|
Veritable Records Of Ming
The ''Ming Shilu'' () contains the imperial annals of the emperors of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). It is the single largest historical source for the dynasty. According to modern historians, it "plays an extremely important role in the historical reconstruction of Ming society and politics." After the fall of the Ming dynasty, the ''Ming Shilu'' was used as a primary source for the compilation of the ''History of Ming'' by the Qing dynasty. Historical sources The Veritable Records (''shilu'') for each emperor was composed after the emperor's death by a History Office appointed by the Grand Secretariat The Grand Secretariat (; Manchu: ''dorgi yamun'') was nominally a coordinating agency but ''de facto'' the highest institution in the imperial government of the Chinese Ming dynasty. It first took shape after the Hongwu Emperor abolished the o ... using different types of historical sources such as: # "The Qiju zhu (), or 'Diaries of Activity and Repose'. These were da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ming
The ''History of Ming'' or the ''Ming History'' (''Míng Shǐ'') is one of the official Chinese historical works known as the ''Twenty-Four Histories''. It consists of 332 volumes and covers the history of the Ming dynasty from 1368 to 1644. It was written by a number of officials commissioned by the court of Qing dynasty, with Zhang Tingyu as the lead editor. The compilation started in the era of the Shunzhi Emperor and was completed in 1739 in the era of the Qianlong Emperor, though most of the volumes were written in the era of the Kangxi Emperor. The sinologist Endymion Wilkinson writes that the ''Mingshi'', the second longest of the ''Twenty-Four Histories'', after the '' History of Song'', is "generally reckoned to be one of the best of the ''Histories'' and one of the easiest to read." Background After the Qing dynasty had extended its rule into the Central Plain, in the second year of the Shunzhi Emperor, the Censor Zhao Jiding ( 趙繼鼎) was asked to compile th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
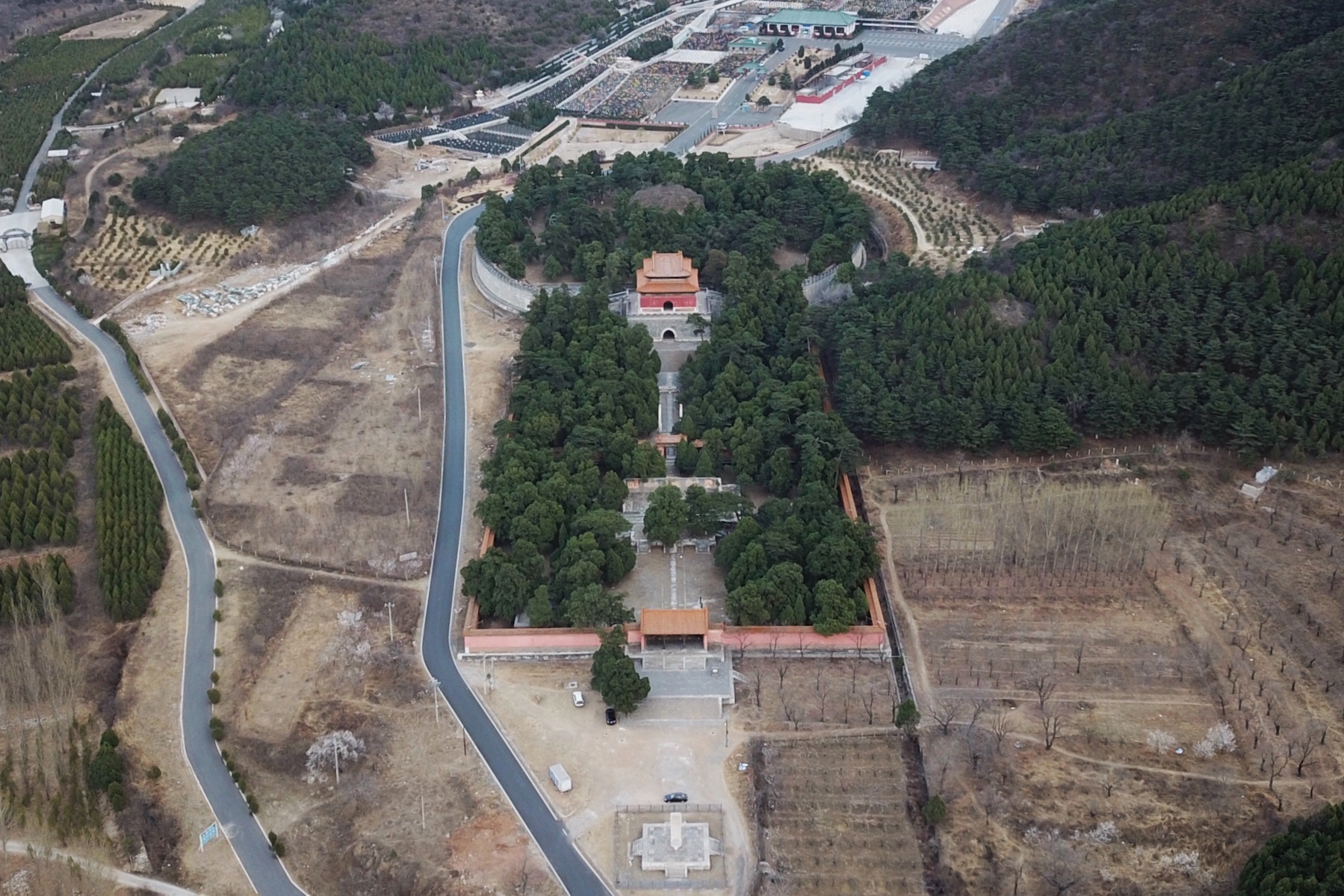
Jiajing Emperor
The Jiajing Emperor (; 16September 150723January 1567) was the 12th List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1521 to 1567. Born Zhu Houcong, he was the former Zhengde Emperor's cousin. His father, Zhu Youyuan (1476–1519), Prince of Xing, was the fourth son of the Chenghua Emperor (reigned from 1464 to 1487) and the eldest son of three sons born to the emperor's concubine, Lady Shao. The Jiajing Emperor's Chinese era name, era name, "Jiajing", means "admirable tranquility". Early years Born as heir apparent of a vassal prince, Zhu Houcong was not brought up to succeed to the throne. However, the throne became vacant in 1521 after the sudden death of the Hongzhi Emperor's son, the Zhengde Emperor, who did not leave an heir. Prior to the Zhengde Emperor's death, the line of succession was as follows: * ''Chenghua Emperor, Zhu Jianshen, the Chenghua Emperor (1447–1487)'' ** ''Unnamed son (1466–1466)'' ** ''Zhu Youji (1469–1472)'' ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Malaysia
Malaysia is located on a strategic sea lane that exposes it to global trade and various cultures. The name "Malaysia" is a modern concept, created in the second half of the 20th century. However, contemporary Malaysia regards the entire history of Malaya and Borneo, spanning thousands of years back to prehistoric times, as its own history. An early western account of the area is seen in Ptolemy's book ''Geographia'', which mentions a " Golden Khersonese," now identified as the Malay Peninsula. Hinduism and Buddhism from India and China dominated early regional history, reaching their peak during the reign of the Palembang, Sumatra, Indonesia - based Srivijaya civilisation, whose influence extended through Sumatra, West Java, East Borneo and the Malay Peninsula from the 7th to the 13th centuries. Although Muslims passed through the Malay Peninsula as early as the 10th century, it was not until the 14th century that Islam first firmly established itself. The adoption of Islam in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Myanmar
The history of Myanmar (also known as Burma; my, မြန်မာ့သမိုင်း) covers the period from the time of first-known human settlements 13,000 years ago to the present day. The earliest inhabitants of recorded history were a Tibeto-Burman-speaking people who established the Pyu city-states ranged as far south as Pyay and adopted Theravada Buddhism. Another group, the Bamar people, entered the upper Irrawaddy valley in the early 9th century. They went on to establish the Pagan Kingdom (1044–1297), the first-ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. The Burmese language and Burma culture slowly came to replace Pyu norms during this period. After the First Mongol invasion of Burma in 1287, several small kingdoms, of which the Kingdom of Ava, the Hanthawaddy Kingdom, the Kingdom of Mrauk U and the Shan States were principal powers, came to dominate the landscape, replete with ever-shifting alliances and constant wars. In the second half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Laos
Evidence for modern human presence in the northern and central highlands of Indochina, that constitute the territories of the modern Laotian nation-state dates back to the Lower Paleolithic. These earliest human migrants are Australo-Melanesians—associated with the Hoabinhian culture—and have populated the highlands and the interior, less accessible regions of Laos and all of South-east Asia to this day. The subsequent Austroasiatic and Austronesian marine migration waves affected landlocked Laos only marginally and direct Chinese and Indian cultural contact had a greater impact on the country.Pittayaporn, Pittayawat (2014). Layers of Chinese loanwords in Proto-Southwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai History
Tai or TAI may refer to: Arts and entertainment *Tai (comics) a fictional Marvel Comics supervillain *Tai Fraiser, a fictional character in the 1995 film ''Clueless'' *Tai Kamiya, a fictional character in ''Digimon'' Businesses and organisations * Avianca El Salvador, an airline, ICAO code TAI * The Australia Institute, a left-wing think tank * Transports Aériens Intercontinentaux (TAI), a defunct French airline * Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI) Ethnic groups and languages *Tai peoples *Tai languages *Tai language (New Guinea) People *Tai (given name), including a list of people with the name *Tai (surname), including a list of people with the name *Dai (surname), a Chinese surname also spelled Tai, including a list of people with the name *Tai, the artist name of poet and painter Kambara Yasushi (1899–1997) Places *Tai (city), a former settlement in China during the Xia dynasty * Tai, Ardabil, Iran *Tai, Lorestan, Iran *Tai, Rivers, Nigeria *Taï, Ivory Coast *Lake Tai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty Literature
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese History Texts
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Korean History
The National Institute of Korean History (NIKH) is a South Korean national organization in charge of researching, collecting, compiling, promoting the study of historical materials on Korean history. It was established as ''Guksagwan'' (국사관 國史館) in March 1946, one year after the liberation of Korea and was changed to the current name in 1949. As a branch of the Ministry of Education, the Institute certifies and supervises drafts of history textbooks used in middle and high schools. It conducts educational programs for government officials and teachers of elementary, middle, and high schools. It also operates a school to train competent translators of historical documents written in classical Chinese and pre-modern Japanese. The Institute holds and supervises the Korean History Proficiency Test four times a year, and sponsors the annual Korean History Competition among middle and high school students. Starting in 2015, two emeritus professors of history served as lead au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Sinica
Academia Sinica (AS, la, 1=Academia Sinica, 3=Chinese Academy; ), headquartered in Nangang, Taipei, is the national academy of Taiwan. Founded in Nanking, the academy supports research activities in a wide variety of disciplines, ranging from mathematical and physical sciences to life sciences, and to humanities and social sciences. As an educational institute, it provides PhD training and scholarship through its English-language Taiwan International Graduate Program in biology, agriculture, chemistry, physics, informatics, and earth and environmental sciences. Academia Sinica is ranked 144th in Nature Publishing Index - 2014 Global Top 200 and 18th in Reuters World's Most Innovative Research Institutions of 2019. The current president since 2016 is James C. Liao, an expert in metabolic engineering, systems biology and synthetic biology. History Academia Sinica, which means "Chinese Academy", was founded in 1928 in Nanking, then capital of the Republic of China, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianqi Emperor
The Tianqi Emperor (23 December 1605 – 30 September 1627), personal name Zhu Youjiao (), was the 16th Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1620 to 1627. He was the eldest son of the Taichang Emperor and a elder brother of the Chongzhen Emperor, who succeeded him. " Tianqi", the era name of his reign, means "heavenly opening". Biography Zhu Youjiao became emperor at the age of 15, following the death of his father, the Taichang Emperor, who ruled less than a month. He did not pay much attention to state affairs, and was accused of failing in his filial duties to his late father by not continuing the latter's wishes. It is possible that Zhu Youjiao suffered from a learning disability or something more. He was illiterate and showed no interest in his studies. However, he was an outstanding carpenter and craftsman, often spending vast amounts of time on woodworking and instructing his servants to sell his creations undercover on the market just to see how much they were wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taichang Emperor
The Taichang Emperor (; 28 August 1582 – 26 September 1620), personal name Zhu Changluo (), was the 15th Emperor of the Ming dynasty. He was the eldest son of the Wanli Emperor and succeeded his father as emperor in 1620. However, his reign came to an abrupt end less than one month after his coronation when he was found dead one morning in the palace following a bout of diarrhea. He was succeeded by his son, Zhu Youjiao, who was enthroned as the Tianqi Emperor. His era name, Taichang, means "grand prosperity." His reign was the shortest in Ming history. Early life Zhu Changluo was born in 1582, the 10th year of the Wanli era, to the Wanli Emperor and a palace attendant, Lady Wang, who served under the Emperor's mother, Empress Dowager Xiaoding. After it was discovered that Lady Wang was pregnant, the Emperor was persuaded by his mother to make her a concubine and awarded her the title "Consort Gong of the Second Grade" (恭妃). However she was never one of the Wanli Emperor' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |