|
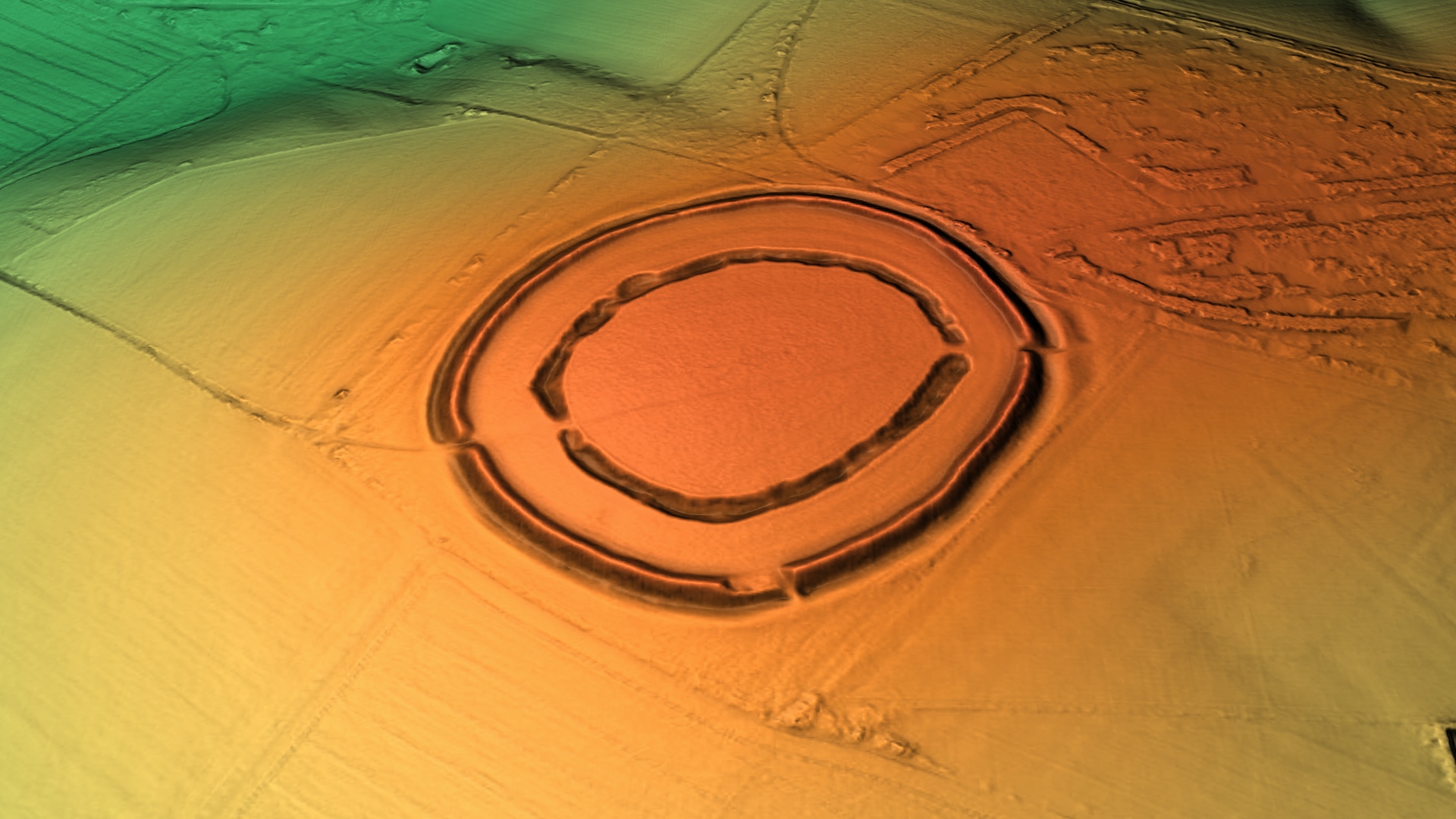
Vespasian's Camp
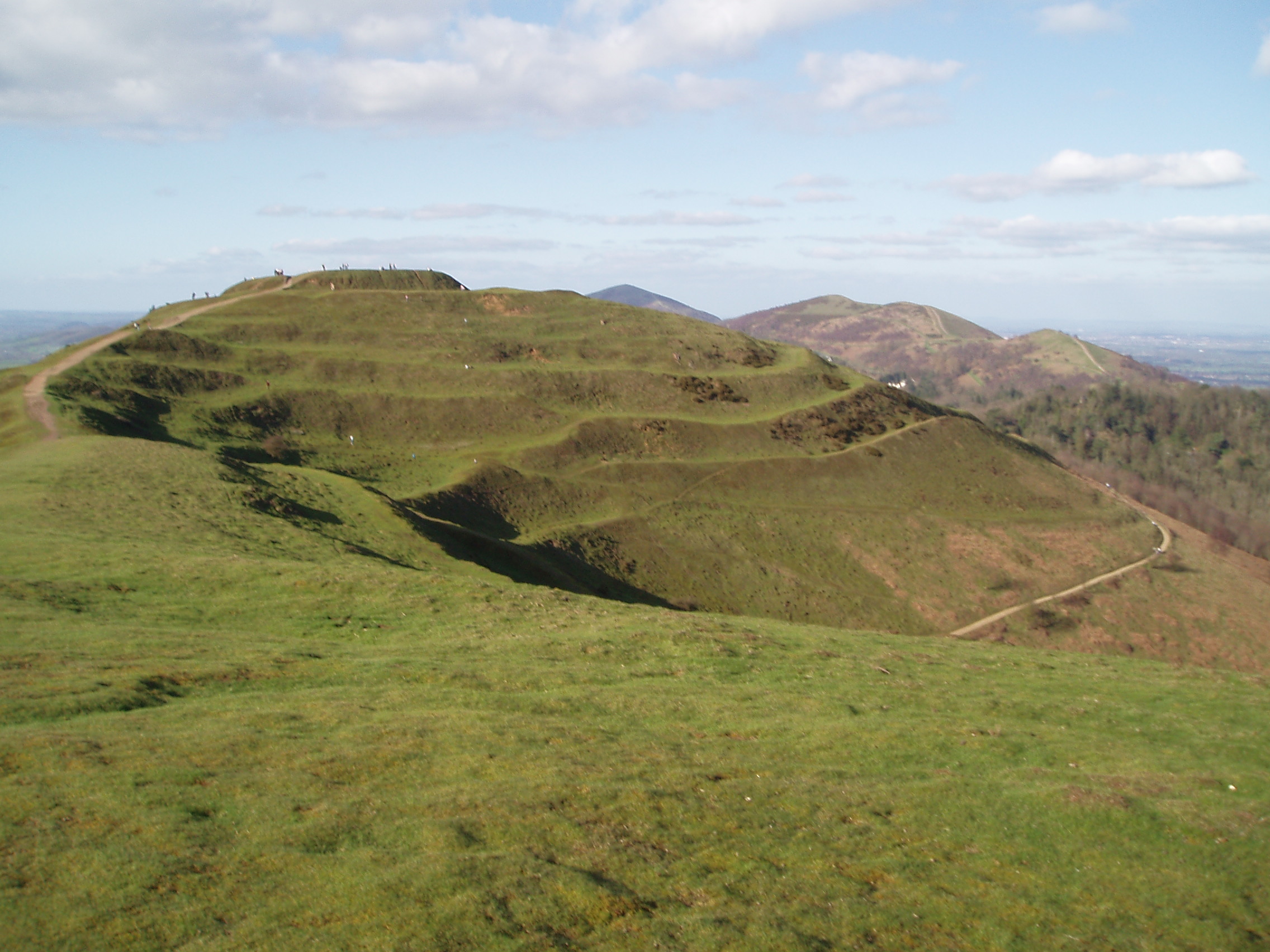
Vespasian's Camp is an Iron Age hillfort just west of the town of Amesbury, Wiltshire, England. The hillfort is less than from the Neolithic and Bronze Age site of Stonehenge, and was built on a hill next to the Stonehenge Avenue; it has the River Avon on its southern side and the A303 road on its northern edge. The site is a scheduled monument and lies within the boundaries of the Stonehenge World Heritage Site. Other hillforts nearby include Danebury to the east, Sidbury Hill and Casterley Camp to the north, Yarnbury Castle to the west and Figsbury Ring and Old Sarum to the south. Ogbury Camp, to the south, may have been a satellite enclosure of Vespasian's Camp. Toponym The earthworks were named "Vespasian's Camp" in the 16th century by William Camden, an Elizabethan antiquarian and historian, during a tour of the area. Although the Roman general Vespasian, who was later Roman emperor from 69 to 79 CE, campaigned through Wessex after the Roman invasion of Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the northeast and Berkshire to the east. The county town was originally Wilton, after which the county is named, but Wiltshire Council is now based in the county town of Trowbridge. Within the county's boundary are two unitary authority areas, Wiltshire and Swindon, governed respectively by Wiltshire Council and Swindon Borough Council. Wiltshire is characterised by its high downland and wide valleys. Salisbury Plain is noted for being the location of the Stonehenge and Avebury stone circles (which together are a UNESCO Cultural and World Heritage site) and other ancient landmarks, and as a training area for the British Army. The city of Salisbury is notable for its medieval cathedral. Swindon is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figsbury Ring
Figsbury Ring () is an 11.2 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Wiltshire, notified in 1975. It is owned and managed by the National Trust. Earthworks Within the wider SSSI mentioned above, the earthworks of Figsbury Ring are sub-circular and enclose 6.4 hectares of grassland on a chalk ridge to the north east of Salisbury, in the parish of Firsdown, Wiltshire at NGR SU188338. It is yet to be fully investigated. Small portions of the site were excavated in 1924 by Ben and Maud Cunnington as it was their belief that the site was the remains of an Iron Age Hill fort. Superficially this description of an earthwork with exterior ditch would seem appropriate, however the presence of an enigmatic inner ditch has led many archaeologists to doubt this interpretation. This ditch is separated from the outer rampart by a berm of up to 30 metres in width and, to many, it seems likely that the site actually began as a late neolithic Henge. A small geophysical survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterscarp
A scarp and a counterscarp are the inner and outer sides, respectively, of a ditch or moat used in fortifications. Attackers (if they have not bridged the ditch) must descend the counterscarp and ascend the scarp. In permanent fortifications the scarp and counterscarp may be encased in stone. In less permanent fortifications, the counterscarp may be lined with paling fence set at an angle so as to give no cover to the attackers but to make advancing and retreating more difficult. If an attacker succeeds in breaching a wall a coupure can be dug on the inside of the wall to hinder the forlorn hope, in which case the side of the ditch farthest from the breached wall and closest to the centre of the fortification is also called the counterscarp. Counterscarp gallery These are tunnels or "galleries" that have been built behind the counterscarp wall inside the moat or ditch. Each gallery is pierced with loopholes for musketry, so that attacking forces that enter the moat can be dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ditch (fortification)
In military engineering, a ditch is an obstacle designed to slow down or break up an attacking force, while a trench is intended to provide cover to the defenders. In military fortifications the side of a ditch farthest from the enemy and closest to the next line of defence is known as the scarp while the side of a ditch closest to the enemy is known as the counterscarp. Uses In early fortifications, ditches were often used in combination with ramparts to slow down the enemy whilst defensive fire could be brought to bear from the relative protection afforded by the rampart and possibly the palisade. In medieval fortification, a ditch was often constructed in front of a defensive wall to hinder mining and escalade activities from an attacker. When filled with water, such a defensive ditch is called a moat. However, moats may also be dry. Later star forts designed by military engineers like Vauban, comprised elaborate networks of ditches and parapets, carefully calculated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a bank or rampart is a length of embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Early fortifications Many types of early fortification, from prehistory through to the Early Middle Ages, employed earth ramparts usually in combination with external ditches to defend the outer perimeter of a fortified site or settlement. Hillforts, ringforts or "raths" and ringworks all made use of ditch and rampart defences, and they are the characteristic feature of circular ramparts. The ramparts could be reinforced and raised in height by the use of palisades. This type of arrangement was a feature of the motte and bailey castle of northern Europe in the early medieval period. Types of ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Invasion Of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Stanegate was established. Conquest of the far north and Scotland took longer with fluctuating success. The Roman army was generally recruited in Italia, Hispania, and Gaul. To control the English Channel they used the newly formed fleet. The Romans under their general Aulus Plautius first forced their way inland in several battles against British tribes, including the Battle of the Medway, the Battle of the Thames, and in later years Caratacus's last battle and the Roman conquest of Anglesey. Following a widespread uprising in AD 60 in which Boudica sacked Camulodunum, VerulamiumChurchill, ''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples'', p. 7 and Londinium, the Romans suppressed the rebellion in the Defeat of Boudica. They went on eventually to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum , conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons , common_name = Wessex , image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg , map_caption = Southern Britain in the ninth century , event_start = Established , year_start = 519 , event_end = English unification , year_end = 12 July 927 , event1 = , date_event1 = , event_pre = Settlement , date_pre = 5th–6th century , event_post = Norman conquest , date_post = 14 October 1066 , border_s2 = no , common_languages = Old English *West Saxon dialect British Latin , religion = PaganismChristianity , leader1 = Cerdic (first) , leader2 = Ine , leader3 = Ecgberht , leader4 = Alfred the Great , leader5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire generated political stability and a vast Roman building program. Vespasian was the first emperor from an equestrian family and only rose later in his lifetime into the senatorial rank as the first member of his family to do so. Vespasian's renown came from his military success; he was legate of Legio II Augusta during the Roman invasion of Britain in 43 and subjugated Judaea during the Jewish rebellion of 66. While Vespasian besieged Jerusalem during the Jewish rebellion, emperor Nero committed suicide and plunged Rome into a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho perished in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifacts, History of archaeology, archaeological and historic Archaeological site, sites, or historic archives and manuscripts. The essence of antiquarianism is a focus on the empirical evidence of the past, and is perhaps best encapsulated in the motto adopted by the 18th-century antiquary Sir Richard Hoare, 2nd Baronet, Sir Richard Colt Hoare, "We speak from facts, not theory." The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' first cites "archaeologist" from 1824; this soon took over as the usual term for one major branch of antiquarian activity. "Archaeology", from 1607 onwards, initially meant what is now seen as "ancient history" generally, with the narrower modern sense first seen in 1837. Today the term "antiquarian" is often used in a pejorative sense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabethan
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personification of Great Britain) was first used in 1572, and often thereafter, to mark the Elizabethan age as a renaissance that inspired national pride through classical ideals, international expansion, and naval triumph over Spain. This "golden age" represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of poetry, music and literature. The era is most famous for its theatre, as William Shakespeare and many others composed plays that broke free of England's past style of theatre. It was an age of exploration and expansion abroad, while back at home, the Protestant Reformation became more acceptable to the people, most certainly after the Spanish Armada was repelled. It was also the end of the period when England was a separate re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |