|
Vesica Piscis
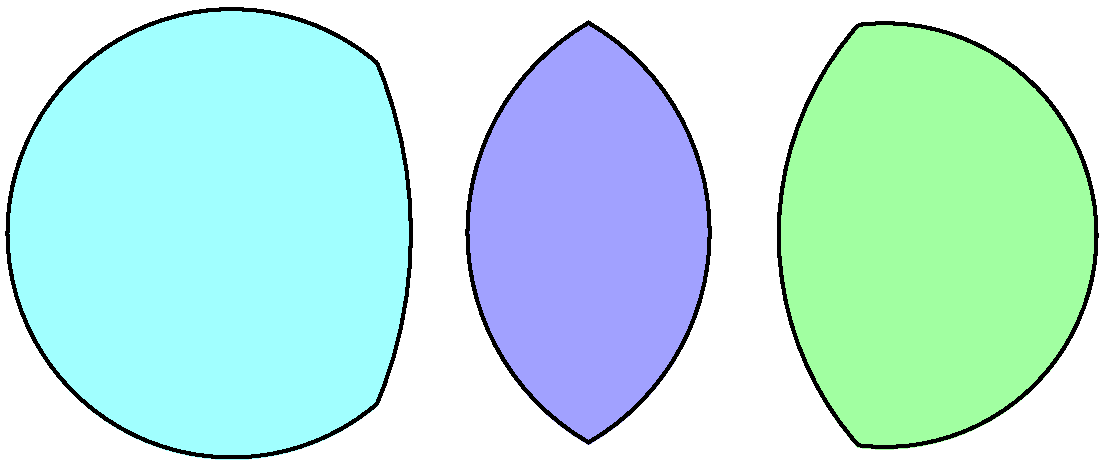
The vesica piscis is a type of lens, a mathematical shape formed by the intersection of two disks with the same radius, intersecting in such a way that the center of each disk lies on the perimeter of the other. In Latin, "vesica piscis" literally means "bladder of a fish", reflecting the shape's resemblance to the conjoined dual air bladders ("swim bladder") found in most fish. In Italian, the shape's name is ''mandorla'' ("almond"). This figure appears in the first proposition of Euclid's ''Elements'', where it forms the first step in constructing an equilateral triangle using a compass and straightedge. The triangle has as its vertices the two disk centers and one of the two sharp corners of the vesica piscis. Mathematical description Mathematically, the vesica piscis is a special case of a lens, the shape formed by the intersection of two disks. The mathematical ratio of the height of the vesica piscis to the width across its center is the square root of 3, or 1.732050 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (geometry)
In 2-dimensional geometry, a lens is a convex region bounded by two circular arcs joined to each other at their endpoints. In order for this shape to be convex, both arcs must bow outwards (convex-convex). This shape can be formed as the intersection of two circular disks. It can also be formed as the union of two circular segments (regions between the chord of a circle and the circle itself), joined along a common chord. Types If the two arcs of a lens have equal radius, it is called a symmetric lens, otherwise is an asymmetric lens. The vesica piscis is one form of a symmetric lens, formed by arcs of two circles whose centers each lie on the opposite arc. The arcs meet at angles of 120° at their endpoints. Area ;Symmetric The area of a symmetric lens can be expressed in terms of the radius ''R'' and arc lengths ''θ'' in radians: :A = R^2\left(\theta - \sin \theta \right). ;Asymmetric The area of an asymmetric lens formed from circles of radii ''R'' and ''r'' with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (geometry)
In 2-dimensional geometry, a lens is a convex region bounded by two circular arcs joined to each other at their endpoints. In order for this shape to be convex, both arcs must bow outwards (convex-convex). This shape can be formed as the intersection of two circular disks. It can also be formed as the union of two circular segments (regions between the chord of a circle and the circle itself), joined along a common chord. Types If the two arcs of a lens have equal radius, it is called a symmetric lens, otherwise is an asymmetric lens. The vesica piscis is one form of a symmetric lens, formed by arcs of two circles whose centers each lie on the opposite arc. The arcs meet at angles of 120° at their endpoints. Area ;Symmetric The area of a symmetric lens can be expressed in terms of the radius ''R'' and arc lengths ''θ'' in radians: :A = R^2\left(\theta - \sin \theta \right). ;Asymmetric The area of an asymmetric lens formed from circles of radii ''R'' and ''r'' with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesica Piscis Circles , a shape formed by the intersection of two circles of the same radius
{{disambiguation ...
Vesica (plural vesicae) is Latin for "bladder", may refer to: Anatomy * Vesica, mainly used for the urinary bladder * Vesica, also used for the gallbladder * Vesica, in entomology used for a part of the male genitals * ''Trigonum vesicae urinariae'', Latin for trigone of urinary bladder Shapes * Vesica piscis The vesica piscis is a type of lens, a mathematical shape formed by the intersection of two disks with the same radius, intersecting in such a way that the center of each disk lies on the perimeter of the other. In Latin, "vesica piscis" literal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (lit. French work); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was reconstructed between 1140 and 1144, draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Heraldry
Ecclesiastical heraldry refers to the use of heraldry within Christianity for dioceses, organisations and Christian clergy. Initially used to mark documents, ecclesiastical heraldry evolved as a system for identifying people and dioceses. It is most formalized within the Catholic Church, where most bishops, including the pope, have a personal coat of arms. Clergy in Anglican, Lutheran, Eastern Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches follow similar customs, as do institutions such as schools and dioceses. Ecclesiastical heraldry differs notably from other heraldry in the use of special insignia around the shield to indicate rank in a church or denomination. The most prominent of these insignia is the low crowned, wide brimmed ecclesiastical hat, commonly the Roman ''galero''. The color and ornamentation of this hat indicate rank. Cardinals are famous for the "red hat", while other offices and churches have distinctive colors of hat, such as black for priests and green for bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthys
The ichthys or ichthus (), from the Koine Greek, Greek (, 1st cent. AD Koine Greek pronunciation: , "fish") is (in its modern rendition) a symbol consisting of two intersecting arcs, the ends of the right side extending beyond the meeting point so as to resemble the profile of a fish. It has been speculated that the symbol was adopted by Early Christianity, early Christians as a secret symbol; a shibboleth to determine if another was indeed Christian.Robert Mowat, “ΙΧΘΥΣ,” in Atti del II° congresso internazionale di archeologica cristi-ana tenuto in Roma nell’ aprile 1900 (Rome: Spithöver, 1902), 1–8Rasimus, T. ,2011''Revisiting the Ichthys: A Suggestion Concerning the Origins of Christological Fish Symbolism'' Pp 327-348 in '' Mystery and Secrecy in the Nag Hammadi Collection and Other Ancient Literature: Ideas and Practices.'' Biblical Studies, Ancient Near East and Early Christianity E-Books Online. "Such solutions, once popular, include the fish as a secret s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Seal
A seal is a device for making an impression in wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, or to prevent interference with a package or envelope by applying a seal which had to be broken to open the container (hence the modern English verb "to seal", which implies secure closing without an actual wax seal). The seal-making device is also referred to as the seal ''matrix'' or ''die''; the imprint it creates as the seal impression (or, more rarely, the ''sealing''). If the impression is made purely as a relief resulting from the greater pressure on the paper where the high parts of the matrix touch, the seal is known as a ''dry seal''; in other cases ink or another liquid or liquefied medium is used, in another color than the paper. In most traditional forms of dry seal the design on the seal matrix is in intaglio (cut below the flat surface) and therefore the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aureola
An aureola or aureole (diminutive of Latin ''aurea'', "golden") is the radiance of luminous cloud which, in paintings of sacred personages, surrounds the whole figure. In Romance languages, the noun Aureola is usually more related to the disc of light surrounding the head of sacred figures and that in English is called Halo or Nimbus. In art In the earliest periods of Christian art it was confined to the figures of the persons of the Christian Godhead, but it was afterwards extended to the Virgin Mary and to several of the saints. The aureola, when enveloping the whole body, generally appears oval or elliptical in form, but occasionally depicted as circular, vesica piscis, or quatrefoil. When it appears merely as a luminous disk round the head, it is called specifically a ''halo'' or ''nimbus'', while the combination of nimbus and aureole is called a '' glory''. The strict distinction between nimbus and aureole is not commonly maintained, and the latter term is most freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Art
Christian art is sacred art which uses subjects, themes, and imagery from Christianity. Most Christian groups use or have used art to some extent, including early Christian art and architecture and Christian media. Images of Jesus and narrative scenes from the Life of Christ are the most common subjects, and scenes from the Old Testament play a part in the art of most denominations. Images of the Virgin Mary and saints are much rarer in Protestant art than that of Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. Christianity makes far wider use of images than related religions, in which figurative representations are forbidden, such as Islam and Judaism. However, there are some that have promoted aniconism in Christianity, and there have been periods of iconoclasm within Christianity, though this is not a common interpretation of Christian theology. History Beginnings Early Christian art survives from dates near the origins of Christianity, although many early Christians associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuleaux Triangle
A Reuleaux triangle is a curved triangle with constant width, the simplest and best known curve of constant width other than the circle. It is formed from the intersection of three circular disks, each having its center on the boundary of the other two. Constant width means that the separation of every two parallel supporting lines is the same, independent of their orientation. Because its width is constant, the Reuleaux triangle is one answer to the question "Other than a circle, what shape can a manhole cover be made so that it cannot fall down through the hole?" Reuleaux triangles have also been called spherical triangles, but that term more properly refers to triangles on the curved surface of a sphere. They are named after Franz Reuleaux,. a 19th-century German engineer who pioneered the study of machines for translating one type of motion into another, and who used Reuleaux triangles in his designs. However, these shapes were known before his time, for instance by the des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

