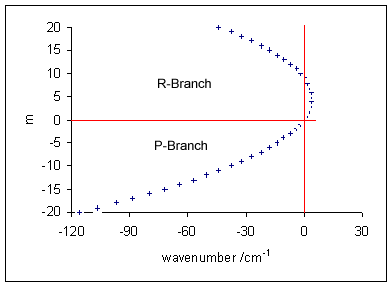
|
Vibrational Frequency
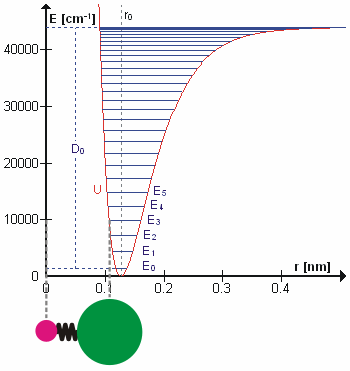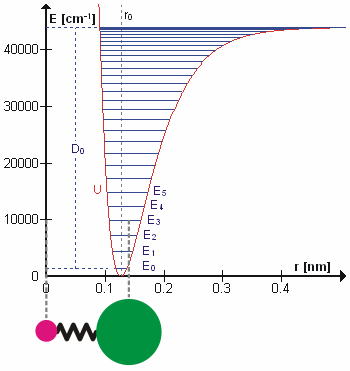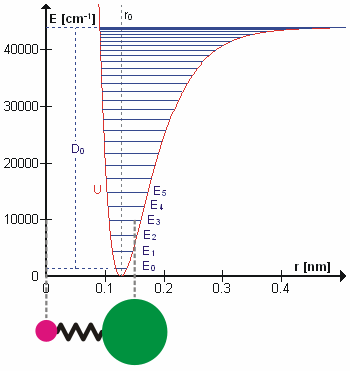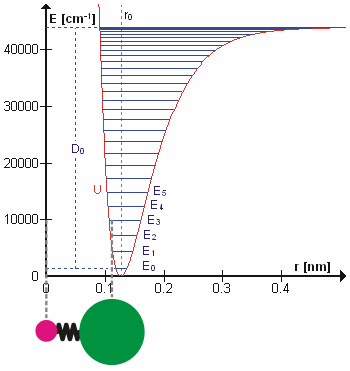
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm. For a diatomic molecule A−B, the vibrational frequency in s−1 is given by \nu = \frac \sqrt , where k is the force constant in dyne/cm or erg/cm2 and μ is the reduced mass given by \frac = \frac+\frac. The vibrational wavenumber in cm−1 is \tilde \;= \frac \sqrt, where c is the speed of light in cm/s. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of different parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has 3''N'' – 6 normal modes of vibration, but a ''linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Function
A periodic function is a function that repeats its values at regular intervals. For example, the trigonometric functions, which repeat at intervals of 2\pi radians, are periodic functions. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations, waves, and other phenomena that exhibit periodicity. Any function that is not periodic is called aperiodic. Definition A function is said to be periodic if, for some nonzero constant , it is the case that :f(x+P) = f(x) for all values of in the domain. A nonzero constant for which this is the case is called a period of the function. If there exists a least positive constant with this property, it is called the fundamental period (also primitive period, basic period, or prime period.) Often, "the" period of a function is used to mean its fundamental period. A function with period will repeat on intervals of length , and these intervals are sometimes also referred to as periods of the function. Geometrically, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Harmonic Motion
In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion (sometimes abbreviated ) is a special type of periodic motion of a body resulting from a dynamic equilibrium between an inertial force, proportional to the acceleration of the body away from the static equilibrium position and a restoring force on the moving object that is directly proportional to the magnitude of the object's displacement and acts towards the object's equilibrium position. It results in an oscillation, described by a sinusoid which continues indefinitely, if uninhibited by friction or any other dissipation of energy. Simple harmonic motion can serve as a mathematical model for a variety of motions, but is typified by the oscillation of a mass on a spring when it is subject to the linear elastic restoring force given by Hooke's law. The motion is sinusoidal in time and demonstrates a single resonant frequency. Other phenomena can be modeled by simple harmonic motion, including the motion of a simple pendulum, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate System
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is significant, and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by a letter, as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas State
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma). A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms (e.g. carbon dioxide). A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. What distinguishes a gas from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation usually makes a colourless gas invisible to the human observer. The gaseous state of matter occurs between the liquid and plasma states, the latter of which provides the upper temperature boundary for gases. Bounding the lower end of the temperature scale lie degenerative quantum gases which are gaining increasing attention. High-density atomic gases super-cooled to very low temperatures are classified by their statistical behavior as either Bose gases or Fermi gases. For a comprehensive listi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Electronic Transition
Molecular electronic transitions take place when electrons in a molecule are excited from one energy level to a higher energy level. The energy change associated with this transition provides information on the structure of a molecule and determines many molecular properties such as colour. The relationship between the energy involved in the electronic transition and the frequency of radiation is given by Planck's relation. Organic molecules and other molecules The electronic transitions in organic compounds and some other compounds can be determined by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, provided that transitions in the ultraviolet (UV) or visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum exist for this compound. Electrons occupying a HOMO of a sigma bond can get excited to the LUMO of that bond. This process is denoted as a σ → σ* transition. Likewise promotion of an electron from a π-bonding orbital to an antibonding π orbital* is denoted as a π → π* transition. Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibronic Transition
Vibronic spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy concerned with vibronic transitions: the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. In the gas phase, vibronic transitions are accompanied by changes in rotational energy also. Vibronic spectra of diatomic molecules have been analysed in detail; emission spectra are more complicated than absorption spectra. The intensity of allowed vibronic transitions is governed by the Franck–Condon principle. Vibronic spectroscopy may provide information, such as bond length, on electronic excited states of stable molecules. It has also been applied to the study of unstable molecules such as dicarbon, C2, in discharges, flames and astronomical objects.Hollas, p. 211. Principles Electronic transitions are typically observed in the visible and ultraviolet regions, in the wavelength range approximately 200–700 nm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet–visible Spectroscopy
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications. The only requirement is that the sample absorb in the UV-Vis region, i.e. be a chromophore. Absorption spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy. Parameters of interest, besides the wavelength of measurement, are absorbance (A) or transmittance (%T) or reflectance (%R), and its change with time. Optical transitions Most molecules and ions absorb energy in the ultraviolet or visible range, i.e., they are chromophores. The absorbed photon excites an electron in the chromophore to higher energy molecular orbitals, giving rise to an excited state. For organic chromophores, four possible types of transitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosymmetry
In crystallography, a centrosymmetric point group contains an inversion center as one of its symmetry elements. In such a point group, for every point (x, y, z) in the unit cell there is an indistinguishable point (-x, -y, -z). Such point groups are also said to have ''inversion'' symmetry. Point reflection is a similar term used in geometry. Crystals with an inversion center cannot display certain properties, such as the piezoelectric effect. The following space groups have inversion symmetry: the triclinic space group 2, the monoclinic 10-15, the orthorhombic 47-74, the tetragonal 83-88 and 123-142, the trigonal 147, 148 and 162-167, the hexagonal 175, 176 and 191-194, the cubic 200-206 and 221-230. Point groups lacking an inversion center (non-centrosymmetric) can be ''polar'', ''chiral'', both, or neither. A ''polar'' point group is one whose symmetry operations leave more than one common point unmoved. A polar point group has no unique origin because each of those un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rule Of Mutual Exclusion
The rule of mutual exclusion in molecular spectroscopy relates the observation of molecular vibrations to molecular symmetry. It states that no normal modes can be both Infrared spectroscopy, Infrared and Raman spectroscopy, Raman active in a molecule that possesses a centre of symmetry. This is a powerful application of Point groups in three dimensions, group theory to vibrational spectroscopy, and allows one to easily detect the presence of this symmetry element by comparison of the IR and Raman spectra generated by the same molecule. The rule arises because in a centrosymmetry, centrosymmetric point group, IR active modes, which must transform according to the same irreducible representation generated by one of the components of the Dipole#Molecular dipoles, dipole moment vector (x, y or z), must be of Parity_(physics), ''ungerade'' (u) symmetry, i.e. their Character theory, character under inversion is -1, while Raman active modes, which transform according to the symmetry of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |