|
Ventilator-associated Pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a type of lung infection that occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation breathing machines in hospitals. As such, VAP typically affects critically ill persons that are in an intensive care unit (ICU) and have been on a mechanical ventilator for at least 48 hours.Cooper A.S. Oral hygiene care to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients. ''Crit. Care Nurs..'' 2021;41(4):80-82. doi:10.4037/ccn2021314 VAP is a major source of increased illness and death. Persons with VAP have increased lengths of ICU hospitalization and have up to a 20–30% death rate. The diagnosis of VAP varies among hospitals and providers but usually requires a new infiltrate on chest x-ray plus two or more other factors. These factors include temperatures of >38 °C or 12 × 109/ml, purulent secretions from the airways in the lung, and/or reduction in gas exchange. A different less studied infection found in mechanically ventilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar. Although found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines, it can cause destructive changes to human and animal lungs if aspirated, specifically to the alveoli resulting in bloody, brownish or yellow colored jelly like sputum. In the clinical setting, it is the most significant member of the genus ''Klebsiella'' of the Enterobacteriaceae. ''K. oxytoca'' and ''K. rhinoscleromatis'' have also been demonstrated in human clinical specimens. In recent years, ''Klebsiella'' species have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections. It naturally occurs in the soil, and about 30% of strains can fix nitrogen in anaerobic conditions. As a free-living diazotroph, its nitrogen-fixation system has been much-studied, and is of agricultural interest, as ''K. pneumoniae'' has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citrobacter
''Citrobacter'' is a genus of Gram-negative coliform bacteria in the family Enterobacteriaceae. The species ''C. amalonaticus'', ''C. koseri'', and ''C. freundii'' can use citrate as a sole carbon source. ''Citrobacter'' species are differentiated by their ability to convert tryptophan to indole (''C. koseri'' is the only citrobacter to be commonly indole-positive), ferment lactose (''C. koseri'' is a lactose fermentor), and use malonate. ''Citrobacter'' shows the ability to accumulate uranium by building phosphate complexes. Clinical significance These bacteria can be found almost everywhere in soil, water, wastewater, etc. They can also be found in the human intestine. They are rarely the source of illnesses, except for infections of the GI Tract, urinary tract and infant meningitis and sepsis. ''Citrobacter freundii'' strains have inducible ''ampC'' genes encoding resistance to ampicillin and first-generation cephalosporins. In addition, isolates of ''Citrobacter'' may be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterobacter
''Enterobacter'' is a genus of common Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. It is the type genus of the order Enterobacterales. Several strains of these bacteria are pathogenic and cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised (usually hospitalized) hosts and in those who are on mechanical ventilation. The urinary and respiratory tracts are the most common sites of infection. The genus ''Enterobacter'' is a member of the coliform group of bacteria. It does not belong to the fecal coliforms (or thermotolerant coliforms) group of bacteria, unlike ''Escherichia coli'', because it is incapable of growth at 44.5 °C in the presence of bile salts. Some of them show quorum sensing properties. One clinically important species from this genus is '' E. cloacae''. Researchers in 2018 reported, after detecting the presence on the International Space Station (ISS) of five '' Enterobacter bugandensis'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratia Marcescens
''Serratia marcescens'' () is a species of rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen in humans. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy.Serratia marcescens. (2011, April). Retrieved from https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Serratia_marcescens ''S. marcescens'' is commonly involved in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), also called nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections, and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of HAI cases in the United States. It is commonly found in the respiratory and urinary tracts of hospitalized adults and in the gastrointestinal systems of children. Due to its abundant presence in the environment, and its preference for damp conditions, ''S. marcescens'' is commonly found growing in bathrooms (especially on tile grout, shower corners, toilet water lines, and basins), where it manife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
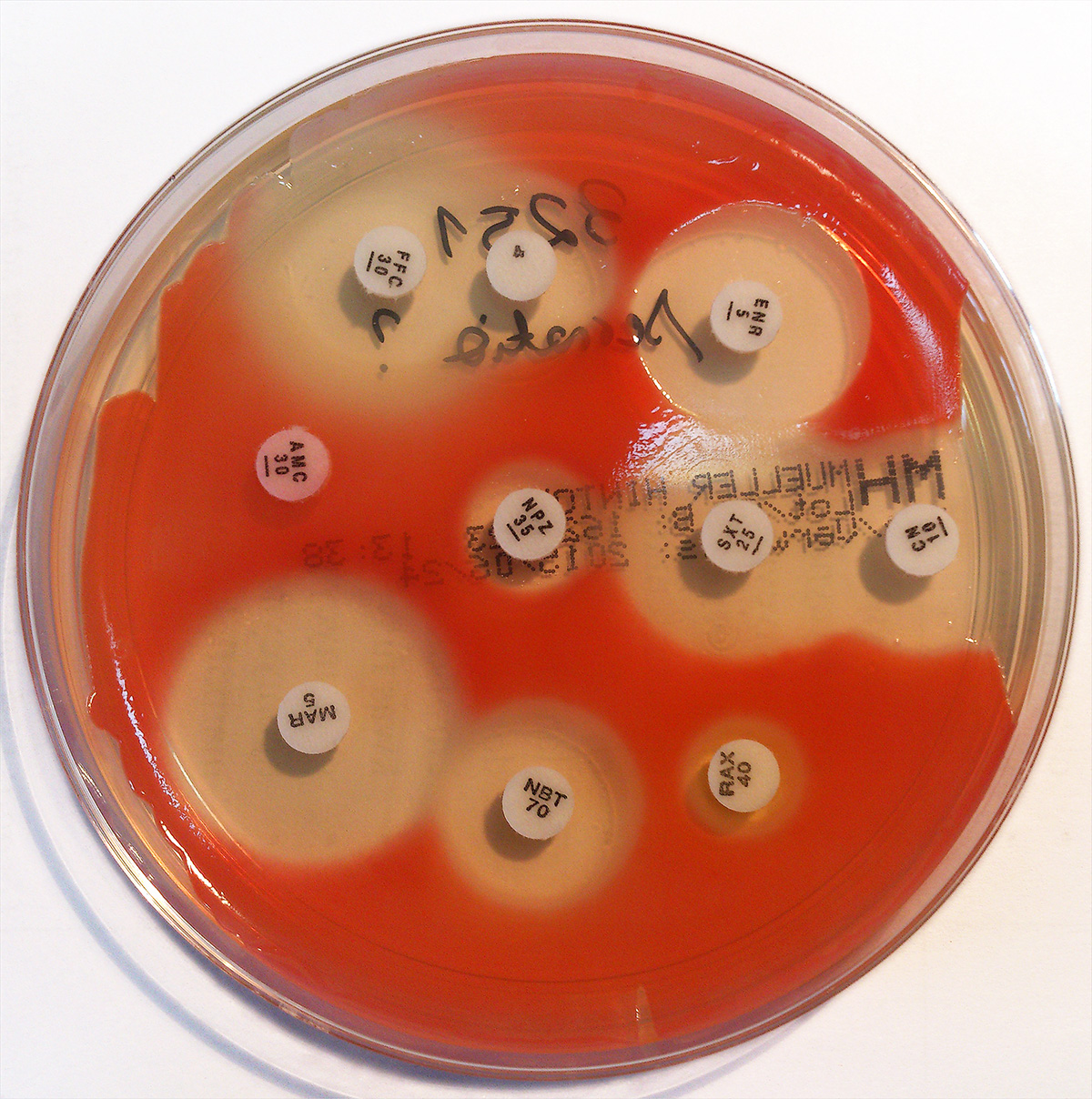
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases, (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to target a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a '' Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Induction And Inhibition
Enzyme induction is a process in which a molecule (''e.g.'' a drug) induces (''i.e.'' initiates or enhances) the expression of an enzyme. Enzyme inhibition can refer to * the inhibition of the expression of the enzyme by another molecule * interference at the enzyme-level, basically with how the enzyme works. This can be competitive inhibition, uncompetitive inhibition, non-competitive inhibition or partially competitive inhibition. If the molecule induces enzymes that are responsible for its own metabolism, this is called auto-induction (or auto-inhibition if there is inhibition). These processes are particular forms of gene expression regulation. These terms are of particular interest to pharmacology, and more specifically to drug metabolism and drug interactions. They also apply to molecular biology. History In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the French molecular biologists François Jacob and Jacques Monod became the first to explain enzyme induction, in the context of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
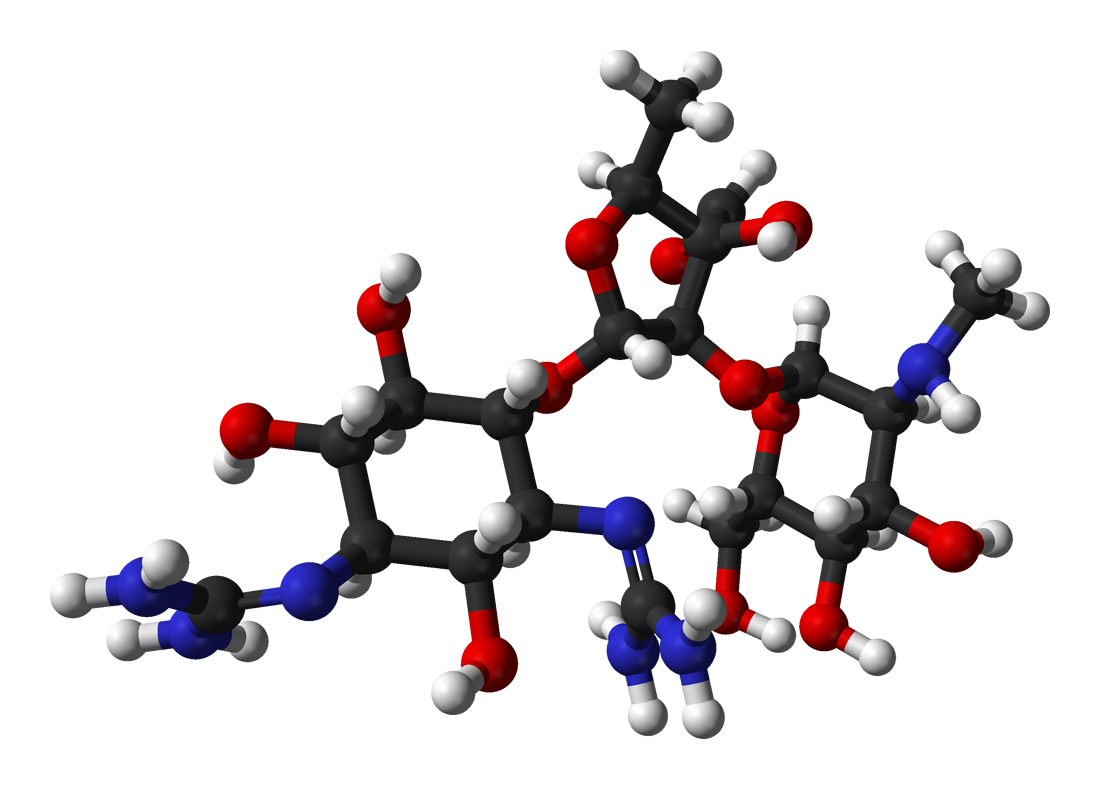
Aztreonam
Aztreonam, sold under the brand name Azactam among others, is an antibiotic used primarily to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. This may include bone infections, endometritis, intra abdominal infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis. It is given by intravenous or intramuscular injection or by inhalation. Common side effects when given by injection include pain at the site of injection, vomiting, and rash. Common side effects when inhaled include wheezing, cough, and vomiting. Serious side effects include ''Clostridium difficile'' infection and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Those who are allergic to other β-lactam have a low rate of allergy to aztreonam. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. It is in the monobactam family of medications. Aztreonam inhibits cell wall synthesis by blocking peptidoglycan crosslinking to cause bacterial death. Aztreonam was approved for medical use in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |