|
Veralipride
Veralipride (Agreal, Agradil) is a typical antipsychotic of the benzamide class. It is indicated for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause. It is a D2 receptor antagonist and it induces prolactin secretion without any estrogenic or progestagenic effects. It was first authorised for use in 1979. Veralipride has never gained approval in the United States. In September 2006, it was withdrawn from the Spanish market. As a result, the European Commission referred the matter to the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In July 2007, the EMA recommended the withdrawal of marketing authorisations for veralipride. See also * Typical antipsychotic * Benzamide * Levosulpiride Levosulpiride, sold under the brand name Neoprad, is a typical antipsychotic and a prokinetic agent of the benzamide class. It is a selective antagonist of the dopamine D2 receptors on both central and peripheral nervous systems. Levosulpiride ... References Allyl compounds Benzamid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levosulpiride
Levosulpiride, sold under the brand name Neoprad, is a typical antipsychotic and a prokinetic agent of the benzamide class. It is a selective antagonist of the dopamine D2 receptors on both central and peripheral nervous systems. Levosulpiride is claimed to have mood elevating properties. Chemically, it is the (''S'')-(−)-enantiomer of sulpiride. Uses Levosulpiride is used in the treatment of: * Psychosis * Negative symptoms of schizophrenia * Anxiety disorders * Dysthymia * Vertigo * Dyspepsia * Irritable bowel syndrome * Premature ejaculation. Levosulpiride is not currently licensed for treatment of premature ejaculation in the UK or other European countries. Side effects Side effects include amenorrhea, gynecomastia, galactorrhea, changes in libido, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. In the U.S., as of 2013 only one case of adverse reaction to levosulpiride had been recorded on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database. A case of rapid onset resistant dystonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typical Antipsychotic
Typical antipsychotics (also known as major tranquilizers, and first generation antipsychotics) are a class of antipsychotic drugs first developed in the 1950s and used to treat psychosis (in particular, schizophrenia). Typical antipsychotics may also be used for the treatment of acute mania, agitation, and other conditions. The first typical antipsychotics to come into medical use were the phenothiazines, namely chlorpromazine which was discovered serendipitously. Another prominent grouping of antipsychotics are the butyrophenones, an example of which is haloperidol. The newer, second-generation antipsychotics, also known as atypical antipsychotics, have largely supplanted the use of typical antipsychotics as first-line agents due to the higher risk of movement disorders in the latter. Both generations of medication tend to block receptors in the brain's dopamine pathways, but atypicals at the time of marketing were claimed to differ from typical antipsychotics in that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamide
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, .... In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasomotor
Vasomotor refers to actions upon a blood vessel which alter its diameter. More specifically, it can refer to vasodilator action and vasoconstrictor action. Control Sympathetic innervation Sympathetic nerve fibers travel around the tunica media of the artery, secrete neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine into the extracellular fluid surrounding the smooth muscle (tunica media) from the terminal knob of the axon. The smooth muscle cell membranes have α and β-adrenergic receptors for these neurotransmitters. Activation of α-adrenergic receptors promotes vasoconstriction, while the activation of β-adrenergic receptors mediates the relaxation of muscle cells, resulting in vasodilation. Normally, α-adrenergic receptors predominates in smooth muscle of resistance vessels.Robert C. Ward et al. (2002). In Foundations for osteopathic medicine'. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2nd edition. p. 98. . Google Book Search. Retrieved on 5 December 2010. Endothelium derived chemicals Endothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often define menopause as having occurred when a woman has not had any menstrual bleeding for a year. It may also be defined by a decrease in hormone production by the ovaries. In those who have had surgery to remove their uterus but still have functioning ovaries, menopause is not considered to have yet occurred. Following the removal of the uterus, symptoms typically occur earlier. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer or shorter in duration or be lighter or heavier in the amount of flow. During this time, women often experience hot flashes; these typically last from 30 seconds to ten minutes and may be associated with shivering, sweating, and reddening of the skin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Receptor D2
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DRD2'' gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined. Function D2 receptors are coupled to Gi subtype of G protein. This G protein-coupled receptor inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity. In mice, regulation of D2R surface expression by the neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) in the dentate gyrus is involved in exploration, synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Studies have shown potential roles for D2R in retrieval of fear memories in the prelimbic cortex and in discrimina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development. Discovered in non-human animals around 1930 by Oscar Riddle and confirmed in humans in 1970 by Henry Friesen, prolactin is a peptide hormone, encoded by the ''PRL'' gene. In mammals, prolactin is associated with milk production; in fish it is thought to be related to the control of water and salt balance. Prolactin also acts in a cytokine-like manner and as an important regulator of the immune system. It has important cell cycle-related functions as a growth-, differentiating- and anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The Commission is divided into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or ministries each headed by a Director-General who is responsible to a Commissioner. There is one member per member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the general interest of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. The Commission President (currently Ursula von der Leyen) is proposed by the European Council (the 27 heads of state/governments) and elected by the European Parliament. The Council of the European Union then nominates the other members of the Commission in agreement with the nominated President, and the 27 members as a team are then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typical Antipsychotic
Typical antipsychotics (also known as major tranquilizers, and first generation antipsychotics) are a class of antipsychotic drugs first developed in the 1950s and used to treat psychosis (in particular, schizophrenia). Typical antipsychotics may also be used for the treatment of acute mania, agitation, and other conditions. The first typical antipsychotics to come into medical use were the phenothiazines, namely chlorpromazine which was discovered serendipitously. Another prominent grouping of antipsychotics are the butyrophenones, an example of which is haloperidol. The newer, second-generation antipsychotics, also known as atypical antipsychotics, have largely supplanted the use of typical antipsychotics as first-line agents due to the higher risk of movement disorders in the latter. Both generations of medication tend to block receptors in the brain's dopamine pathways, but atypicals at the time of marketing were claimed to differ from typical antipsychotics in that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzamide
Benzamide is a organic compound with the chemical formula of C6H5C(O)NH2. It is the simplest amide derivative of benzoic acid Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, .... In powdered form, it appears as a white solid, while in crystalline form, it appears as colourless crystals. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents. It is a natural alkaloid found in the herbs of Berberis pruinosa. Chemical derivatives A number of substituted benzamides are commercial drugs, including: See also * References External links Physical characteristics {{Authority control Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
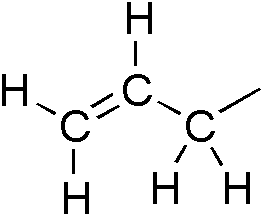
Allyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |