|
Via Popillia
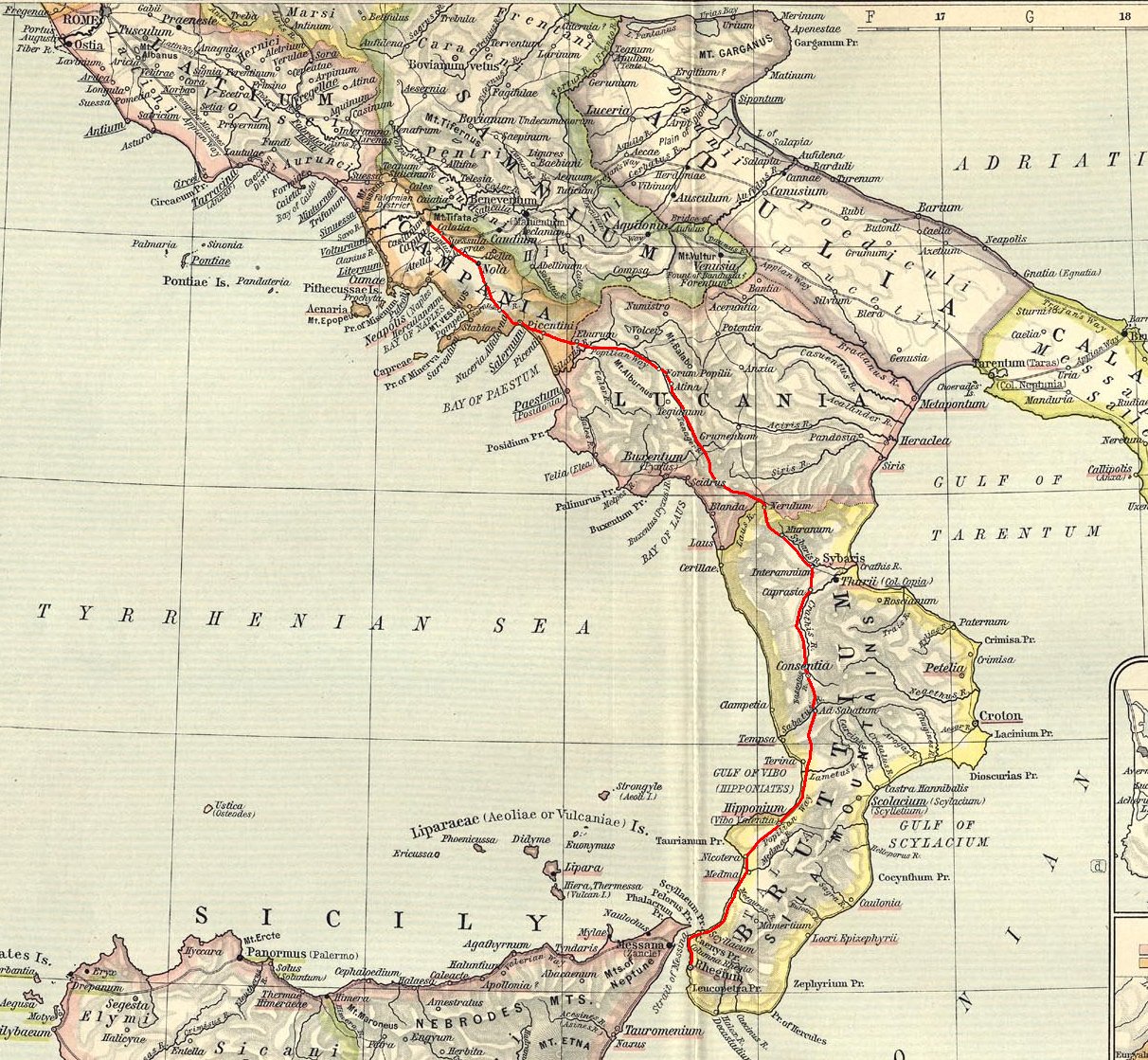
__NOTOC__ The Via Popilia is the name of two different ancient Roman roads begun in the consulship of Publius Popilius Laenas. One was in southern Italy and the other was in north-eastern Italy. Road in southern Italy The road in southern Italy ran from the Via Appia at Capua to Rhegium on the Straits of Messina. An archaeological discovery of part of its itinerarium on an engraved on stone (The Polla Tablet) brought it more fully into the light of history. It ran a distance of through southern Campania and Calabria, through the interior of the country, not along the coast. There are the remains of at least one Roman bridge along the road, the Ponte sul Savuto. Road in north-eastern Italy The road in north-eastern Italy connected ''Ariminum'' (modern Rimini) to Atria (modern Adria). At Atria it joined the Via Annia which went to ''Patavium'' (modern Padua), Altinum and Aquileia. It was an extension of the Via Flaminia which connected Rome and ''Ariminum''. ''Ariminum'' was als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Popilia
__NOTOC__ The Via Popilia is the name of two different ancient Roman roads begun in the consulship of Publius Popilius Laenas. One was in southern Italy and the other was in north-eastern Italy. Road in southern Italy The road in southern Italy ran from the Via Appia at Capua to Rhegium on the Straits of Messina. An archaeological discovery of part of its itinerarium on an engraved on stone (The Polla Tablet) brought it more fully into the light of history. It ran a distance of through southern Campania and Calabria, through the interior of the country, not along the coast. There are the remains of at least one Roman bridge along the road, the Ponte sul Savuto. Road in north-eastern Italy The road in north-eastern Italy connected ''Ariminum'' (modern Rimini) to Atria (modern Adria). At Atria it joined the Via Annia which went to ''Patavium'' (modern Padua), Altinum and Aquileia. It was an extension of the Via Flaminia which connected Rome and ''Ariminum''. ''Ariminum'' was als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altinum
Altinum (in Altino, a ''frazione'' of Quarto d'Altino) was an ancient town of the Veneti 15 km SE of modern Treviso, close to the mainland shore of the Lagoon of Venice. It was also close to the mouths of the rivers Dese, Zero and Sile. A flourishing port and trading centre during the Roman period, it was destroyed by Attila the Hun in 452. The town recovered, but was later abandoned when sea-borne sand began to cover it over. Its inhabitants moved to Torcello and other islands of the northern part of the lagoon. Today Altinum is an archaeological area and has a national archaeological museum. Pre-Roman Altinum Altium was a Venetic settlement. The earliest human presence in the area is dated to the 10th century BCE and is related to hunter gatherer groups. The earliest evidence of a settlement nucleus is dated from the mid-8th century to the mid-7th century BCE. In the 7th century BCE the settlement moved slightly to the northwest, in its historical location. A sacred ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chioggia
Chioggia (; vec, Cióxa , locally ; la, Clodia) is a coastal town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Venice in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Geography The town is situated on a small island at the southern entrance to the Lagoon of Venice about south of Venice ( by road); causeways connect it to the mainland and to its ''frazione'', nowadays a quarter, of Sottomarina. The population of the ''comune'' is around 50,000, with the town proper accounting for about half of that and Sottomarina for most of the rest. The municipality, located in south of the province, close to the provinces of Padua and Rovigo, borders with Campagna Lupia, Cavarzere, Codevigo, Cona, Correzzola, Loreo, Rosolina and Venice. History Chioggia and Sottomarina were not prominent in antiquity, although they are first mentioned in Pliny as the ''fossa Clodia''. Local legend attributes this name to its founding by a ''Clodius'', but the origin of this belief is not known. The name of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariano Nel Polesine
Ariano nel Polesine Ariano nel Polesine is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Rovigo in the Italian region Veneto, located about southwest of Venice and about southeast of Rovigo. Geography Ariano nel Polesine borders the following municipalities: Berra, Corbola, Goro, Mesola, Papozze, Taglio di Po Taglio di Po is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Rovigo in the Italian region Veneto, located about south of Venice and about east of Rovigo, in the lower Polesine. Taglio di Po borders the municipalities of Adria, Ariano nel Pole .... References External links Cities and towns in Veneto {{Veneto-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina
Spina was an Etruscan port city, established by the end of the 6th century BCE, on the Adriatic at the ancient mouth of the Po. Discovery The site of Spina was lost until modern times, when drainage schemes in the delta of the Po River in 1922 first officially revealed a necropolis of Etruscan Spina about four miles west of the commune of Comacchio. The fishermen of Comacchio, it soon turned out, had been the source of "Etruscan" vases (actually ancient imports from Greece) and other artifacts that had appeared for years on the archeological black market. The archaeological finds from the burials of Spina were discovered with the help of aerial photography. Aside from the white reflective surfaces of the modern drainage channels there appeared in the photographs a ghostly network of dark lines and light rectangles, the former indicating richer vegetation on the sites of ancient canals. Thus the layout of the ancient trading port was revealed, now miles from the sea, due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Po (river)
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. The headwaters of the Po are a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face of Monviso. The Po then extends along the 45th parallel north before ending at a delta projecting into the Adriatic Sea near Venice. It is characterized by its large discharge (several rivers over 1,000 km have a discharge inferior or equal to the Po). It is, with the Rhône and Nile, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge. As a result of its characteristics, the river is subject to heavy flooding. Consequently, over half its length is controlled with embankments. The river flows through many important Italian cities, including Turin, Piacenza, Cremona and Ferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the ''Pax Romana'' or ''Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comacchio
Comacchio (; egl, label= Comacchiese, Cmâc' ) is a town and ''comune'' of Emilia Romagna, Italy, in the province of Ferrara, from the provincial capital Ferrara. It was founded about two thousand years ago; across its history it was first governed by the Exarchate of Ravenna, then by the Duchy of Ferrara, and eventually returned to be part of the territories of the Papal States. For its landscape and its history, it is considered one of the major centres of the Po delta. Geography Comacchio is situated in a lagoon just north of the present mouth of the Reno. It is built on more than thirteen different islets, joined by bridges. The most important resources of these wetlands are the fish farming and the salt ponds. The seaport of Porto Garibaldi lies to the east. The wetlands south of the town, the ''Valli di Comacchio'', are classified as a Site of Community Importance and a Special Protection Area in Italy. They are also rated internationally important by the Ramsar Conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervia
Cervia ( rgn, Zirvia) is a seaside resort town in the province of Ravenna, located in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna. Cervia is a major seaside resort in Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Its population was 28,700 at the 2018 census. History Originally called Ficocle, it was probably of Greek origin and was located midway between current Cervia and Ravenna. It is known that this original settlement was destroyed in 709 by patrician Theodore for its alliance with Ravenna against the loyal Byzantines. Later the centre was rebuilt in a more secure position, in the '' Salina''. This medieval city grew until it was provided with three fortified entrances, a Palaces of Priors, seven churches and a castle (''Rocca'') which, according to the legend, was built by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. The name also changed from Ficocle to Cervia, probably referring to the ''Acervi'', great amounts of salt left in the local evaporation ponds. After a long series of events, it became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains more than 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of . The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin Language, Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the ''cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire. The map is a 13th-century parchment copy of a possible Roman original. It covers Europe (without the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles), North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and India. According to one hypothesis, the existing map is based on a document of the 4th or 5th century that contained a copy of the world map originally prepared by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Agrippa during the reign of the emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14). However, Emily Albu has suggested that the existing map could instead be based on an original from the Carolingian period. The map was likely stolen by the renowned humanist Conrad Celtes, who bequeathed it to his friend, the economist and archaeologist Konrad Peutinger, who gave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous ''itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes the roads of the Roman Empire. Owing to the scarcity of other extant records of this type, it is a valuable historical record. Almost nothing is known of its date or author. Scholars consider it likely that the original edition was prepared at the beginning of the 3rd century. Although it is traditionally ascribed to the patronage of the 2nd-century Antoninus Pius, the oldest extant copy has been assigned to the time of Diocletian and the most likely imperial patron—if the work had one—would have been Caracalla. ''Iter Britanniarum'' The British section is known as the ''Iter Britanniarum'', and can be described as the 'road map' of Roman Britain. There are 15 such itinerari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |