's Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) obtained a number of Soviet-built MiG-17 Fresco-A day fighters, designated J-4 in the early 1950s. To introduce modern production methods to Chinese industry the PLAAF obtained plans for the MiG-17F Fresco-C day fighter in 1955, along with two completed pattern aircraft, 15 knockdown kits, and parts for ten aircraft. The first Chinese-built MiG-17F, (serialed ''Zhong 0101''), produced by the Shenyang factory, performed its initial flight on 19 July 1956 with test pilot Wu Keming at the controls. Plans were obtained in 1961 for the MiG-17PF interc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryan Firebee
The Ryan Firebee is a series of target drones developed by the Ryan Aeronautical Company beginning in 1951. It was one of the first jet-propelled drones, and remains one of the most widely used target drones ever built. Development Ryan Firebee I Q-2/KDA-1 Firebee The Firebee I was the result of a 1948 U.S. Air Force request and contract to Ryan for a jet-powered gunnery target. The first flight of the XQ-2 Firebee prototype took place in early 1951. The drone featured swept flight surfaces and a circular nose inlet. The initial models had distinctive "arrowhead" shaped endplates on the tailplane. The Firebee could be air-launched from a specially modified launch aircraft (Douglas A-26 Invader was first to be used for this), or ground-launched with a single RATO booster. Following successful evaluation the target was ordered into production for the USAF as the Q-2A, powered by a Continental J69-T-19B turbojet engine with of thrust. The Air Force then obtained small number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop F-5 Freedom Fighter
The Northrop F-5 is a family of supersonic light fighter aircraft initially designed as a privately funded project in the late 1950s by Northrop Corporation. There are two main models, the original F-5A and F-5B Freedom Fighter variants and the extensively updated F-5E and F-5F Tiger II variants. The design team wrapped a small, highly aerodynamic fighter around two compact and high-thrust General Electric J85 engines, focusing on performance and a low cost of maintenance. Smaller and simpler than contemporaries such as the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, the F-5 cost less to procure and operate, making it a popular export aircraft. Though primarily designed for a day air superiority role, the aircraft is also a capable ground-attack platform. The F-5A entered service in the early 1960s. During the Cold War, over 800 were produced through 1972 for U.S. allies. Though at the time the United States Air Force (USAF) did not have a need for a light fighter, it did procure approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
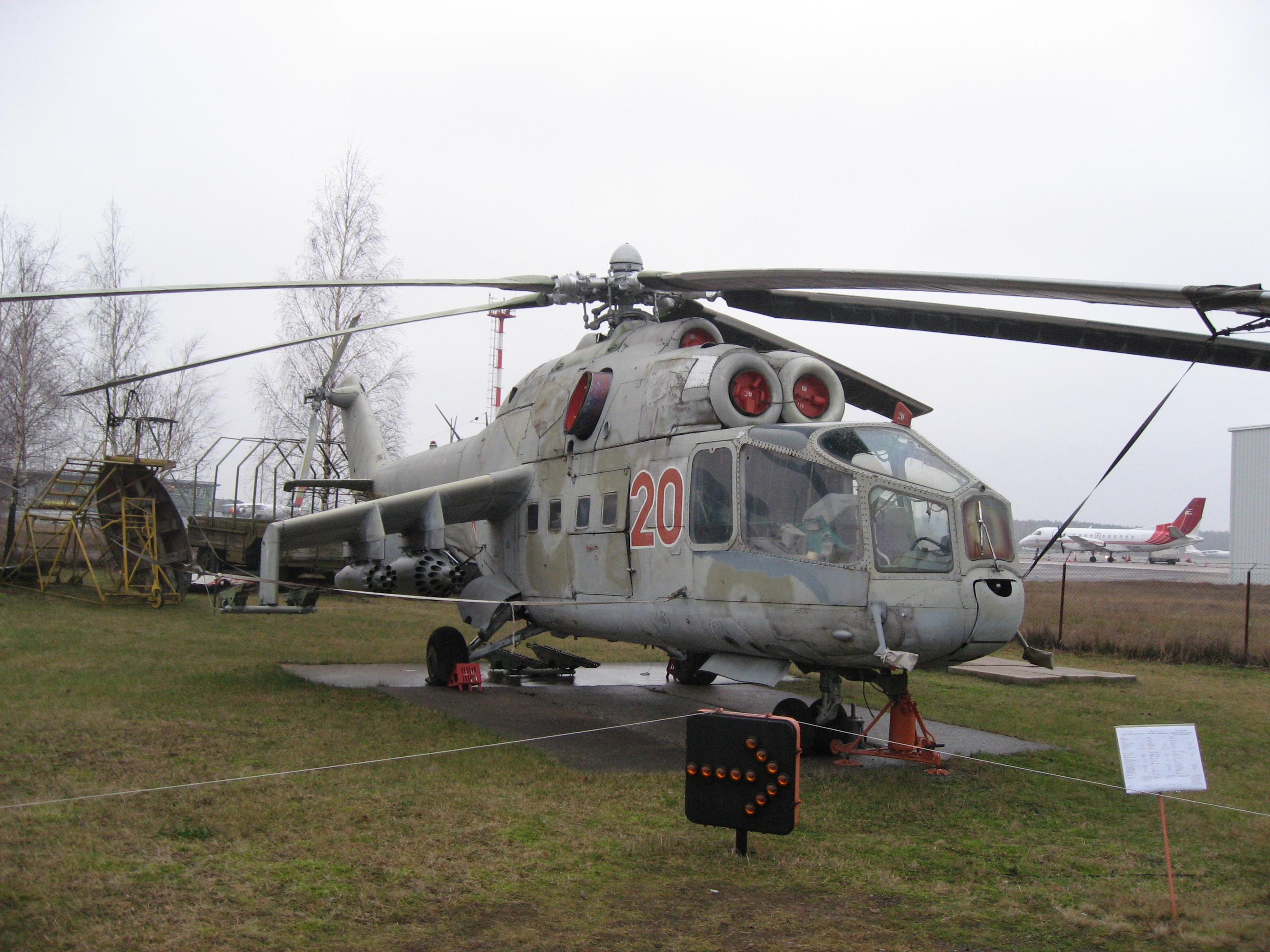
Mil Mi-24
The Mil Mi-24 (russian: Миль Ми-24; NATO reporting name: Hind) is a large helicopter gunship, attack helicopter and low-capacity troop transport with room for eight passengers. It is produced by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant and has been operated since 1972 by the Soviet Air Force and its successors, along with 48 other nations. In NATO circles, the export versions, Mi-25 and Mi-35, are denoted with a letter suffix as "Hind D" and "Hind E". Soviet pilots called the Mi-24 the "flying tank" (russian: летающий танк, letayushchiy tank, links=no), a term used historically with the famous World War II Soviet Il-2 ''Shturmovik'' armored ground attack aircraft. More common unofficial nicknames were "Galina" (or "Galya"), "Crocodile" (russian: Крокодил, Krokodil, links=no), due to the helicopter's camouflage scheme, and "Drinking Glass" (russian: Стакан, Stakan, links=no), because of the flat glass plates that surround earlier Mi-24 variants' cockpits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mil Mi-6
The Mil Mi-6 (NATO reporting name Hook), given the article number ''izdeliye 50'' and company designation V-6, is a Soviet/Russian heavy transport helicopter that was designed by the Mil design bureau. It was built in large numbers for both military and civil roles and used to be the largest helicopter in production until Mil Mi-26 was put in production in 1980. Design and development The Mi-6 resulted from a joint civil-military requirement for a very large vertical-lift aircraft, which could be used to add mobility in military operations as well as assist in the exploration and development of the expansive central and eastern regions of the USSR. Flown for the first time on 5 June 1957, the Mi-6 was the first Soviet turboshaft-powered production helicopter. The R-7 gearbox and rotor head developed for the project have a combined weight of 3200 kg, which is greater than the two turboshaft engines. Variable-incidence winglets were first mounted on the craft's sides in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ho Chi Minh
(: ; born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), commonly known as ('Uncle Hồ'), also known as ('President Hồ'), (' Old father of the people') and by other aliases, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and statesman. He served as Prime Minister of Vietnam from 1945 to 1955 and as President from 1945 until his death in 1969. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist, he served as Chairman and First Secretary of the Workers' Party of Vietnam. was born in Nghệ An province in the French protectorate of Annam. He led the independence movement from 1941 onward. Initially, it was an umbrella group for all parties fighting for Vietnam's independence, but the Communist Party gained majority support after 1945. led the Communist-led Democratic Republic of Vietnam in 1945, defeating the French Union in 1954 at the Battle of , ending the First Indochina War, and resulting in the division of Vietnam, with the Communists in control of North Vietnam. He was a key figure in the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mil Mi-4
The Mil Mi-4 (USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 36", NATO reporting name "Hound") is a Soviet transport helicopter that served in both military and civilian roles. Design and development The Mi-4 was designed in response to the American H-19 Chickasaw and the deployment of U.S. helicopters during the Korean War. While the Mi-4 strongly resembles the H-19 Chickasaw in general layout, including the innovative engine position in front of the cockpit, it is a larger helicopter, able to lift more weight and built in larger numbers. The first model entered service in 1953. The helicopter was first displayed to the outside world in 1952 at the Soviet Aviation Day in Tushino Airfield. One Mi-4 was built with a jettisonable rotor. It served as an experimental vehicle for future pilots' means of safety and ejection designs. Operational history The Mi-4 transport helicopter laid the beginning of the Soviet Army Aviation. It was widely used both in the armed forces and in Soviet civil aviat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AA-2 Atoll
The Vympel K-13 (NATO reporting name: AA-2 "Atoll") is a short-range, infrared homing air-to-air missile developed by the Soviet Union. It is similar in appearance and function to the American AIM-9B Sidewinder from which it was reverse-engineered. Although it since has been replaced by more modern missiles in frontline service, it saw widespread service in many nations. Background - the Sidewinder missile During the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis in 1958, Taiwan's F-86 Sabres faced the much higher performance mainland Chinese PLAAF MiG-17s. The MiG-17s had speed, maneuverability, and altitude advantages over the Sabres, allowing them to engage only when they desired, normally at advantageous times. In response, the US Navy rushed to modify 100 ROCAF Sabres to carry the newly introduced AIM-9 Sidewinder missile. These were introduced into combat on 24 September 1958, when a group of MiG-17s cruised past a flight of Sabres, only to find themselves under attack by missile fire. This w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AA-1 Alkali
The Kaliningrad K-5 (NATO reporting name AA-1 ''Alkali''), also known as RS-1U or product ShM, was an early Soviet air-to-air missile. History The development of the K-5 began in 1951. The first test firings were in 1953. It was tested (but not operationally carried) by the Yakovlev Yak-25. The weapon entered service as the Grushin/Tomashevich (russian: Грушин/Томашевич) RS-2U (also known as the R-5MS or K-5MS) in 1957. The initial version was matched to the RP-2U (Izumrud-2) radar used on the MiG-17PFU, MiG-19PM. An improved variant, K-5M or RS-2US in PVO service, entered production in 1959, matched to the RP-9/RP-9U (Sapfir) radar of the Sukhoi Su-9. The People's Republic of China developed a copy under the designation PL-1, for use by their J-6B fighters. The difficulties associated with beam-riding guidance, particularly in a single-seat fighter aircraft, were substantial, making the 'Alkali' primarily a short-range anti-bomber missile. Around 1967 the K-5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)