|
Ventrifilosa
Ventrifilosa () is a highly diverse group of phagotrophic protists that glide through their flagella and emit filose pseudopods from their ventral side for feeding. Because of their mixture of amoeba and flagellate characteristics, they are amoeboflagellates. Members of this group are the Imbricatea, Sarcomonadea and Thecofilosea. Morphology Protists in the group Ventrifilosa ancestrally have a rigid extracellular theca on the dorsal side, and emit non-granular filose pseudopods from a ventral aperture. This aperture is called "cleft" when belonging to an amoeboflagellate, or "astropyle" when belonging to a phaeodarian. The group includes descendants that have lost or modified some of these characteristics. For example, some have lost their pseudopods (such as the spongomonads and '' Ebria''), some have lost their theca (such as '' Pseudopirsonia''), and some have acquired axopodia (in Phaeodaria). The loss of flagella and scales has occurred in this group several times indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomonadea
The sarcomonads () or class Sarcomonadea are a group of amoeboid biciliate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are characterized by a propensity to move through gliding on their posterior cilium or through filopodia, a lack of scales or external theca, a soft cell surface without obvious cortical filamentous or membranous skeleton, two cilia without scales or hairs, tubular mitochondrial cristae, near-spherical extrusomes, and a microbody (probably a peroxisome) attached to the nucleus. History In 1993 Cavalier-Smith described the sarcomonads as a subclass known as “Sarcomonadia”, an assemblage of unrelated cercozoans ( thaumatomonads, proteomyxids, cercomonads...) and excavates (jakobids), in the now defunct class “Heteromitea”, in the old phylum “Opalozoa”. This subclass was created to lump together protozoa that have an anisokont type of zoospore (i.e. two cilia of different lengths), are non-thecate and have isodiametric extrusomes. Sarcomonadia was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomonad
The sarcomonads () or class Sarcomonadea are a group of amoeboid biciliate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are characterized by a propensity to move through gliding on their posterior cilium or through filopodia, a lack of scales or external theca, a soft cell surface without obvious cortical filamentous or membranous skeleton, two cilia without scales or hairs, tubular mitochondrial cristae, near-spherical extrusomes, and a microbody (probably a peroxisome) attached to the nucleus. History In 1993 Cavalier-Smith described the sarcomonads as a subclass known as “Sarcomonadia”, an assemblage of unrelated cercozoans ( thaumatomonads, proteomyxids, cercomonads...) and excavates (jakobids), in the now defunct class “Heteromitea”, in the old phylum “Opalozoa”. This subclass was created to lump together protozoa that have an anisokont type of zoospore (i.e. two cilia of different lengths), are non-thecate and have isodiametric extrusomes. Sarcomonadia was composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglypha
''Euglypha'' is a genus of cercozoa Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eu .... It includes the species ''Euglypha rotunda''. References External links * * Cercozoa genera Imbricatea {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongomonad
The spongomonads are a group of flagellated protists in the phylum Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they compose the family Sarcomonadidae and order Sarcomonadida. They were originally placed among the Reticulofilosa, but were later transferred to Monadofilosa. It includes only two genera: *''Spongomonas'' *''Rhipidodendron The spongomonads are a group of flagellated protist A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ...'' References Filosa SAR supergroup unranked clades {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercomonadida
Cercomonads are small flagellates, widespread in aqueous habitats and common in soils. Characteristics The cells are generally around 10 μm in length, without any shell or covering. They produce filose pseudopods to capture bacteria, but do not use them for locomotion, which usually takes place by gliding along surfaces. Most members have two flagella, one directed forward and one trailing under the cell, inserted at right angles near its anterior. The nucleus is connected to the flagellar bases and accompanied by a characteristic paranuclear body. Classification Genetic studies place the cercomonads among the Cercozoa, a diverse group of amoeboid and flagellate protozoans. They are divided into two families. * The Heteromitidae tend to be relatively rigid, and produce only temporary pseudopods. * The Cercomonadidae are more plastic, and when food supplies are plentiful may become amoeboid and even multinucleate. The classification of genera and species continues to un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediglissa
Pediglissa () is a subclass of phagotrophic protists that inhabit soil or freshwater habitats. They were defined in 2018 according to phylogenetic analyses that showed a clade containing the orders Cercomonadida and Glissomonadida. They're the sister group of Paracercomonadida. Morphology and behavior Pediglissa are biciliate protists that glide on their posterior cilium and have a strong tendency to become amoeboid during feeding, unlike the metromonads. Their pseudopodia are more often shaped like rounded lamellae than finger-like or filose pseudopodia, unlike the paracercomonads. Their anterior cilium is often well developed, unlike in helkesids, but can be short in glissomonads; it moves with an undulating oar-like beat. The trophic cells (i.e. feeding forms) are naked, without a theca, scales, or perles, unlike in Thecofilosea and many freshwater Imbricatea. Diversity Pediglissa includes the majority of known cercozoan soil flagellates, all gliding on a single posterior c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracercomonadida
The paracercomonads are a group of cercozoan protists. Taxonomically, they comprise the family Paracercomonadidae, order Paracercomonadida and subclass Paracercomonada. Due to their morphological similarities to the cercomonads, members of this family were grouped with ''Cercomonas'' and similar taxa from the beginning. However, their similarities are due to convergent evolution. Classification There are currently 5 genera of paracercomonads: *'' Brevimastigomonas'' *'' Metabolomonas'' *'' Nucleocercomonas'' *''Paracercomonas ''Paracercomonas'' is a genus of rhizaria. It includes the species ''Paracercomonas marina''. Species * '' P. ambulans'' Howe & Cavalier-Smith 2009 * '' P. astra'' Howe & Cavalier-Smith 2009 * '' P. baikali'' Howe et al. 2011 * '' P. bassi'' B ...'' *'' Phytocercomonas'' References {{Cercozoa-stub Cercozoa families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracercomonada
The paracercomonads are a group of cercozoan protists. Taxonomically, they comprise the family Paracercomonadidae, order Paracercomonadida and subclass Paracercomonada. Due to their morphological similarities to the cercomonads, members of this family were grouped with ''Cercomonas'' and similar taxa from the beginning. However, their similarities are due to convergent evolution. Classification There are currently 5 genera of paracercomonads: *'' Brevimastigomonas'' *'' Metabolomonas'' *'' Nucleocercomonas'' *''Paracercomonas ''Paracercomonas'' is a genus of rhizaria. It includes the species ''Paracercomonas marina''. Species * '' P. ambulans'' Howe & Cavalier-Smith 2009 * '' P. astra'' Howe & Cavalier-Smith 2009 * '' P. baikali'' Howe et al. 2011 * '' P. bassi'' B ...'' *'' Phytocercomonas'' References {{Cercozoa-stub Cercozoa families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katabiidae
''Katabia'' is a genus of soil-dwelling heterotrophic flagellate cercozoans containing the single species ''Katabia gromovi'', and the only member of family Katabiidae. Morphology ''Katabia'' are drop-shaped unicellular flagellates with a broad anterior end and a tapering posterior end. They have two heterodynamic (with different movements) flagella. Inside their cells are a microbody, refractile granules shaped like mushrooms, kinetocysts and a well-developed cytoskeleton similar to the one found in '' Heteromita''. Their life cycle has two forms: a free-living trophozoite that feeds on bacteria through pseudopodia while swimming, and a cyst that is surrounded by a thick mucilage-like wall. Instead of gliding upon the substrate, like other cercozoans, they have secondarily lost the ability to glide with cilia, and only swim freely using their flagella. In particular, the species ''Katabia gromovi'' is a soil-dwelling flagellate with a prominent dorsal side and a flattened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of convergent evolution. The arrangement of the members of a polyphyletic group is called a polyphyly .. ource for pronunciation./ref> It is contrasted with monophyly and paraphyly. For example, the biological characteristic of warm-bloodedness evolved separately in the ancestors of mammals and the ancestors of birds; "warm-blooded animals" is therefore a polyphyletic grouping. Other examples of polyphyletic groups are algae, C4 photosynthetic plants, and edentates. Many taxonomists aim to avoid homoplasies in grouping taxa together, with a goal to identify and eliminate groups that are found to be polyphyletic. This is often the stimulus for major revisions of the classification schemes. Researchers concerned more with ecology than with systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
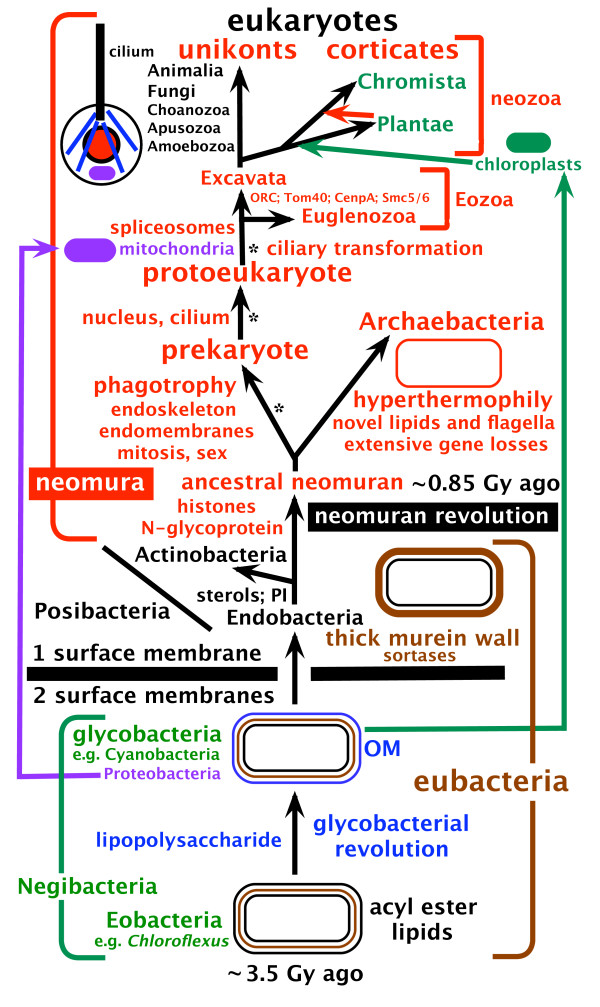
Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |